Explain foreign exchange market in economics – The foreign exchange market, a dynamic global arena where currencies are traded, plays a pivotal role in international economics. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricate workings of this market, exploring its significance, participants, and the factors shaping its ever-changing landscape.
Definition and Overview

The foreign exchange market, often known as the forex market, is a global marketplace where currencies are traded. It is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume of over $5 trillion. The forex market plays a crucial role in international trade and finance, facilitating the exchange of currencies for businesses, individuals, and governments.
Purpose and Significance
The primary purpose of the forex market is to facilitate the exchange of currencies for international trade and investment. Businesses and individuals involved in international transactions need to convert their currency into the currency of the country they are trading with. The forex market provides a platform for these currency conversions to occur.
The forex market also plays a significant role in global finance. Investors use the forex market to hedge against currency risk, speculate on currency movements, and diversify their portfolios. Central banks and governments use the forex market to manage their foreign exchange reserves and influence the value of their currencies.
Participants and Roles
The foreign exchange market involves a diverse range of participants, each playing a crucial role in facilitating global trade and financial transactions.
Find out about how foreign exchange market advantages can deliver the best answers for your issues.
These participants can be broadly categorized into the following groups:
Central Banks
- Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States or the European Central Bank, are responsible for managing the monetary policy of their respective countries. They participate in the foreign exchange market to influence the value of their currencies and maintain economic stability.
Commercial Banks
- Commercial banks act as intermediaries between businesses and individuals, facilitating international payments and currency exchange. They also participate in the foreign exchange market to manage their own foreign exchange risk and provide services to their clients.
Corporations
- Multinational corporations engage in cross-border trade and investment, which requires them to exchange currencies. They participate in the foreign exchange market to manage their foreign exchange risk and facilitate international transactions.
Hedge Funds and Investment Funds
- Hedge funds and investment funds seek to generate profits by investing in a variety of assets, including currencies. They participate in the foreign exchange market to speculate on currency movements and capitalize on market inefficiencies.
Retail Investors, Explain foreign exchange market in economics
- Retail investors, including individuals and small businesses, participate in the foreign exchange market primarily for speculative purposes. They trade currencies in the hopes of profiting from fluctuations in their values.
Currency Pairs and Exchange Rates
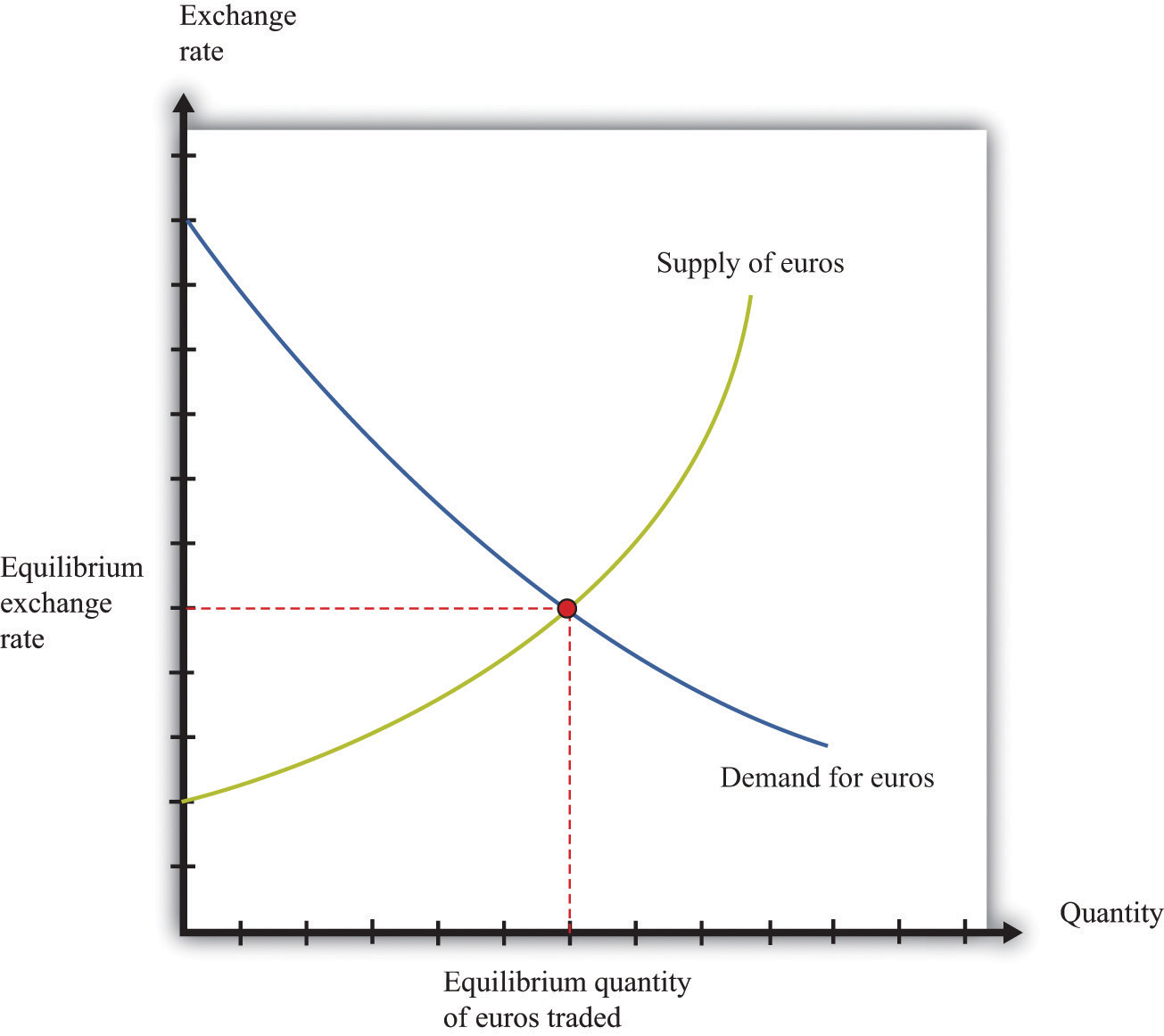
The foreign exchange market involves the trading of currencies in pairs, with one currency being bought and the other sold simultaneously. These currency pairs are typically denoted as “base currency” and “quote currency.”
Notice foreign exchange market khan academy for recommendations and other broad suggestions.
The exchange rate between two currencies indicates how much of one currency is required to purchase one unit of the other. Factors that influence exchange rates include economic growth, interest rates, inflation, political stability, and supply and demand.
Explore the different advantages of foreign exchange indonesia that can change the way you view this issue.
Major Currency Pairs
Major currency pairs are the most actively traded pairs in the forex market. They include:
- EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar)
- USD/JPY (US Dollar/Japanese Yen)
- GBP/USD (British Pound/US Dollar)
- USD/CHF (US Dollar/Swiss Franc)
- AUD/USD (Australian Dollar/US Dollar)
As of [current date], the exchange rates for these pairs are:
| Currency Pair | Exchange Rate |
|---|---|
| EUR/USD | 1.0542 |
| USD/JPY | 113.84 |
| GBP/USD | 1.2260 |
| USD/CHF | 0.9352 |
| AUD/USD | 0.6873 |
Foreign Exchange Transactions
Foreign exchange transactions involve the buying and selling of currencies between parties. These transactions occur for various reasons, such as international trade, investment, and tourism.
The process of buying and selling currencies is typically facilitated by brokers or other intermediaries, who act as agents for their clients. These intermediaries connect buyers and sellers and facilitate the execution of trades at the best available rates.
Types of Foreign Exchange Transactions
There are two main types of foreign exchange transactions:
- Spot transactions involve the immediate delivery of currencies. These transactions are typically used for small amounts of currency and are executed at the current spot rate.
- Forward transactions involve the agreement to buy or sell currencies at a specified rate on a future date. These transactions are typically used for larger amounts of currency and are executed at a forward rate, which is based on the spot rate plus or minus a premium or discount.
Role of Brokers and Other Intermediaries
Brokers and other intermediaries play a crucial role in the foreign exchange market. They provide liquidity to the market by matching buyers and sellers, and they offer a range of services to their clients, including:
- Execution of trades
- Currency conversion
- Hedging strategies
- Market analysis and advice
Market Structure and Regulation
The foreign exchange market is a decentralized, over-the-counter (OTC) market, meaning that it does not have a central exchange where all transactions take place. Instead, trades are conducted directly between participants via electronic networks or through brokers. This structure allows for a high degree of flexibility and efficiency, as participants can access the market from anywhere in the world and trade at any time.
Central Banks and Regulatory Bodies
Central banks and other regulatory bodies play a significant role in the foreign exchange market. They are responsible for setting monetary policy, which can impact exchange rates and market activity. Central banks also intervene in the market to stabilize exchange rates or manage currency reserves. Regulatory bodies, such as the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the UK, ensure that the market operates fairly and transparently.
Impact of Regulations
Regulations have a significant impact on market activity. They can affect the liquidity of the market, the cost of transactions, and the risk exposure of participants. Regulations can also impact the way that participants conduct their business, such as by requiring them to use certain trading platforms or to report their transactions to regulators.
Risk Management in Foreign Exchange
Risk management is crucial in foreign exchange trading due to the inherent volatility and uncertainty associated with currency markets. Understanding and mitigating these risks is essential for traders and investors.
There are several types of risks involved in foreign exchange trading, including:
– Currency Risk: The risk of losses due to fluctuations in exchange rates.
– Interest Rate Risk: The risk of losses due to changes in interest rates, which can affect the value of currencies.
– Political Risk: The risk of losses due to political events or changes in government policies that impact currency values.
– Liquidity Risk: The risk of being unable to buy or sell a currency at a desired price due to a lack of liquidity in the market.
– Counterparty Risk: The risk of losses due to the failure of a counterparty to fulfill its obligations in a foreign exchange transaction.
To manage these risks, traders and investors can employ various strategies, such as:
– Hedging: Using financial instruments like forward contracts or options to offset potential losses from adverse currency movements.
– Diversification: Investing in multiple currencies to reduce the impact of fluctuations in any single currency.
– Risk Limits: Setting limits on the amount of risk they are willing to take, based on their risk tolerance and financial capacity.
– Stop-Loss Orders: Placing orders to automatically sell a currency if it falls below a predetermined price, limiting potential losses.
Hedging
Hedging is a common risk management strategy in foreign exchange trading. It involves using financial instruments like forward contracts or options to offset potential losses from adverse currency movements.
– Forward Contracts: Contracts that lock in an exchange rate for a future date, protecting against potential currency fluctuations.
– Options: Contracts that give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a currency at a specified price on a future date. Options provide flexibility and allow traders to limit their potential losses.
By using hedging instruments, traders can reduce their exposure to currency risk and protect their profits.
Technology and Innovation
Technology has revolutionized the foreign exchange market, transforming it from a manual and fragmented system to a highly automated and interconnected one.
Electronic trading platforms have emerged as the primary venue for foreign exchange transactions, providing real-time access to liquidity and enabling faster and more efficient trade execution. These platforms offer a wide range of tools and functionalities, including real-time quotes, order matching, and risk management features.
Emerging Trends and Innovations
The foreign exchange market continues to embrace technological advancements, with emerging trends and innovations driving further efficiency and innovation. These include:
– Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered algorithms are being used to analyze market data, identify trading opportunities, and execute trades automatically.
– Blockchain Technology: Blockchain-based solutions are being explored to improve transparency, reduce settlement times, and enhance security in the foreign exchange market.
– Cloud Computing: Cloud-based platforms provide scalable and cost-effective infrastructure for foreign exchange trading, enabling access to advanced analytics and trading tools.
– Mobile Trading: Mobile trading apps allow traders to access the foreign exchange market and execute trades from anywhere, anytime.
Closure: Explain Foreign Exchange Market In Economics

From currency pairs and exchange rate dynamics to risk management strategies and technological advancements, this guide has provided a thorough examination of the foreign exchange market. Understanding the intricacies of this market empowers individuals and businesses alike to navigate its complexities and harness its potential.
