The economics foreign exchange market – The economics of the foreign exchange market, a fascinating realm of global finance, holds immense significance in shaping the world’s economic landscape. This intricate network, where currencies are traded and exchanged, plays a pivotal role in facilitating international commerce, investments, and economic growth. Join us as we delve into the depths of this dynamic market, exploring its intricacies and unraveling its impact on the global economy.
In this comprehensive guide, we will embark on a journey through the foreign exchange market, examining its purpose, functions, and major players. We will analyze the factors that influence exchange rates, including economic and political dynamics, supply and demand, and the role of central banks. Furthermore, we will explore the various foreign exchange instruments available, such as spot contracts, forward contracts, and options, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages.
Overview of the Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market, also known as the forex market or currency market, is a global decentralized market where currencies are traded. It is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with an average daily trading volume of over $5 trillion.
The purpose of the foreign exchange market is to facilitate the exchange of currencies for various reasons, including international trade, investment, tourism, and speculation. It enables businesses and individuals to convert one currency into another to settle international transactions, hedge against currency risks, and make speculative investments.
Major Participants in the Foreign Exchange Market
The major participants in the foreign exchange market include:
- Commercial banks: They are the largest participants in the forex market, facilitating currency exchange for their corporate and retail clients.
- Investment banks: They trade currencies on behalf of their clients, providing liquidity and execution services.
- Hedge funds: They use sophisticated trading strategies to profit from currency fluctuations.
- Central banks: They intervene in the forex market to manage their countries’ exchange rates and monetary policies.
- Corporations: They exchange currencies to settle international transactions and manage currency risks.
- Retail traders: They speculate on currency movements and trade currencies in smaller amounts.
Types of Foreign Exchange Transactions, The economics foreign exchange market
There are different types of foreign exchange transactions, including:
- Spot transactions: These involve the immediate exchange of currencies at the current market rate.
- Forward transactions: These involve the exchange of currencies at a predetermined rate on a future date.
- Swap transactions: These involve the simultaneous buying and selling of different currencies at different maturities.
- Option transactions: These give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to exchange currencies at a specified rate on or before a certain date.
Factors Affecting Foreign Exchange Rates
Foreign exchange rates are influenced by a multitude of economic and political factors, as well as the forces of supply and demand.
Discover how foreign exchange market instruments has transformed methods in RELATED FIELD.
Economic Factors
Economic factors that affect foreign exchange rates include:
- Interest rates: Higher interest rates in a country tend to attract foreign investment, increasing demand for the country’s currency and leading to an appreciation in its value.
- Inflation: High inflation can erode the purchasing power of a currency, reducing its value relative to other currencies.
- Economic growth: Strong economic growth can increase demand for a country’s goods and services, boosting the demand for its currency.
- Balance of payments: A country’s balance of payments measures the difference between the value of its exports and imports. A positive balance of payments indicates that the country is exporting more than it is importing, which can lead to an appreciation in its currency.
Political Factors
Political factors that can affect foreign exchange rates include:
- Political stability: Political instability or uncertainty can lead to a decrease in investor confidence and a depreciation in the country’s currency.
- Government policies: Government policies, such as fiscal and monetary policies, can have a significant impact on foreign exchange rates.
- International relations: Diplomatic tensions or conflicts between countries can lead to a decrease in demand for a country’s currency.
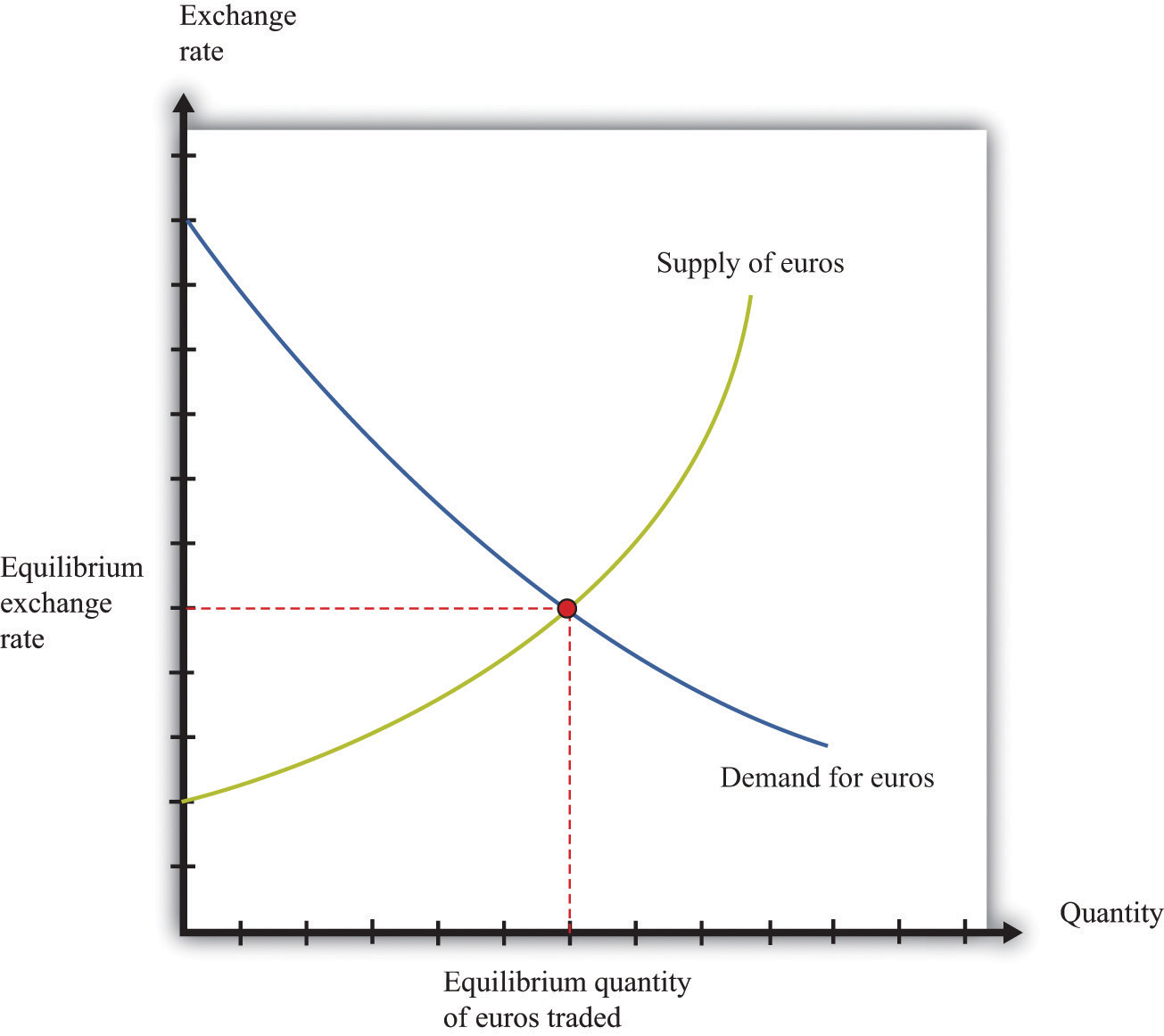
Supply and Demand
The supply and demand for a currency also plays a crucial role in determining its exchange rate. When there is more demand for a currency than there is supply, its value will increase. Conversely, when there is more supply of a currency than there is demand, its value will decrease.
When investigating detailed guidance, check out foreign exchange rates market kenya now.
Role of Central Banks
Central banks play a significant role in managing foreign exchange rates through monetary policy. They can intervene in the foreign exchange market by buying or selling currencies to influence their value. For example, if a central bank wants to depreciate its currency, it can sell its currency in the market, increasing the supply and reducing its value.
Foreign Exchange Market Instruments
Foreign exchange instruments are financial contracts that facilitate the exchange of currencies. They enable businesses and individuals to manage currency risk, speculate on exchange rate fluctuations, and facilitate international trade. There are various types of foreign exchange instruments, each with unique characteristics and purposes.
Spot Contracts
Spot contracts are agreements to exchange currencies at the current market rate, with settlement occurring within two business days. They are used for immediate currency needs, such as settling international payments or purchasing foreign goods. Spot contracts offer transparency and immediacy, but they do not provide protection against future exchange rate fluctuations.
Forward Contracts
Forward contracts are agreements to exchange currencies at a predetermined rate on a specified future date. They are used to hedge against currency risk by locking in an exchange rate for future transactions. Forward contracts provide certainty and reduce uncertainty, but they are less flexible than spot contracts and may incur additional costs.
Options
Options are contracts that give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specified amount of currency at a predetermined price within a certain time frame. There are two types of options: calls and puts. Calls give the buyer the right to buy a currency at a set price, while puts give the buyer the right to sell a currency at a set price. Options provide flexibility and the potential for profit, but they also involve premiums that can reduce profitability.
Foreign Exchange Market Risks
The foreign exchange market involves inherent risks that can impact traders and investors. Understanding and managing these risks is crucial for successful participation in the market.
For descriptions on additional topics like biggest foreign exchange market in the world, please visit the available biggest foreign exchange market in the world.
There are several types of risks associated with foreign exchange trading, including:
- Currency Risk: The risk of loss due to fluctuations in the value of one currency against another.
- Interest Rate Risk: The risk of loss due to changes in interest rates, which can affect the value of currencies.
- Political Risk: The risk of loss due to political events or changes in government policies that can impact currency values.
- Economic Risk: The risk of loss due to changes in economic conditions, such as inflation, recession, or economic growth, which can affect currency values.
- Liquidity Risk: The risk of loss due to the inability to buy or sell a currency quickly and at a fair price.
Managing Foreign Exchange Risk
Managing foreign exchange risk involves implementing strategies to mitigate potential losses. These strategies include:
- Diversification: Spreading investments across different currencies to reduce the impact of fluctuations in any single currency.
- Hedging: Using financial instruments, such as forwards, futures, or options, to offset the risk of currency fluctuations.
- Natural Hedging: Matching foreign exchange exposures with natural offsets, such as importing and exporting in different currencies.
- Risk Monitoring: Continuously monitoring foreign exchange market conditions and adjusting risk management strategies as needed.
Hedging in Foreign Exchange Risk Mitigation
Hedging plays a significant role in mitigating foreign exchange risk. Hedging involves using financial instruments to offset the risk of currency fluctuations. These instruments include:
- Forward Contracts: Agreements to buy or sell a currency at a specified price on a future date.
- Futures Contracts: Standardized contracts to buy or sell a currency at a specified price on a future date, traded on exchanges.
- Options: Contracts that give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a currency at a specified price on or before a specified date.
By using hedging instruments, traders and investors can reduce their exposure to foreign exchange risk and protect their profits.
The Economics of the Foreign Exchange Market: The Economics Foreign Exchange Market

The foreign exchange market plays a crucial role in facilitating global trade and investment. It enables businesses to conduct transactions across borders and individuals to send remittances to their home countries.
Foreign exchange rate fluctuations can significantly impact trade and investment. When the value of a country’s currency appreciates, its exports become more expensive and less competitive in the global market, while imports become cheaper. Conversely, a depreciation in the currency value makes exports more competitive and imports more expensive.
Impact on Trade
- Currency appreciation can lead to a decrease in exports and an increase in imports, resulting in a trade deficit.
- Currency depreciation can boost exports and reduce imports, leading to a trade surplus.
Impact on Investment
- Investors may be more likely to invest in countries with stable or appreciating currencies, as their investments are less exposed to foreign exchange risk.
- Currency depreciation can make investments in a country less attractive, as investors fear potential losses due to exchange rate fluctuations.
Furthermore, foreign exchange rates have a close relationship with economic growth. A stable and competitive exchange rate can foster economic growth by promoting trade and investment. On the other hand, large and volatile fluctuations in exchange rates can create uncertainty and disrupt economic activity.
Conclusion

As we conclude our exploration of the economics of the foreign exchange market, it becomes evident that this dynamic arena serves as a barometer of global economic health. Exchange rate fluctuations have far-reaching implications for trade, investment, and economic growth. Understanding the intricacies of this market empowers individuals and businesses alike to navigate the complexities of international finance and make informed decisions.
