Foreign exchange market and their functions – The foreign exchange market, a global financial hub, plays a pivotal role in facilitating international trade, providing liquidity, and influencing economic stability. Join us as we delve into the functions and intricate workings of this dynamic marketplace.
Foreign Exchange Market Overview
The foreign exchange market, also known as the forex market, is a global decentralized market for the trading of currencies. It is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume of over $5 trillion.
The forex market is a two-way market, meaning that there is always a buyer and a seller for every currency pair. The exchange rate between two currencies is determined by supply and demand. When there is more demand for a currency than there is supply, the price of that currency will rise. Conversely, when there is more supply of a currency than there is demand, the price of that currency will fall.
Participants in the Forex Market
The participants in the forex market include banks, hedge funds, investment funds, corporations, and individual traders. Banks are the largest participants in the forex market, accounting for over 50% of all trading volume. Hedge funds and investment funds are also major participants in the forex market, using it to speculate on currency movements and to hedge against risk.
Finish your research with information from arbitrage in foreign exchange market pdf.
History of the Forex Market
The forex market has its origins in the early days of international trade. Merchants would exchange currencies to facilitate trade between different countries. The first formal forex market was established in London in the 18th century. The market has grown exponentially since then, and it is now the largest and most liquid financial market in the world.
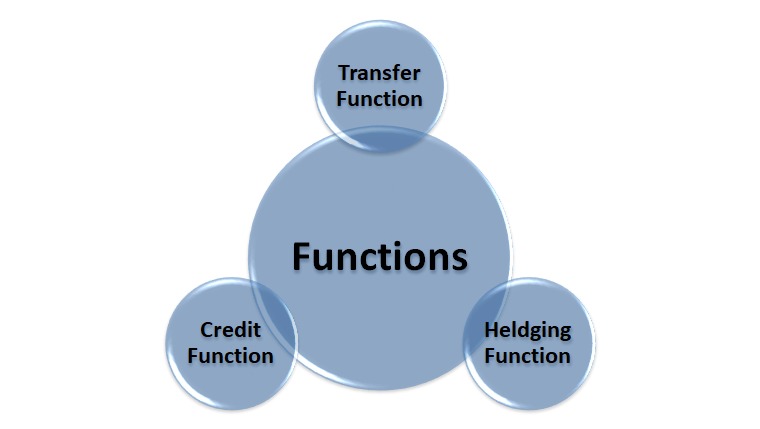
Functions of the Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange (forex) market is a global, decentralized marketplace where currencies are traded. It plays a crucial role in facilitating international trade, providing liquidity, and ensuring price discovery. The forex market also contributes to global economic stability by allowing countries to manage their exchange rates and mitigate financial risks.
Facilitating International Trade, Foreign exchange market and their functions
The forex market is essential for international trade. When businesses import or export goods and services, they need to convert their domestic currency into the currency of the country they are trading with. The forex market provides the platform for these currency exchanges, enabling businesses to conduct international transactions smoothly.
Providing Liquidity and Price Discovery
The forex market is one of the most liquid markets in the world, with trillions of dollars traded daily. This liquidity ensures that businesses and investors can easily buy or sell currencies at fair market prices. The forex market also provides price discovery, which refers to the process of determining the equilibrium price of a currency based on supply and demand. The constant buying and selling in the forex market helps to establish the value of currencies relative to each other.
Impact on Global Economic Stability
The forex market contributes to global economic stability by allowing countries to manage their exchange rates. Central banks and governments can intervene in the forex market to influence the value of their currencies. This can be done to stabilize the economy, promote economic growth, or mitigate financial risks.
Factors Influencing Foreign Exchange Rates
Exchange rates are constantly fluctuating due to various economic and political factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for businesses, investors, and policymakers.
One of the primary factors influencing exchange rates is supply and demand. When the demand for a currency increases, its value tends to appreciate. Conversely, when the supply of a currency exceeds demand, its value tends to depreciate.
Browse the implementation of explain functions of foreign exchange market in real-world situations to understand its applications.
Impact of Supply and Demand on Exchange Rates
- Increased demand for a currency can result from factors such as economic growth, political stability, or favorable interest rates.
- Increased supply of a currency can occur due to factors such as economic weakness, political instability, or unfavorable interest rates.
Another significant factor influencing exchange rates is the role of central banks. Central banks intervene in the foreign exchange market to manage their currencies’ values.
Find out further about the benefits of foreign exchange market meaning with example that can provide significant benefits.
Role of Central Banks in Managing Exchange Rates
- Central banks can buy or sell their currencies to influence their value.
- Central banks can also adjust interest rates to make their currencies more or less attractive to investors.
Types of Foreign Exchange Transactions

In the foreign exchange market, various types of transactions facilitate the exchange of currencies. These transactions cater to different needs and time frames, enabling businesses and individuals to manage currency risk and facilitate international trade and investment.
Spot Transactions
Spot transactions involve the immediate exchange of currencies at the current market rate. The settlement typically occurs within two business days, making them suitable for short-term currency needs.
For example, an importer may need to purchase foreign currency to pay for imported goods. A spot transaction allows them to obtain the currency at the prevailing market rate, facilitating the immediate settlement of the transaction.
Forward Transactions
Forward transactions are contracts to exchange currencies at a predetermined rate on a future date. They are used to lock in exchange rates and mitigate currency risk over longer time frames.
Consider a company expecting to receive foreign currency in the future. A forward contract allows them to secure the exchange rate today, protecting against potential fluctuations that could impact their profits.
Swap Transactions
Swap transactions involve the simultaneous buying and selling of currencies with different value dates. They are often used for complex currency management strategies and can be customized to meet specific requirements.
For instance, a multinational corporation with subsidiaries in multiple countries may use a swap transaction to exchange currencies between subsidiaries, optimizing their cash flow and reducing transaction costs.
Foreign Exchange Market Structure

The foreign exchange market is a global, decentralized market where currencies are traded. It is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume of over $5 trillion.
The forex market is divided into two main segments: the interbank market and the retail market. The interbank market is where large banks and other financial institutions trade currencies with each other. The retail market is where individual investors and small businesses trade currencies.
Electronic Trading Platforms
Electronic trading platforms have revolutionized the forex market. These platforms allow traders to execute trades directly with each other, without the need for a broker. Electronic trading platforms have made the forex market more accessible to individual investors and small businesses.
Types of Orders
There are a variety of different types of orders that can be used in the forex market. The most common types of orders are market orders, limit orders, and stop orders.
- Market orders are executed at the current market price.
- Limit orders are executed at a specified price or better.
- Stop orders are executed when the market price reaches a specified level.
Executing Foreign Exchange Trades
The process of executing a foreign exchange trade is relatively simple. The trader simply needs to place an order with their broker or electronic trading platform. The broker or platform will then execute the trade on the trader’s behalf.
Foreign Exchange Market Regulation: Foreign Exchange Market And Their Functions
Regulating the foreign exchange market is crucial to maintain its stability, transparency, and integrity. It helps prevent market manipulation, insider trading, and other unethical practices that can disrupt the market’s efficiency and fairness.
Various regulatory bodies oversee the forex market, including central banks, financial authorities, and international organizations. They establish rules and regulations to ensure orderly trading and protect market participants.
Key Regulations and Compliance Requirements
Forex market participants must adhere to strict regulations and compliance requirements set by regulatory bodies. These include:
- Registration and licensing requirements for forex brokers and dealers
- Capital adequacy and risk management guidelines
- Anti-money laundering and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations
- Reporting and disclosure obligations
- Market surveillance and enforcement mechanisms
Final Review
In conclusion, the foreign exchange market stands as a cornerstone of global finance, facilitating trade, providing liquidity, and influencing economic stability. Understanding its functions and dynamics empowers individuals and businesses to navigate the ever-changing financial landscape effectively.
