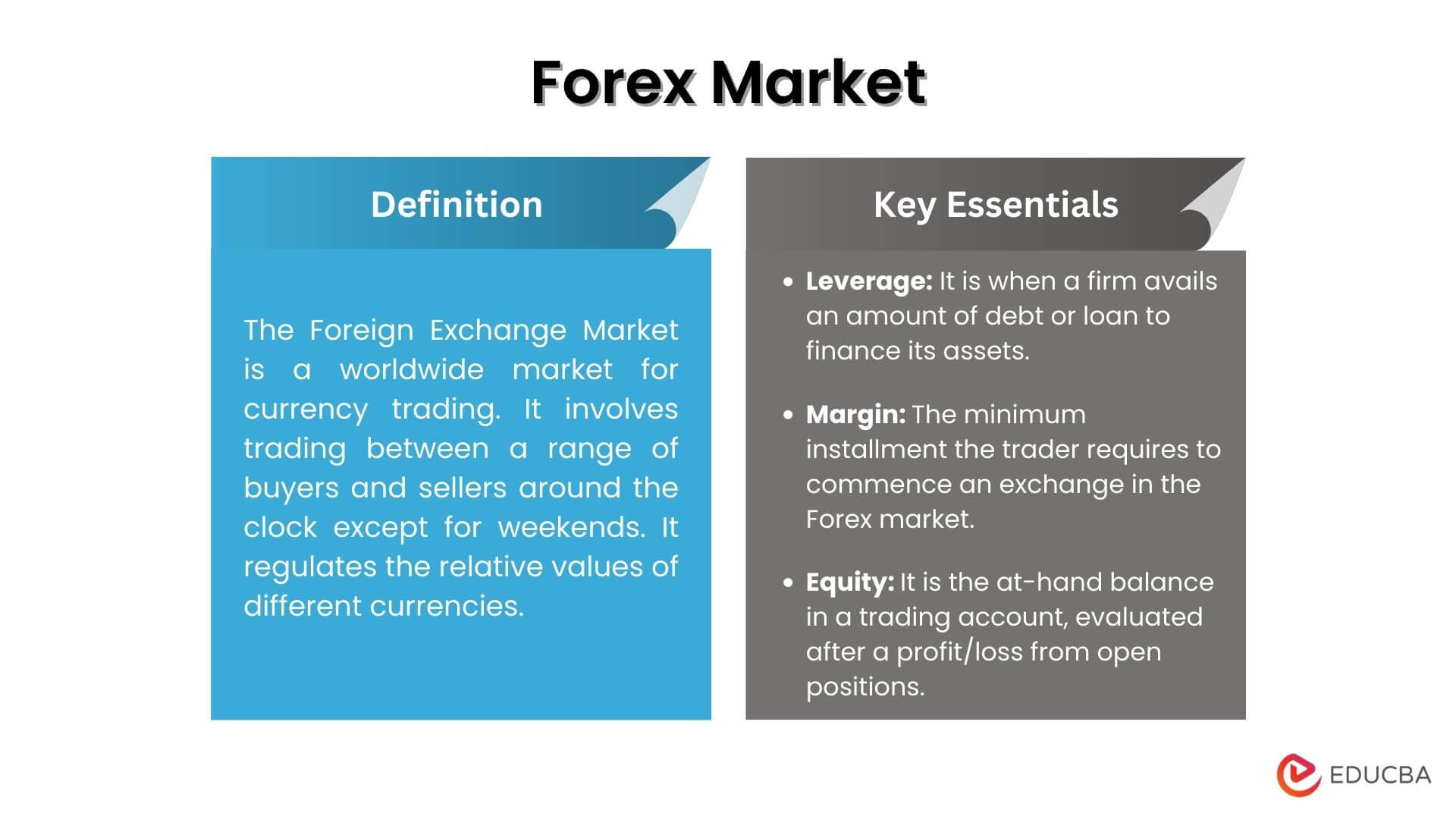
Definition of foreign exchange market – The foreign exchange market, the world’s largest financial marketplace, is the central hub where currencies are traded and exchanged. It facilitates international trade, investments, and tourism, playing a pivotal role in the global economy.
The foreign exchange market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, with participants from diverse backgrounds, including banks, corporations, investment funds, and individual traders.
Definition of Foreign Exchange Market
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Exchange-Rate-1b1df02db6a14eee998e1b76d5c9b82d.jpg)
The foreign exchange market, also known as the forex market or currency market, is a global decentralized marketplace where currencies are traded. It is the largest financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume of over $5 trillion.
The purpose of the foreign exchange market is to facilitate the exchange of currencies for international trade and investment. It allows businesses, individuals, and governments to convert one currency into another at a market-determined exchange rate.
Find out further about the benefits of foreign exchange market share that can provide significant benefits.
Currencies Traded in the Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market trades a wide range of currencies, including major currencies like the US dollar, euro, Japanese yen, British pound, and Swiss franc, as well as emerging market currencies like the Chinese yuan, Indian rupee, and Brazilian real.
Participants in the Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market is a global, decentralized market where currencies are traded. The participants in this market are diverse and include individuals, businesses, banks, and governments.
Check forex news today to inspect complete evaluations and testimonials from users.
Individuals
Individuals participate in the foreign exchange market for various reasons, such as travel, business, or investment. When individuals travel to a foreign country, they need to exchange their home currency for the local currency. Similarly, businesses that import or export goods and services need to exchange currencies to facilitate international trade.
Businesses
Businesses participate in the foreign exchange market to manage their foreign currency exposure. Foreign currency exposure arises when a business has assets or liabilities denominated in a foreign currency. Businesses use foreign exchange hedging strategies to mitigate the risks associated with currency fluctuations.
Banks
Banks play a crucial role in the foreign exchange market as they act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers of currencies. Banks provide a platform for currency trading and offer a range of foreign exchange services, such as currency exchange, currency forwards, and currency options.
Governments
Governments participate in the foreign exchange market to manage their currency reserves and influence the value of their currencies. Central banks, which are responsible for managing a country’s monetary policy, often intervene in the foreign exchange market to stabilize the currency’s value or to achieve specific economic goals.
Factors Affecting Foreign Exchange Rates
Foreign exchange rates are influenced by a multitude of economic, political, and social factors. These factors can have significant impacts on currency values, leading to fluctuations in the market.
Economic Factors
- Interest rates: Central banks set interest rates to influence inflation and economic growth. Higher interest rates make a currency more attractive to investors, leading to an appreciation in its value.
- Inflation: Inflation erodes the purchasing power of a currency, making it less valuable relative to others. High inflation can lead to currency depreciation.
- Economic growth: A strong economy attracts foreign investment, boosting demand for the currency and causing it to appreciate. Conversely, a weak economy can lead to currency depreciation.
Political Factors
- Political stability: Currency values are sensitive to political uncertainty and instability. Political turmoil or changes in government can lead to currency depreciation.
- Government policies: Government policies, such as fiscal and monetary policies, can impact currency values. For example, expansionary fiscal policies can lead to inflation and currency depreciation.
Social Factors
- Cultural events: Major cultural events, such as the Olympics or World Cup, can lead to increased demand for a currency and cause it to appreciate.
- Natural disasters: Natural disasters can disrupt economic activity and lead to currency depreciation.
Foreign Exchange Market Trading

Foreign exchange market trading involves the buying and selling of currencies between parties. It is a global market where participants exchange currencies for various purposes, including international trade, investment, and hedging against currency fluctuations.
Discover the crucial elements that make foreign exchange market trading the top choice.
Types of Foreign Exchange Market Transactions
There are several types of foreign exchange market transactions:
- Spot Transactions: The immediate exchange of currencies at the current market rate.
- Forward Transactions: Contracts to exchange currencies at a specified rate and date in the future.
- Swap Transactions: Simultaneous buying and selling of the same amount of different currencies at different dates.
li>Options Transactions: Contracts that give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a currency at a specified price on or before a certain date.
Process of Executing a Foreign Exchange Trade
Executing a foreign exchange trade involves the following steps:
- Finding a Counterparty: Identifying a party willing to exchange currencies at the desired rate.
- Negotiating the Terms: Agreeing on the currency pair, amount, rate, and settlement date.
- Executing the Trade: Confirming the trade details and exchanging the currencies through a broker or bank.
- Settlement: Transferring the currencies between the parties’ accounts on the agreed settlement date.
Foreign Exchange Market Regulation
The foreign exchange market is a vast and complex global marketplace, and as such, it is subject to a variety of regulatory frameworks designed to ensure its stability and integrity.
These frameworks are typically implemented by central banks and other government agencies, and they cover a wide range of issues, including:
Key Regulatory Bodies
- Central banks: Central banks play a key role in regulating the foreign exchange market by setting interest rates, managing the money supply, and intervening in the market to stabilize exchange rates.
- Financial regulatory authorities: Financial regulatory authorities are responsible for overseeing the activities of banks and other financial institutions that participate in the foreign exchange market.
- International organizations: International organizations such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) play a role in promoting cooperation and coordination among national regulatory authorities.
Importance of Regulation
Regulation of the foreign exchange market is essential for several reasons:
- To ensure the stability of the financial system: A stable foreign exchange market is essential for the smooth functioning of the global economy.
- To protect investors: Regulation helps to protect investors from fraud and abuse in the foreign exchange market.
- To prevent money laundering and other illegal activities: Regulation helps to prevent the foreign exchange market from being used for money laundering and other illegal activities.
Impact of Foreign Exchange Market on Businesses and Economies
The foreign exchange market plays a crucial role in facilitating international trade and influencing macroeconomic conditions.
Impact on Businesses, Definition of foreign exchange market
For businesses engaged in international trade, foreign exchange rates directly impact their profitability and competitiveness.
- Exchange rate fluctuations: When the value of a currency changes, it affects the cost of goods and services imported or exported by businesses.
- Profitability: If the value of a business’s home currency depreciates, its exports become cheaper and more competitive in foreign markets, potentially increasing profits.
- Competitiveness: Conversely, if the home currency appreciates, imports become cheaper, and domestic businesses face increased competition from foreign companies.
Macroeconomic Implications
Foreign exchange rate fluctuations can have significant macroeconomic implications, including:
- Inflation: Depreciation of a currency can lead to higher inflation as imported goods become more expensive.
- Economic growth: A depreciated currency can stimulate exports and economic growth by making domestic goods more competitive.
- Balance of payments: Exchange rates influence a country’s balance of payments by affecting the value of its exports and imports.
Emerging Trends in the Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing global economic conditions. These trends are reshaping the way that businesses and individuals trade currencies, and they are likely to have a significant impact on the future of the market.
One of the most important emerging trends in the foreign exchange market is the rise of electronic trading. In the past, most foreign exchange trading was conducted over the phone or through a broker. However, today, the majority of trading is done electronically through online platforms.
Electronic Trading
- Electronic trading platforms offer a number of advantages over traditional methods, including lower costs, faster execution times, and greater transparency.
- As a result, electronic trading is likely to continue to grow in popularity in the years to come.
Another emerging trend in the foreign exchange market is the increasing use of mobile trading. With the advent of smartphones and tablets, traders can now access the foreign exchange market from anywhere in the world.
Mobile Trading
- Mobile trading platforms offer a number of advantages over traditional methods, including convenience, portability, and the ability to trade on the go.
- As a result, mobile trading is likely to continue to grow in popularity in the years to come.
Finally, the foreign exchange market is also being affected by the rise of blockchain technology. Blockchain is a distributed ledger system that is used to record transactions in a secure and transparent way.
Blockchain Technology
- Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize the foreign exchange market by making it more efficient, secure, and transparent.
- As a result, blockchain technology is likely to play an increasingly important role in the foreign exchange market in the years to come.
Final Thoughts: Definition Of Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market is a complex and dynamic system that continues to evolve, driven by technological advancements and geopolitical shifts. Understanding its intricacies is essential for businesses operating in the global arena and for individuals seeking to navigate the international financial landscape.
