Introducing the foreign exchange market economics graph, an indispensable tool for understanding the dynamics of currency markets. This graph provides a visual representation of exchange rate fluctuations, allowing traders, investors, and businesses to make informed decisions. Dive into the world of forex economics and discover how this graph empowers market participants with insights into global economic trends.
The foreign exchange market, where currencies are traded, is a vast and complex ecosystem influenced by a myriad of economic factors. The foreign exchange market economics graph captures these influences, enabling us to track the ebb and flow of currency values over time.
Foreign Exchange Market Definition

The foreign exchange market, also known as the forex market, is a global marketplace where currencies are traded. It is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume exceeding $5 trillion.
You also will receive the benefits of visiting role of rbi in foreign exchange market pdf today.
Currencies are essential for international trade. When a country imports goods or services from another country, it must pay for those goods or services in the currency of the exporting country. The foreign exchange market provides a mechanism for businesses and individuals to exchange currencies so that they can conduct international transactions.
Do not overlook the opportunity to discover more about the subject of foreign exchange market exchange rate risk and hedging techniques.
Major Currency Pairs
The most commonly traded currency pairs in the forex market are:
- EUR/USD (euro/US dollar)
- USD/JPY (US dollar/Japanese yen)
- GBP/USD (British pound/US dollar)
- USD/CHF (US dollar/Swiss franc)
- AUD/USD (Australian dollar/US dollar)
Economic Factors Influencing Forex Market
The foreign exchange market, often known as the forex market, is influenced by a multitude of economic factors. These factors, which include interest rates, inflation, and economic growth, can have a significant impact on the value of currencies and the overall trends in the forex market.
Interest Rates
Interest rates play a crucial role in determining the value of a currency. When interest rates are high in a particular country, it becomes more attractive for foreign investors to invest in that country’s bonds and other financial instruments. This increased demand for the country’s currency leads to an appreciation in its value.
For example, in 2016, the US Federal Reserve raised interest rates for the first time in nearly a decade. This led to an immediate appreciation of the US dollar against other major currencies, as investors sought to take advantage of the higher returns available in the United States.
Inflation
Inflation, or the rate at which prices for goods and services increase over time, is another key factor that can impact currency values. When inflation is high in a particular country, it can erode the purchasing power of its currency. This makes the currency less attractive to foreign investors, leading to a depreciation in its value.
For example, in the 1970s, the United States experienced a period of high inflation, which led to a significant depreciation of the US dollar against other major currencies.
Economic Growth, Foreign exchange market economics graph
The overall economic growth of a country can also have a significant impact on the value of its currency. When a country’s economy is growing strongly, it attracts foreign investment and leads to an appreciation in the value of its currency. Conversely, when a country’s economy is struggling, it can lead to a depreciation in the value of its currency.
For example, in the 1990s, the Chinese economy experienced a period of rapid economic growth. This led to a significant appreciation of the Chinese yuan against other major currencies.
Graphing Forex Market Data
Visualizing forex market data through graphs is crucial for analyzing exchange rate trends and making informed trading decisions. This section will explore different ways to graph forex data, including live rates and historical fluctuations.
HTML Table for Live Forex Rates
An HTML table can be used to display live forex rates for multiple currency pairs in real-time. Here’s an example:
| Currency Pair | Bid Price | Ask Price |
|---|---|---|
| EUR/USD | 1.0865 | 1.0868 |
| USD/JPY | 110.55 | 110.58 |
| GBP/USD | 1.2460 | 1.2463 |
Line Chart for Historical Exchange Rate Fluctuations
A line chart is a common way to visualize historical exchange rate fluctuations over time. The x-axis typically represents the time period, while the y-axis shows the exchange rate. Here’s an example of a line chart:
[Image of a line chart showing the historical exchange rate fluctuations of EUR/USD over the past year]
Interpreting Forex Market Graphs
Interpreting forex market graphs involves identifying patterns and trends. Some common patterns to look for include:
- Upward Trend: A series of higher highs and higher lows, indicating a rising exchange rate.
- Downward Trend: A series of lower highs and lower lows, indicating a falling exchange rate.
- Range-Bound: The exchange rate fluctuates within a defined range, with no clear upward or downward trend.
- Support and Resistance Levels: Areas where the exchange rate has consistently found support or resistance, acting as potential turning points.
Trading Strategies in Forex Market
Trading in the forex market involves employing various strategies to capitalize on market fluctuations and generate profits. These strategies are categorized into technical analysis, fundamental analysis, and risk management.
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis involves studying historical price data to identify patterns and trends. Traders use technical indicators and chart patterns to predict future price movements. Some commonly used technical indicators include moving averages, Bollinger Bands, and relative strength index (RSI).
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis focuses on economic and geopolitical factors that influence currency values. Traders analyze economic data, such as interest rates, inflation, and GDP growth, to assess the underlying strength of a currency. They also consider political events, central bank policies, and global economic conditions.
You also can investigate more thoroughly about foreign exchange market course in delhi to enhance your awareness in the field of foreign exchange market course in delhi.
Risk Management
Risk management is crucial in forex trading to protect against potential losses. Traders use stop-loss orders, position sizing, and hedging strategies to manage risk. Stop-loss orders automatically close trades when a predetermined price level is reached, limiting potential losses. Position sizing involves determining the appropriate trade size based on the trader’s risk tolerance and account balance.
Trading Signals and Indicators
Forex traders often rely on trading signals and indicators to identify potential trading opportunities. Trading signals are generated by software or third-party providers and provide buy or sell recommendations based on technical analysis or fundamental factors. Indicators, such as moving averages and Bollinger Bands, help traders visualize price trends and identify potential support and resistance levels.
Risk and Regulation in Forex Market: Foreign Exchange Market Economics Graph

The forex market, while potentially lucrative, carries inherent risks that traders must be aware of. Understanding these risks and implementing appropriate risk management strategies is crucial for successful trading.
Leverage and Margin Trading
Leverage is a double-edged sword in forex trading. It allows traders to control a larger position size with a smaller amount of capital. However, it amplifies both potential profits and losses. Margin trading, which involves borrowing funds from a broker to increase trading capital, further magnifies the risk associated with leverage.
Regulatory Bodies
To ensure market integrity and protect traders, various regulatory bodies oversee the forex market. These bodies include:
- Financial Conduct Authority (FCA)
- Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC)
- Swiss Financial Market Supervisory Authority (FINMA)
These regulatory bodies enforce rules and regulations to prevent fraud, manipulation, and ensure fair trading practices.
End of Discussion
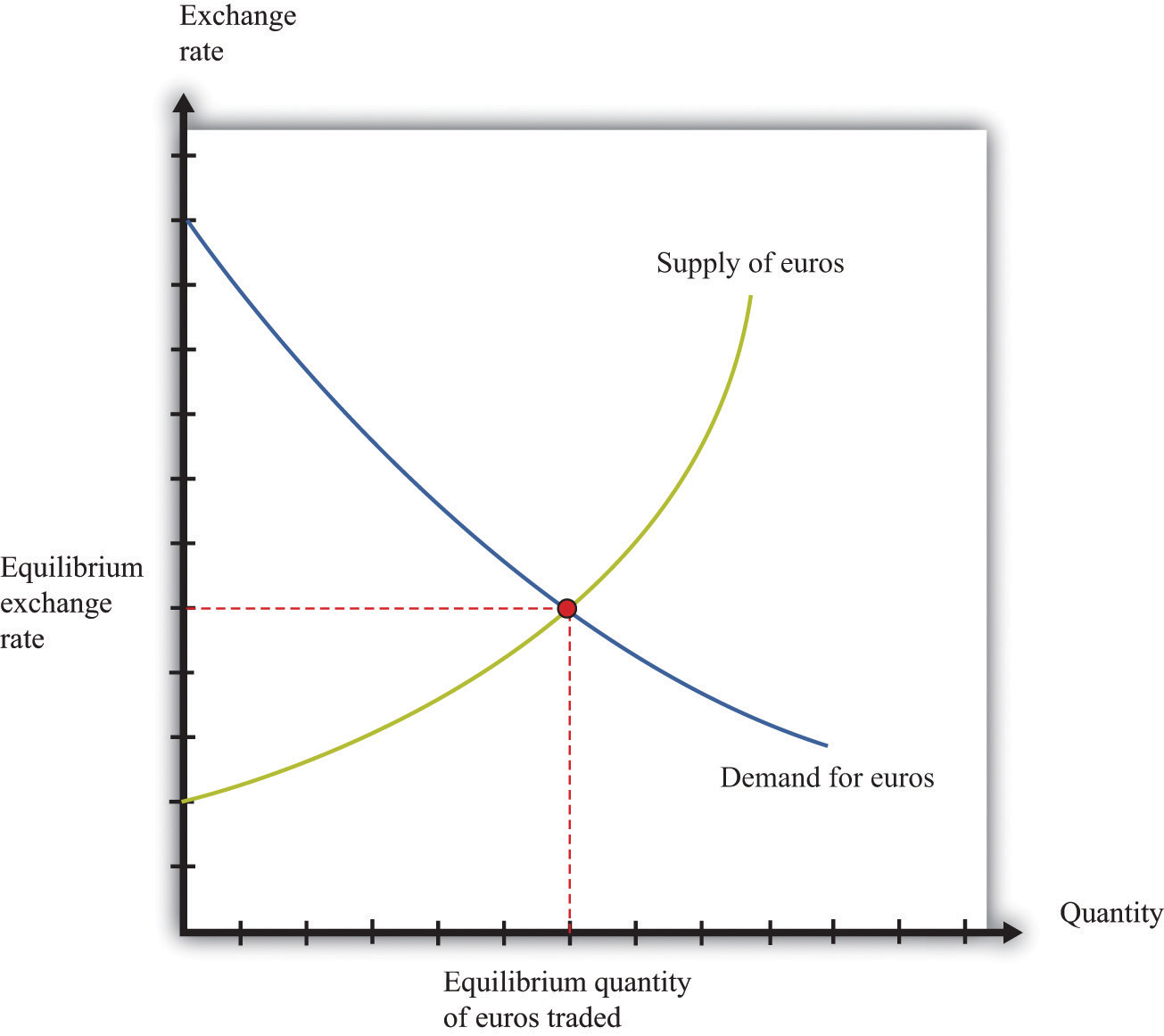
In conclusion, the foreign exchange market economics graph is a powerful tool that unlocks the complexities of currency markets. By visualizing exchange rate data, this graph empowers traders, investors, and businesses with the knowledge to navigate the dynamic world of forex. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or just starting to explore the realm of currency trading, the foreign exchange market economics graph is an invaluable resource that will guide your journey.
