Brief definition of foreign exchange market – The foreign exchange market, also known as forex, is a global decentralized marketplace where currencies are traded. It facilitates international trade, investment, and tourism, and its participants range from banks and corporations to institutional investors and retail traders.
The forex market is vast and complex, with a daily trading volume exceeding $5 trillion. It operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, across different time zones, ensuring that there is always a market for currency exchange.
Definition of Foreign Exchange Market
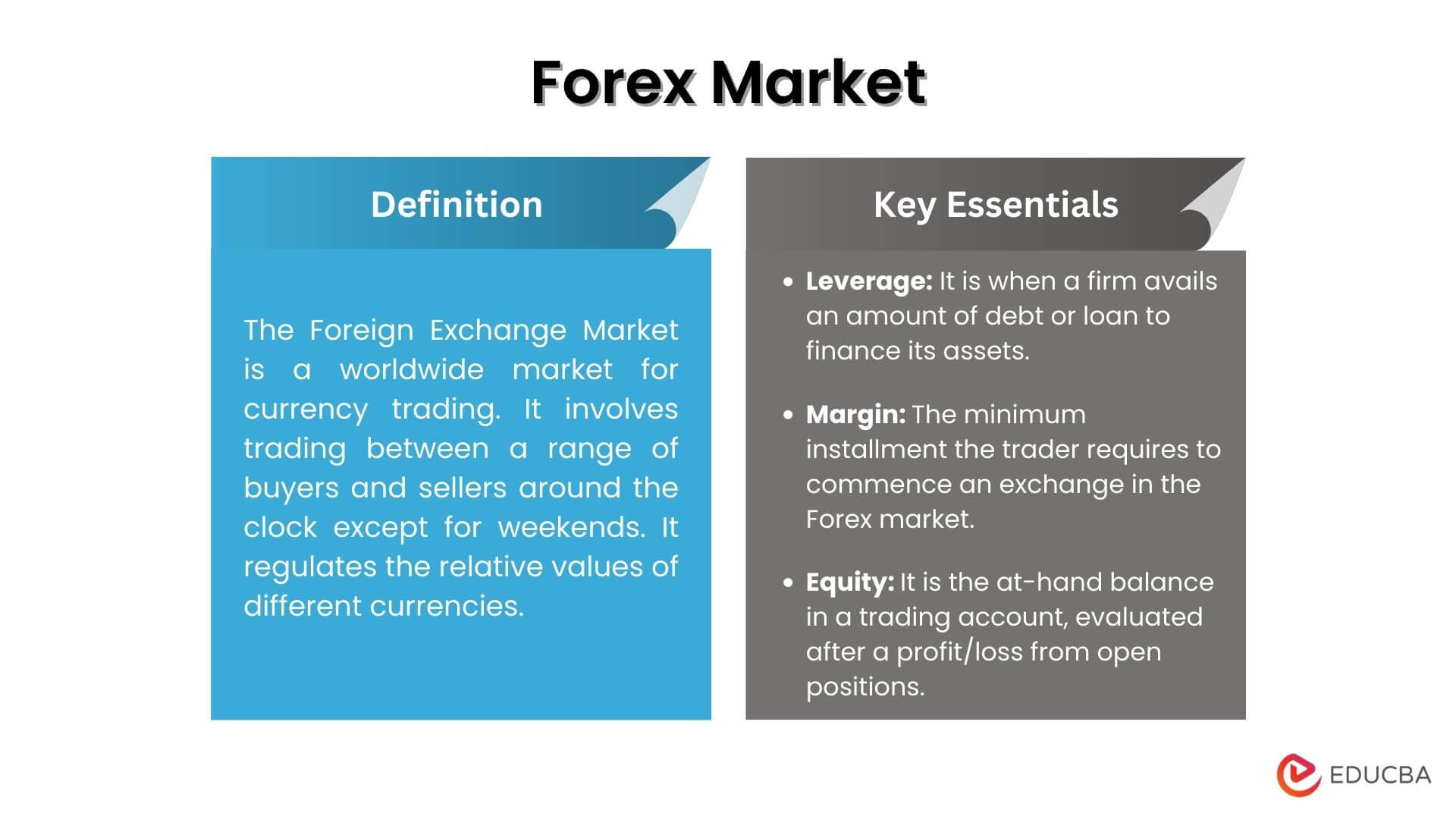
The foreign exchange market, also known as Forex or FX, is a global decentralized marketplace where currencies are traded. It facilitates the conversion of one currency into another and plays a crucial role in international trade, investment, and tourism.
History and Evolution of the Foreign Exchange Market
The origins of the foreign exchange market can be traced back to ancient times, when merchants exchanged currencies to facilitate trade. The modern foreign exchange market emerged in the late 19th century with the advent of international trade and the development of communication technologies. The market has since evolved into a sophisticated electronic network that operates 24 hours a day, 5 days a week.
Participants in the Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market, also known as the forex market, is a global marketplace where currencies are traded. The participants in this market are diverse and play different roles in the trading process.
- Banks: Banks are the largest participants in the foreign exchange market. They act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers, facilitating the exchange of currencies and providing liquidity to the market.
- Corporations: Corporations participate in the foreign exchange market to manage their international business operations. They buy and sell currencies to facilitate cross-border payments, investments, and hedging against currency fluctuations.
- Institutional Investors: Institutional investors, such as hedge funds, pension funds, and mutual funds, actively trade in the foreign exchange market to diversify their portfolios, manage risk, and generate returns.
- Retail Traders: Retail traders are individuals who trade currencies on a smaller scale. They may participate in the market for speculative purposes or to hedge against personal financial risks.
Factors Affecting Foreign Exchange Rates
The foreign exchange market is constantly influenced by a complex interplay of economic and political factors, as well as supply and demand dynamics. Understanding these factors is crucial for businesses, investors, and individuals engaged in international transactions.
Explore the different advantages of foreign exchange market definition en francais that can change the way you view this issue.
Economic factors that affect exchange rates include:
- Interest rates: Countries with higher interest rates tend to attract foreign investment, increasing demand for their currency and strengthening its value.
- Inflation: High inflation can erode the purchasing power of a currency, making it less desirable and leading to depreciation.
- Economic growth: Strong economic growth typically leads to increased demand for a country’s goods and services, boosting its currency’s value.
- Fiscal policy: Government spending and taxation can influence the value of a currency by affecting the supply and demand for it.
Political factors that can impact exchange rates include:
- Political stability: Uncertainty and instability can lead to currency depreciation, as investors seek safer havens.
- Government policies: Changes in government policies, such as trade agreements or foreign exchange controls, can affect currency values.
- International relations: Tensions or conflicts between countries can have a negative impact on their currencies.
In addition to these factors, supply and demand dynamics also play a significant role in determining exchange rates.
When there is high demand for a currency, its value increases, and when supply exceeds demand, its value decreases. Factors that influence supply and demand include:
- Trade flows: Countries with large trade surpluses typically experience appreciation in their currencies, while those with large trade deficits face depreciation.
- Investment flows: Foreign investment can increase demand for a currency, while capital outflows can lead to depreciation.
- Currency speculation: Currency traders can buy and sell currencies in anticipation of future changes in their value, affecting supply and demand.
Understanding the factors that affect foreign exchange rates is essential for making informed decisions in international business and finance.
Examine how curve of foreign exchange market can boost performance in your area.
Types of Foreign Exchange Transactions

The foreign exchange market facilitates various types of transactions to cater to different needs and risk appetites. These transactions can be broadly categorized into spot, forward, and swap transactions, each offering unique advantages and considerations.
In this topic, you find that market for foreign exchange ppt is very useful.
Spot Transactions
- Involve the immediate exchange of currencies at the prevailing market rate.
- Typically used for immediate settlement of international payments or for speculative trading.
- Advantages:
- Simple and straightforward.
- Low transaction costs.
- Disadvantages:
- Exposure to exchange rate fluctuations if settlement is delayed.
- May not be suitable for large transactions due to potential liquidity constraints.
Forward Transactions
- Contracts that agree on the exchange of currencies at a specified future date and rate.
- Used to lock in exchange rates and mitigate foreign exchange risk.
- Advantages:
- Protection against adverse exchange rate movements.
- Suitable for long-term planning and budgeting.
- Disadvantages:
- Less flexibility compared to spot transactions.
- May incur additional costs, such as margin requirements.
Swap Transactions
- Simultaneous spot and forward transactions in opposite directions involving the same currencies.
- Used to exchange currencies for a specific period and then reverse the exchange at a later date.
- Advantages:
- Can be used for currency conversion and interest rate arbitrage.
- Flexibility in managing foreign exchange exposure.
- Disadvantages:
- Complex and may require specialized knowledge.
- Higher transaction costs compared to spot or forward transactions.
Foreign Exchange Market Regulation: Brief Definition Of Foreign Exchange Market

The foreign exchange market is a global, decentralized market where currencies are traded. It is the largest financial market in the world, with an average daily trading volume of over $5 trillion. Due to its size and importance, the foreign exchange market is subject to regulation by central banks and international organizations.
Role of Central Banks, Brief definition of foreign exchange market
Central banks play a key role in regulating the foreign exchange market. They do this by:
– Setting interest rates: Interest rates affect the value of currencies. By raising or lowering interest rates, central banks can influence the demand for and supply of currencies, thereby affecting their exchange rates.
– Intervening in the market: Central banks can also intervene in the foreign exchange market by buying or selling currencies. This can be done to stabilize exchange rates or to achieve other policy objectives.
Role of International Organizations
In addition to central banks, international organizations also play a role in regulating the foreign exchange market. These organizations include:
– The International Monetary Fund (IMF): The IMF is a global organization that works to promote international monetary cooperation. It provides financial assistance to countries that are experiencing balance of payments problems. The IMF also monitors the foreign exchange market and provides advice to countries on how to manage their exchange rates.
– The Bank for International Settlements (BIS): The BIS is an international organization that serves as a central bank for central banks. It provides financial services to central banks and promotes cooperation among them. The BIS also conducts research on the foreign exchange market and provides advice to central banks on how to regulate it.
Technology in the Foreign Exchange Market
Technology has played a pivotal role in the evolution of the foreign exchange market, transforming it from a traditional, over-the-counter (OTC) market to a modern, electronic, and global marketplace.
Electronic Trading Platforms
Electronic trading platforms have revolutionized the foreign exchange market, providing a centralized marketplace where traders can execute trades electronically. These platforms offer real-time market data, transparent pricing, and increased liquidity, enabling faster and more efficient trading.
Algorithmic Trading
Algorithmic trading, also known as algo trading, uses computer programs to automate the trading process based on predefined criteria. Algo trading algorithms can analyze market data, identify trading opportunities, and execute trades without human intervention. This has led to increased trading volume and reduced trading costs.
Other Technological Advancements
Other technological advancements, such as cloud computing, big data analytics, and mobile trading apps, have also impacted the foreign exchange market. Cloud computing provides scalable and cost-effective infrastructure for trading platforms, while big data analytics allows traders to analyze vast amounts of market data to make informed decisions. Mobile trading apps have made it possible for traders to access the market from anywhere, anytime.
End of Discussion
The foreign exchange market plays a vital role in the global economy, facilitating international trade and investment. It is a complex and dynamic market, influenced by a wide range of economic, political, and technological factors.
Understanding the brief definition of foreign exchange market is essential for businesses, investors, and anyone involved in international transactions. By staying informed about the latest developments in the forex market, individuals and organizations can make informed decisions and mitigate risks.
