Various participants of foreign exchange market – In the dynamic world of foreign exchange, a diverse cast of participants shapes the market’s ebb and flow. From central banks to retail traders, each player brings unique motivations, strategies, and impacts to the table, influencing exchange rates and driving market dynamics.
Central banks, as monetary authorities, set interest rates and intervene in the market to manage inflation and currency stability. Commercial banks facilitate currency exchange for individuals and businesses, while investment banks engage in large-scale trading for their clients. Hedge funds employ sophisticated strategies to capitalize on market fluctuations, and retail traders participate in the market with varying degrees of experience and investment goals.
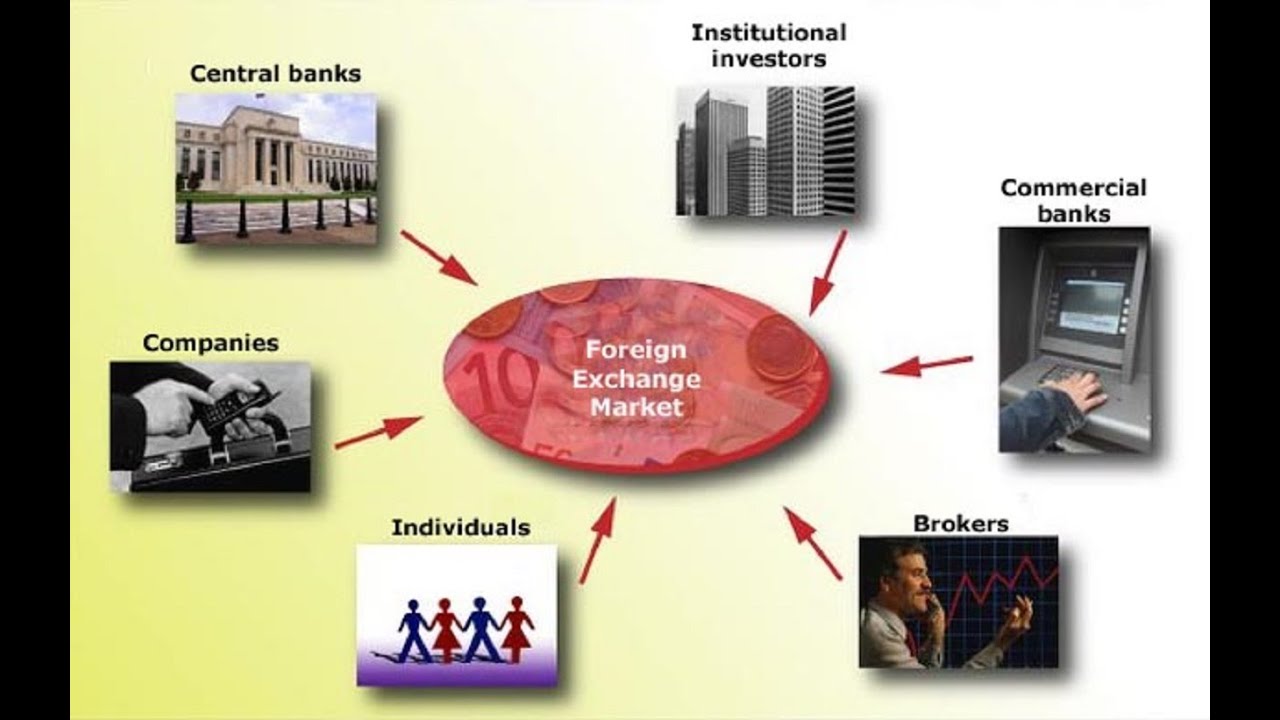
Various Participants of Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market is a vast and complex ecosystem, involving a diverse range of participants with varying roles and responsibilities. These participants can be broadly categorized into three main groups: individuals, financial institutions, and central banks.
Individuals
Individual participants in the forex market include retail traders, who trade currencies for personal profit or speculation. They typically have smaller trading volumes compared to institutional participants and may use online trading platforms or brokers to execute their trades.
Financial Institutions
Financial institutions play a significant role in the forex market, facilitating currency exchange for their clients and engaging in proprietary trading activities. Major financial institutions involved in forex trading include commercial banks, investment banks, and hedge funds. Commercial banks provide currency exchange services to businesses and individuals, while investment banks and hedge funds engage in speculative trading and currency arbitrage.
Central Banks
Central banks are responsible for managing the monetary policy of their respective countries. They participate in the forex market to influence the value of their currency, manage foreign exchange reserves, and maintain economic stability.
Finish your research with information from foreign exchange market volume.
Types of Forex Market Participants

The foreign exchange market is a vast and complex ecosystem, with a wide range of participants playing diverse roles. These participants can be broadly classified into several categories, each with its unique motivations, strategies, and impact on the market.
The main types of participants in the forex market include:
Central Banks
Central banks are government institutions responsible for managing a country’s monetary policy and financial system. They play a significant role in the forex market by intervening to influence the value of their currency. Central banks buy and sell foreign currencies to stabilize exchange rates, manage inflation, and support economic growth.
Commercial Banks
Commercial banks are financial institutions that provide a range of services to individuals and businesses, including foreign exchange trading. They facilitate the exchange of currencies for their customers and also engage in proprietary trading for their own profit.
Investment Banks
Investment banks are financial institutions that specialize in providing financial services to corporations and governments. They play a major role in the forex market by facilitating large-scale currency transactions and offering hedging and advisory services to their clients.
Hedge Funds
Hedge funds are investment funds that use sophisticated strategies to generate high returns for their investors. They often engage in currency trading as part of their investment strategies, taking advantage of exchange rate fluctuations to enhance their portfolio performance.
Notice foreign exchange market control meaning for recommendations and other broad suggestions.
Retail Traders, Various participants of foreign exchange market
Retail traders are individuals who trade currencies on a smaller scale, typically using online platforms. They may trade for various reasons, such as speculation, hedging, or as a hobby.
Motivations and Strategies of Participants
Participants in the forex market exhibit diverse motivations and employ distinct strategies to achieve their financial objectives. These motivations and strategies vary depending on the type of participant, their risk tolerance, and their investment goals.
Generally, the primary motivation for participation in the forex market is to generate profits through currency trading. However, the specific goals and objectives of participants can vary significantly, influencing their trading decisions and strategies.
Explore the different advantages of foreign exchange market import quotas that can change the way you view this issue.
Retail Traders, Various participants of foreign exchange market
Retail traders are individuals who trade currencies on a smaller scale, typically using their own capital. Their motivations for trading can range from short-term profit-making to long-term investment and diversification of portfolios.
- Short-term trading: Retail traders often engage in short-term trading, aiming to capitalize on short-term market fluctuations. They typically use technical analysis and leverage to increase their potential returns.
- Long-term investment: Some retail traders view the forex market as a long-term investment opportunity. They may invest in currencies based on economic fundamentals and hold their positions for an extended period, seeking to benefit from currency appreciation.
- Diversification: Retail traders may also participate in the forex market to diversify their portfolios. By investing in currencies, they can reduce their overall risk exposure and potentially enhance their returns.
Institutional Traders
Institutional traders represent financial institutions, such as banks, hedge funds, and pension funds. They trade currencies on a large scale, typically managing billions of dollars in assets. Their motivations and strategies are often more complex and sophisticated than those of retail traders.
- Risk management: Institutional traders often use the forex market to manage currency risk associated with their global operations or investments. They may engage in hedging strategies to protect against adverse currency fluctuations.
- Profit generation: While risk management is a primary focus, institutional traders also seek to generate profits through currency trading. They may employ advanced trading strategies, such as algorithmic trading and high-frequency trading, to maximize their returns.
- Liquidity provision: Institutional traders often act as market makers, providing liquidity to the forex market. They facilitate currency trading for other participants, earning profits from the bid-ask spread.
Central Banks
Central banks are responsible for managing the monetary policy of their respective countries. They participate in the forex market to influence exchange rates, manage inflation, and maintain economic stability.
- Monetary policy implementation: Central banks use the forex market to implement monetary policy objectives, such as targeting inflation or exchange rate stability. They may buy or sell currencies to influence their value.
- Reserve management: Central banks hold foreign currency reserves to support their domestic currency and manage external imbalances. They may intervene in the forex market to maintain the value of their reserves.
- Financial stability: Central banks may intervene in the forex market to promote financial stability. They may take actions to prevent excessive volatility or speculative bubbles that could destabilize the financial system.
Impact of Participants on Forex Market Dynamics: Various Participants Of Foreign Exchange Market
The forex market is a highly dynamic and complex environment, and the actions of its participants have a significant impact on its dynamics. These participants, ranging from central banks to individual traders, bring diverse motivations and strategies to the market, creating a constant interplay of forces that shape exchange rates and market volatility.
Central Banks
Central banks are the primary regulators of the foreign exchange market, and their actions can have a profound impact on currency values. By setting interest rates, intervening in the market to buy or sell currencies, and managing their foreign exchange reserves, central banks can influence the supply and demand for currencies, thereby affecting their exchange rates.
Commercial Banks
Commercial banks play a crucial role in facilitating foreign exchange transactions for businesses and individuals. They provide currency exchange services, trade finance, and other related products, acting as intermediaries between market participants. The activities of commercial banks contribute to the liquidity of the forex market and help to ensure the smooth functioning of international trade and investment.
Institutional Investors
Institutional investors, such as hedge funds, pension funds, and asset managers, are major players in the forex market. They use complex strategies to speculate on currency movements, often trading large volumes of currencies to capitalize on market inefficiencies. The actions of institutional investors can contribute to market volatility and influence exchange rates.
Retail Traders, Various participants of foreign exchange market
Retail traders, including individual investors and small businesses, participate in the forex market primarily for speculative purposes. They trade currencies in relatively small amounts compared to institutional investors, but their collective actions can still impact market dynamics, especially during periods of high volatility.
Impact on Exchange Rates
The interplay of these participants’ actions influences the supply and demand for currencies, which in turn affects their exchange rates. Central banks’ monetary policies, commercial banks’ trading activities, and institutional investors’ speculative strategies all contribute to the formation of exchange rates.
Impact on Market Volatility
The actions of market participants can also impact market volatility. Sudden changes in sentiment or large-scale trading by institutional investors can trigger sharp fluctuations in exchange rates, leading to increased volatility. Retail traders’ speculative activities can also contribute to market volatility, especially during periods of high uncertainty or market stress.
Regulatory Framework for Forex Market Participants
The foreign exchange market is a highly regulated industry, with regulatory bodies playing a crucial role in ensuring market integrity and protecting investors. These regulatory frameworks provide guidelines and rules that govern the activities of forex market participants, including banks, brokers, and individual traders.
The regulatory framework for forex market participants typically includes the following components:
Licensing and Registration
Forex market participants are required to obtain a license or register with the relevant regulatory body in their jurisdiction. This process involves meeting certain criteria, such as demonstrating financial stability, having adequate risk management systems in place, and adhering to ethical conduct standards.
Capital Requirements
Regulatory bodies often impose capital requirements on forex market participants to ensure they have sufficient financial resources to cover potential losses and meet their obligations to clients. These requirements vary depending on the type of participant and the level of risk involved in their activities.
Risk Management
Regulatory frameworks require forex market participants to have robust risk management systems in place to identify, assess, and mitigate risks. These systems should include measures such as setting stop-loss orders, using leverage prudently, and diversifying portfolios.
Market Conduct Rules
Regulatory bodies establish market conduct rules to ensure fair and orderly trading practices. These rules prohibit activities such as insider trading, market manipulation, and conflicts of interest. They also require forex market participants to provide clear and accurate information to clients and to treat them fairly.
Enforcement
Regulatory bodies have the authority to enforce their rules and regulations through a range of measures, including fines, suspensions, and revocations of licenses. They also work closely with law enforcement agencies to investigate and prosecute cases of fraud or other illegal activities in the forex market.
Ethical Considerations for Forex Market Participants
The foreign exchange market, being a global and dynamic marketplace, demands ethical conduct from its participants to maintain its integrity and stability. Forex market participants have a responsibility to uphold ethical principles, ensuring transparency, fairness, and avoidance of market manipulation.
Transparency and Disclosure
Transparency is crucial in the forex market. Participants must disclose all relevant information that may impact market dynamics, such as their positions, trades, and any potential conflicts of interest. By doing so, they promote trust and confidence among market participants, reducing the risk of insider trading and market manipulation.
Fair Trading Practices
Fair trading practices are essential for maintaining a level playing field in the forex market. Participants must refrain from engaging in any form of market manipulation, such as spreading false or misleading information, creating artificial demand or supply, or colluding with others to influence market prices.
Compliance with Regulations
Forex market participants must adhere to the regulations and guidelines set forth by regulatory authorities. These regulations are designed to protect the integrity of the market, prevent fraud, and ensure fair competition. By complying with these regulations, participants contribute to the stability and credibility of the forex market.
Avoiding Insider Trading
Insider trading, which involves using non-public information to gain an unfair advantage in the market, is strictly prohibited in the forex market. Participants must refrain from engaging in any activity that could give them access to privileged information that is not available to the general public.
Protecting Client Interests
Forex market participants, particularly those providing services to retail clients, have a responsibility to protect their clients’ interests. This includes providing clear and accurate information about products and services, handling client funds responsibly, and acting in their best interests.
Consequences of Unethical Conduct
Violations of ethical principles in the forex market can have severe consequences. Unethical conduct can damage the reputation of the market, erode trust among participants, and lead to legal and regulatory sanctions. Therefore, it is imperative for all participants to adhere to ethical standards and contribute to the integrity and stability of the forex market.
Closing Summary

The interplay of these participants creates a complex and ever-evolving market landscape. Their decisions and actions ripple through the global economy, affecting businesses, investors, and individuals alike. Understanding the motivations, strategies, and impact of various participants is crucial for navigating the complexities of the foreign exchange market.
