Participants in the foreign exchange market, a dynamic and ever-evolving arena, play a crucial role in shaping the global financial landscape. From central banks to multinational corporations, each participant brings unique motivations and objectives to the table, influencing market dynamics and driving currency valuations. This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse world of foreign exchange market participants, exploring their roles, strategies, and impact on the market.
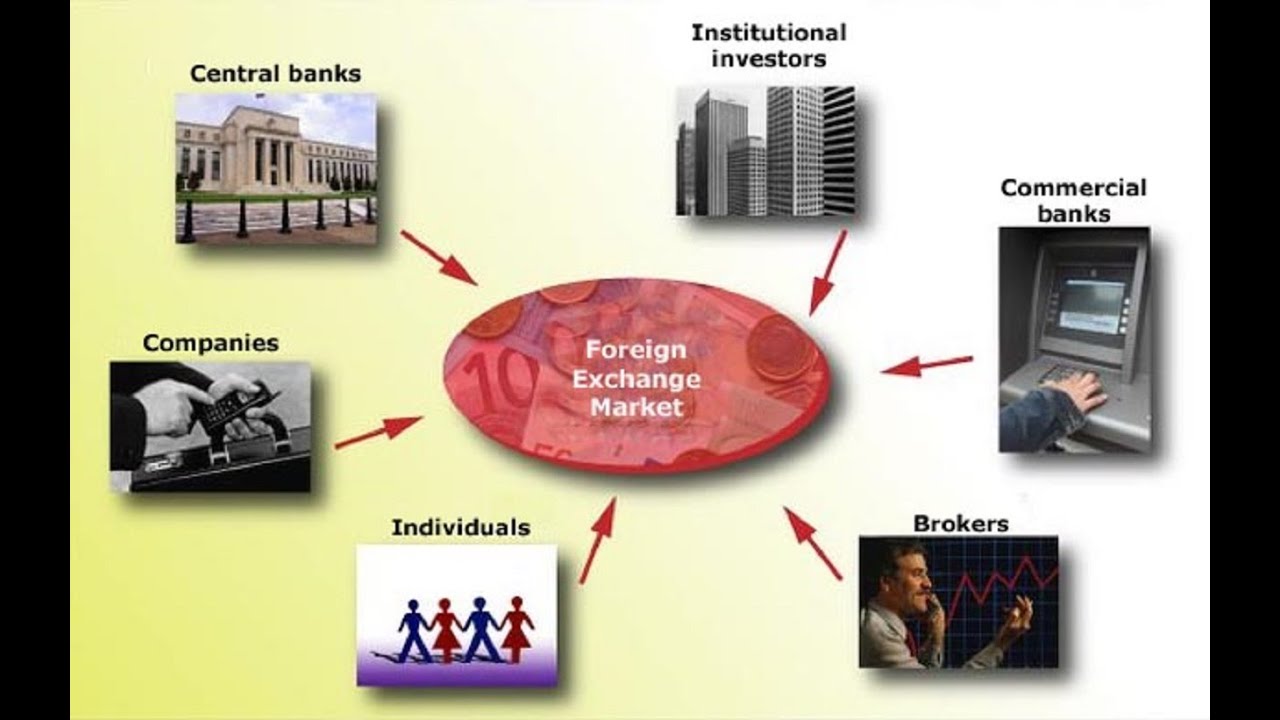
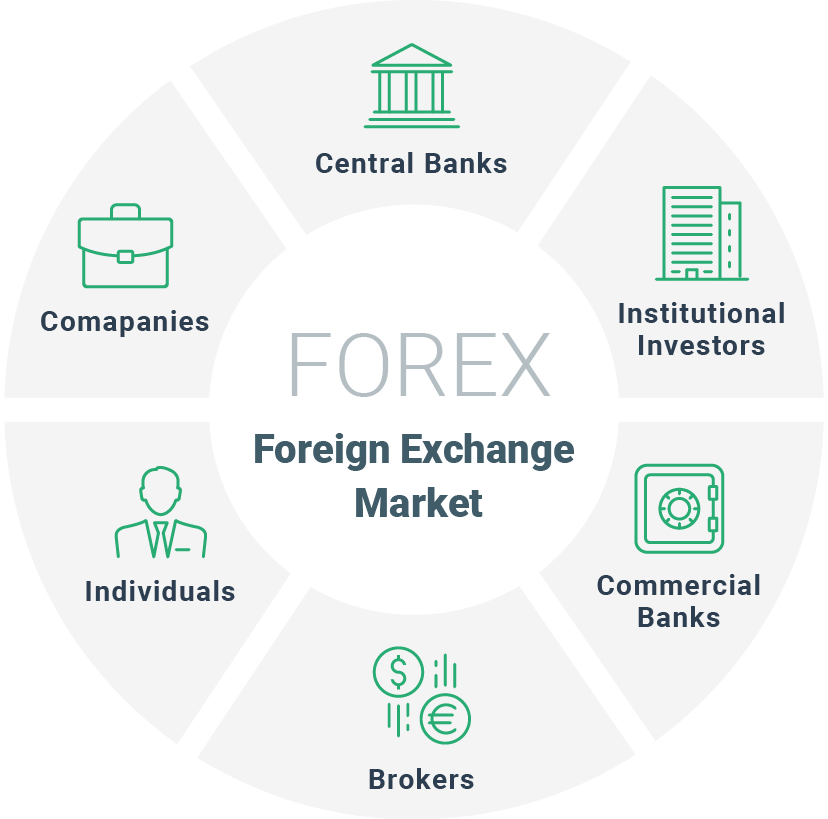
The foreign exchange market, also known as forex or FX, is a decentralized global marketplace where currencies are traded. It facilitates international trade, investment, and tourism, enabling businesses and individuals to exchange currencies seamlessly. The participants in this vast market can be broadly categorized into three main groups: commercial participants, financial participants, and central banks.
Participants in the Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange (forex) market is a global decentralized market for the trading of currencies. Participants in the forex market can be broadly classified into three main categories: commercial entities, financial institutions, and central banks.
Find out about how foreign exchange market data analysis can deliver the best answers for your issues.
Commercial Entities
Commercial entities engage in foreign exchange transactions to facilitate international trade and investment. These include:
- Importers and exporters: Companies that import or export goods and services need to convert their domestic currency into foreign currency and vice versa.
- Multinational corporations: Companies with operations in multiple countries require foreign exchange to manage their global cash flows and investments.
Financial Institutions
Financial institutions play a crucial role in facilitating foreign exchange transactions. They include:
- Commercial banks: Offer foreign exchange services to their retail and corporate customers, such as currency exchange, wire transfers, and hedging products.
- Investment banks: Engage in large-scale foreign exchange trading for their clients and for their own proprietary accounts.
- Foreign exchange brokers: Provide a platform for traders to execute foreign exchange transactions and offer liquidity.
Central Banks
Central banks are responsible for managing the monetary policy of their respective countries. They participate in the foreign exchange market to:
- Manage exchange rates: Central banks may intervene in the foreign exchange market to influence the value of their currency against other currencies.
- Maintain foreign exchange reserves: Central banks hold foreign exchange reserves to support their currency and meet international obligations.
Motivations and Objectives of Participants: Participants In The Foreign Exchange Market
Participants in the foreign exchange market engage in currency trading for a variety of motivations and objectives. These motivations influence their trading behavior and impact the overall dynamics of the market.
One primary motivation is profit-making. Currency traders seek to capitalize on fluctuations in exchange rates by buying and selling currencies at opportune moments. Speculators, in particular, engage in short-term trading strategies with the aim of generating profits from currency price movements.
Explore the different advantages of foreign exchange market economics definition that can change the way you view this issue.
Hedging Risk
Another significant motivation is risk management. Companies and individuals involved in international trade or investment often use foreign exchange to hedge against currency risk. By engaging in currency forwards or options contracts, they can lock in exchange rates and protect themselves from adverse fluctuations that could impact their financial positions.
Do not overlook the opportunity to discover more about the subject of foreign exchange market regulated by.
Transaction Settlement
Foreign exchange transactions are essential for facilitating international trade and investment. Businesses need to convert their currencies into the currencies of their trading partners, and foreign exchange markets provide the platform for these conversions. Importers and exporters use foreign exchange to settle their transactions, ensuring the smooth flow of goods and services across borders.
Official Intervention
Central banks and governments may also participate in the foreign exchange market to influence exchange rates. They intervene to maintain economic stability, manage inflation, or support their national currencies. Official intervention can significantly impact the market, particularly when it involves large-scale purchases or sales of currencies.
Market Conditions
Market conditions can significantly influence the motivations and objectives of participants. In periods of high volatility, speculators may become more active, seeking to capitalize on rapid currency price movements. Conversely, in stable market conditions, hedgers may dominate the market, seeking to protect their exposures against currency fluctuations.
Trading Strategies and Techniques
Participants in the foreign exchange market employ various trading strategies and techniques to achieve their objectives. These strategies involve different approaches to market analysis, risk management, and trade execution.
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis involves studying historical price data to identify patterns and trends that can predict future price movements. It focuses on chart patterns, technical indicators, and other market data to make trading decisions.
- Advantages: Objective and data-driven, identifies potential trading opportunities, suitable for short-term trading.
- Disadvantages: Relies on historical data, which may not always predict future outcomes, can be complex and time-consuming to master.
- Examples: Trend following, support and resistance levels, moving averages.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis focuses on the underlying economic and political factors that influence currency values. It involves analyzing economic data, news events, and geopolitical developments to make informed trading decisions.
- Advantages: Provides a deeper understanding of market fundamentals, can identify long-term trends, suitable for long-term investing.
- Disadvantages: Time-consuming and requires a high level of knowledge, can be influenced by unexpected events.
- Examples: Interest rate differentials, economic growth rates, political stability.
Scalping
Scalping involves taking small, frequent profits by trading within a short time frame, typically within minutes or hours. It requires a high level of market knowledge and execution speed.
- Advantages: Can generate consistent profits in a trending market, suitable for experienced traders.
- Disadvantages: Requires high trading volume, can be stressful and emotionally demanding.
- Examples: Pipsing, range trading.
News Trading
News trading involves trading based on the release of important economic or political news events. It requires a deep understanding of market fundamentals and the ability to react quickly to news.
- Advantages: Can generate large profits in a short time frame, suitable for experienced traders.
- Disadvantages: Requires constant monitoring of news events, can be highly volatile and risky.
- Examples: Trading around central bank announcements, geopolitical events.
Risk Management and Mitigation

The foreign exchange market involves various risks that participants must manage and mitigate to protect their investments. These risks include market risk, liquidity risk, credit risk, and operational risk.
Market Risk
Market risk arises from fluctuations in exchange rates, which can result in losses if the value of a currency moves against a participant’s position. To mitigate this risk, participants can use hedging strategies, such as forward contracts or options, to lock in exchange rates and reduce exposure to adverse price movements.
Liquidity Risk, Participants in the foreign exchange market
Liquidity risk refers to the difficulty or inability to buy or sell a currency at a desired price and quantity. This risk is particularly prevalent in less liquid currency pairs. To mitigate liquidity risk, participants can choose more liquid currency pairs, maintain sufficient capital reserves, and use limit orders to control the price and quantity of their trades.
Credit Risk
Credit risk arises from the possibility that a counterparty in a foreign exchange transaction may default on its obligations. To mitigate credit risk, participants can choose counterparties with strong credit ratings, use credit default swaps, or limit their exposure to individual counterparties.
Operational Risk
Operational risk refers to the potential for losses due to internal processes, human error, or technology failures. To mitigate operational risk, participants can implement robust risk management systems, conduct thorough due diligence on counterparties, and use reliable technology platforms.
Regulation and Oversight
The foreign exchange market, being a vast and complex global marketplace, requires a robust regulatory framework to ensure its stability, transparency, and integrity. This framework is established by regulatory bodies in various jurisdictions to oversee the activities of market participants and maintain market order.
Regulatory Bodies
Regulatory bodies play a crucial role in overseeing the foreign exchange market. They are responsible for setting regulations, monitoring market activities, enforcing compliance, and taking disciplinary actions against non-compliant entities. Some notable regulatory bodies include the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the United Kingdom, the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) in the United States, and the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) in the European Union.
Regulations and Oversight Measures
Regulations and oversight measures implemented in the foreign exchange market aim to address various risks and promote fair and orderly trading practices. These include:
- Capital requirements: Regulators set minimum capital requirements for foreign exchange participants to ensure they have sufficient financial resources to cover potential losses.
- Risk management frameworks: Participants are required to implement robust risk management frameworks to identify, assess, and mitigate risks associated with their trading activities.
- Anti-money laundering and counter-terrorism financing measures: Regulations are in place to prevent the use of the foreign exchange market for money laundering or terrorist financing activities.
- Market surveillance: Regulatory bodies conduct market surveillance to monitor trading activities, detect suspicious behavior, and investigate potential misconduct.
- Enforcement actions: Regulators have the authority to impose sanctions, including fines, suspensions, or revocations of licenses, on entities that violate regulations or engage in misconduct.
These regulations and oversight measures help to maintain the integrity of the foreign exchange market, protect investors, and promote fair competition among market participants.
Last Word
In conclusion, the foreign exchange market is a complex and multifaceted ecosystem where a diverse range of participants interact to facilitate global currency exchange. Understanding the motivations, objectives, and strategies of these participants is essential for navigating the complexities of the forex market. By delving into the world of foreign exchange market participants, we gain a deeper appreciation for the forces that shape currency valuations and drive economic activity around the globe.
