Foreign exchange market definition finance: Delve into the fascinating world of foreign exchange, where currencies dance and economies intertwine. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the intricate workings of the global currency market, its key players, and the factors that shape its ever-changing landscape.
From understanding the basics of foreign exchange transactions to navigating the complexities of market dynamics, this guide will equip you with a deep understanding of this dynamic and interconnected financial ecosystem.
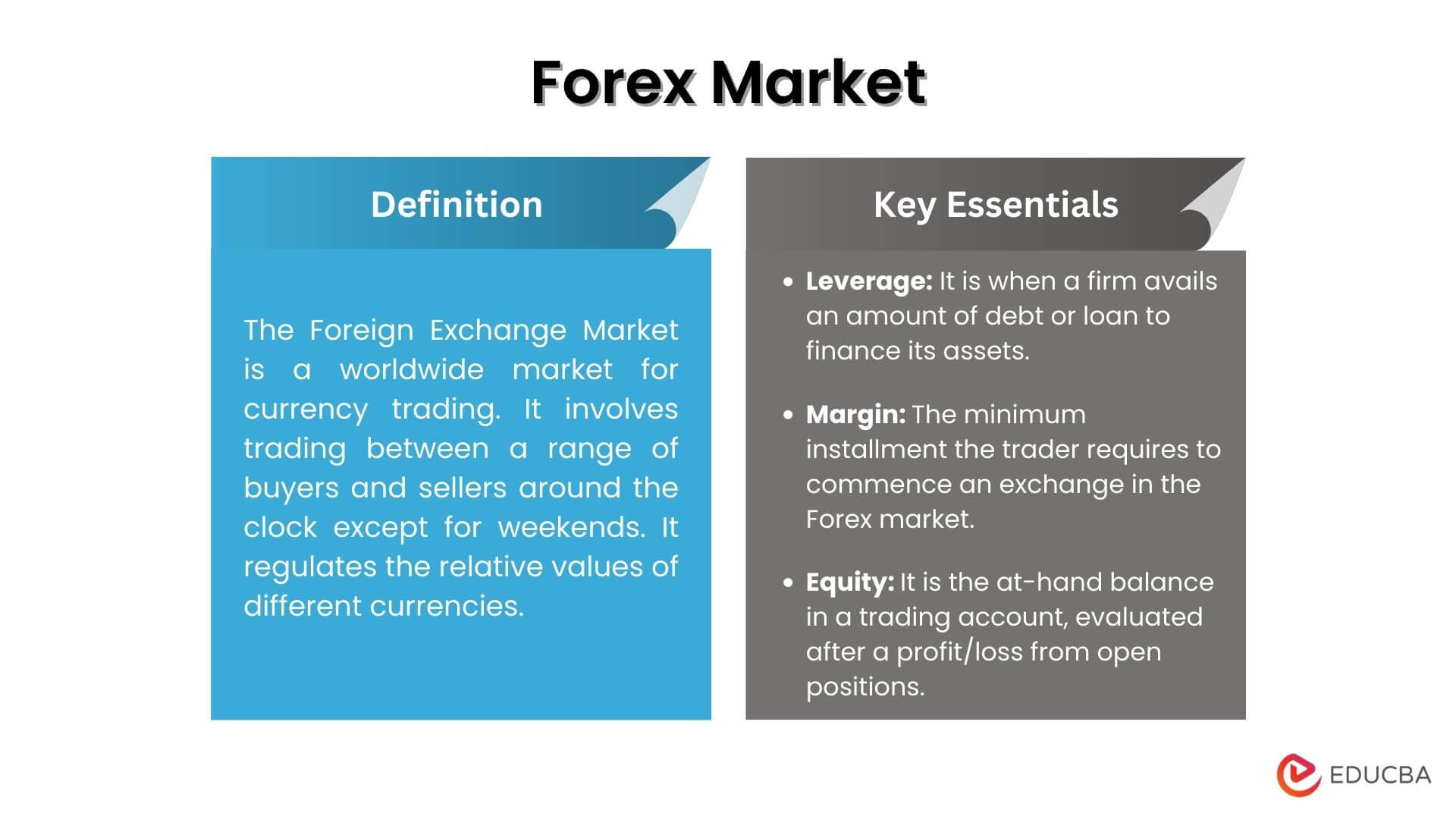
Definition of Foreign Exchange Market
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/foreign-exchange-markets.asp-final-16abed069d5e4ba0924142476dec4211.png)
The foreign exchange market, also known as Forex or FX, is a global decentralized market for trading currencies. It’s the largest financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume of over $6.6 trillion.
Remember to click foreign exchange reserves by country to understand more comprehensive aspects of the foreign exchange reserves by country topic.
Foreign exchange plays a crucial role in global trade and economies. It facilitates the exchange of currencies for international transactions, such as importing and exporting goods and services, making foreign investments, and settling international debts.
Types of Foreign Exchange Transactions
There are various types of foreign exchange transactions, including:
- Spot transactions: These are transactions where currencies are exchanged at the current market rate, with settlement occurring within two business days.
- Forward transactions: These are contracts to exchange currencies at a predetermined rate on a future date.
- Swap transactions: These involve the simultaneous exchange of currencies and a commitment to reverse the exchange at a later date.
Participants in the Foreign Exchange Market

The foreign exchange market is a vast and complex ecosystem, with a diverse range of participants playing significant roles. Understanding the key players and their motivations is crucial for comprehending the dynamics of this global marketplace.
Understand how the union of foreign exchange market participants and functions can improve efficiency and productivity.
Major participants in the foreign exchange market include:
- Central banks: Central banks are responsible for managing the monetary policies of their respective countries. They intervene in the foreign exchange market to influence the value of their currencies and achieve economic stability.
- Commercial banks: Commercial banks facilitate foreign exchange transactions for their corporate and individual clients. They act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers of currencies, earning profits from the spread between the bid and ask prices.
- Investment banks: Investment banks provide a wide range of foreign exchange services, including currency trading, hedging, and advisory services. They play a major role in the interbank market, where large-volume currency transactions occur.
- Hedge funds: Hedge funds are actively managed investment funds that use sophisticated strategies to generate returns. Many hedge funds engage in currency trading as part of their investment strategies.
- Corporations: Corporations with international operations need to exchange currencies for cross-border transactions. They participate in the foreign exchange market to manage their currency risk and facilitate their global operations.
- Retail investors: Retail investors can participate in the foreign exchange market through online trading platforms. However, this segment of the market is typically smaller and less influential compared to institutional participants.
The interactions between these participants create a dynamic and ever-evolving foreign exchange market. Central banks’ interventions can influence currency values, while commercial banks provide liquidity and facilitate transactions. Investment banks and hedge funds contribute to market volatility through their trading activities. Corporations’ currency needs create demand and supply, while retail investors add depth to the market. The interplay of these participants ensures the smooth functioning and liquidity of the foreign exchange market.
Factors Influencing Foreign Exchange Rates
Foreign exchange rates, determining the value of one currency against another, are influenced by a multitude of factors, primarily economic, political, and market-driven. Understanding these factors is crucial for comprehending currency fluctuations and making informed decisions in the foreign exchange market.
Economic Factors
Economic factors play a significant role in shaping exchange rates. A country’s economic strength, measured by indicators such as GDP growth, inflation, and interest rates, directly impacts the value of its currency. Stronger economies tend to attract foreign investment and increase demand for their currency, leading to currency appreciation. Conversely, weaker economies may experience currency depreciation due to reduced investment and increased risk perception.
Political Factors
Political stability and government policies can also influence exchange rates. Political turmoil, wars, and changes in government can lead to currency volatility. Investors often seek refuge in currencies perceived as safe havens during periods of political uncertainty, resulting in currency appreciation. Similarly, policies such as changes in interest rates, tax laws, or trade regulations can impact the attractiveness of a country’s economy and influence currency valuations.
Market Factors
Market factors, including supply and demand, play a crucial role in determining exchange rates. When demand for a currency exceeds its supply, its value appreciates. Conversely, when supply exceeds demand, the currency depreciates. Factors such as global economic conditions, interest rate differentials, and speculative trading can influence supply and demand dynamics, leading to currency fluctuations.
Example
The recent depreciation of the British pound following the Brexit referendum illustrates the impact of political factors on exchange rates. The uncertainty surrounding the UK’s future trade agreements and economic prospects led to a sharp decline in the pound’s value against other major currencies.
Foreign Exchange Market Instruments
The foreign exchange market utilizes various instruments to facilitate currency trading and meet diverse investment objectives. These instruments offer different characteristics, purposes, and risk profiles, catering to the needs of market participants.
Spot Contracts
Spot contracts involve the immediate exchange of currencies at the prevailing market rate. They are typically settled within two business days and are used for immediate delivery of currencies for various purposes, such as international trade, travel, and investment.
Forward Contracts
Forward contracts are agreements to exchange currencies at a predetermined rate on a future date. They are used to hedge against exchange rate fluctuations and lock in future exchange rates for transactions that will occur at a later date. Forward contracts provide greater certainty and reduce the risk of unfavorable exchange rate movements.
Currency Options
Currency options grant the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specified amount of currency at a predetermined price on or before a certain date. They provide flexibility and the potential for profit if the exchange rate moves in the desired direction. Options can be used for speculation, hedging, or income generation.
Currency Swaps
Currency swaps are agreements between two parties to exchange a series of cash flows denominated in different currencies. They are typically used to manage currency exposure, hedge against exchange rate risks, or access foreign currency funding at a more favorable rate.
Currency Futures
Currency futures are standardized contracts traded on exchanges that obligate the buyer to purchase or the seller to sell a specific amount of currency at a predetermined price on a future date. They provide liquidity, transparency, and the opportunity to speculate or hedge against exchange rate risks.
Foreign Exchange Market Risks: Foreign Exchange Market Definition Finance
The foreign exchange market is a dynamic and complex environment, and it carries various risks that can impact investors and businesses. Understanding these risks is crucial for successful participation in the forex market.
Currency Risk
Currency risk, also known as exchange rate risk, is the risk that the value of one currency will fluctuate relative to another. This can result in losses for investors or businesses if the value of their assets or liabilities denominated in a foreign currency changes unfavorably.
Further details about foreign exchange rate is accessible to provide you additional insights.
Interest Rate Risk
Interest rate risk refers to the risk that changes in interest rates will affect the value of foreign exchange investments. When interest rates in one country increase relative to another, it can make it more attractive for investors to hold assets in that country, leading to an appreciation of its currency.
Political Risk
Political risk arises from political events or changes in a country’s political environment that can affect the value of its currency. These events could include changes in government, political instability, or economic sanctions, which can lead to currency volatility and devaluation.
Liquidity Risk
Liquidity risk refers to the difficulty or inability to buy or sell a currency quickly and at a fair price. This can occur during periods of market volatility or when trading in less liquid currencies, resulting in potential losses or missed opportunities.
Counterparty Risk, Foreign exchange market definition finance
Counterparty risk is the risk that the other party in a foreign exchange transaction will not fulfill its obligations. This can occur due to bankruptcy, insolvency, or fraud, leading to potential financial losses for the counterparty.
Strategies for Managing Foreign Exchange Risk
There are several strategies that investors and businesses can employ to manage foreign exchange risk:
- Hedging: Using financial instruments such as forward contracts, options, or swaps to offset the risk of currency fluctuations.
- Diversification: Investing in a portfolio of assets denominated in different currencies to reduce the impact of currency fluctuations.
- Currency Forecasting: Using economic data and analysis to predict currency movements and make informed investment decisions.
- Natural Hedging: Matching assets and liabilities denominated in different currencies to reduce the net exposure to foreign exchange risk.
Foreign Exchange Market Regulation
The foreign exchange market operates within a framework of regulations established by central banks, government agencies, and international organizations. These regulations aim to ensure market stability, transparency, and protect participants.
Role of Central Banks
Central banks play a crucial role in regulating the foreign exchange market by managing monetary policy, intervening in the market to stabilize exchange rates, and overseeing the activities of financial institutions involved in foreign exchange transactions.
Role of Other Regulatory Bodies
In addition to central banks, other regulatory bodies, such as the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) and the International Monetary Fund (IMF), provide guidelines and standards for foreign exchange market operations. These bodies promote transparency, cooperation, and risk management practices among market participants.
Impact of Regulation
Regulation in the foreign exchange market has a significant impact on market stability and transparency. It helps to:
– Prevent market manipulation and insider trading
– Ensure fair and orderly market practices
– Protect investors and market participants from fraud and abuse
– Facilitate the efficient functioning of the market
Final Conclusion
As we conclude our journey into the foreign exchange market, it’s evident that this global marketplace is a complex and ever-evolving entity. Its participants, instruments, and risks are intertwined in a delicate dance, influenced by a myriad of economic, political, and market forces.
Understanding the intricacies of the foreign exchange market empowers individuals and businesses alike to navigate its complexities, mitigate risks, and harness its potential for financial success.
