Participants of foreign exchange market play a pivotal role in the global financial landscape. From commercial banks facilitating currency exchange to central banks managing exchange rates, the diverse array of participants shapes the dynamics of the market. This comprehensive guide delves into the roles, motivations, and strategies of these key players.
The foreign exchange market, also known as the forex market, is the largest financial market globally, with a daily trading volume exceeding $6 trillion. It serves as a platform for exchanging currencies, enabling international trade, investment, and hedging against currency fluctuations.
Overview of Participants in the Foreign Exchange Market

The foreign exchange market (Forex or FX) is a global marketplace where currencies are traded. It is the largest financial market in the world, with an average daily trading volume of over $5 trillion.
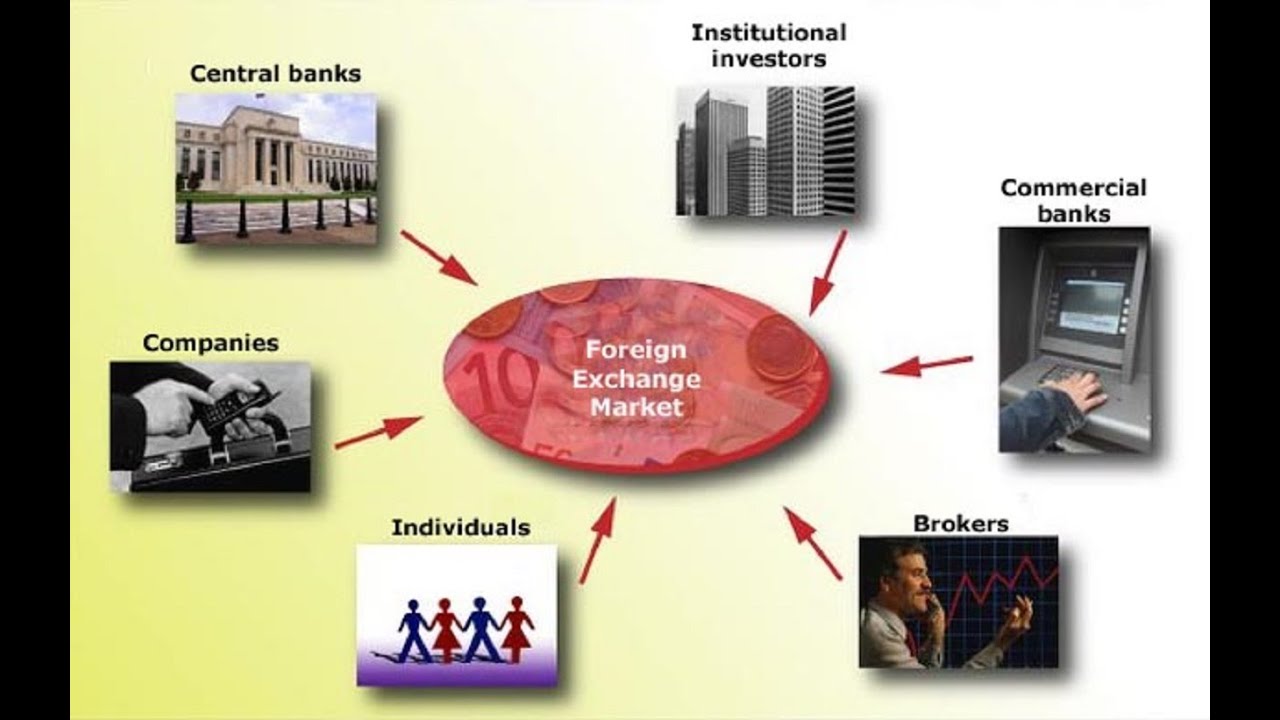
There are many different types of participants in the Forex market, including:
Central Banks
Central banks are the monetary authorities of their respective countries. They play a major role in the Forex market by managing their country’s foreign exchange reserves and intervening in the market to influence the value of their currency.
Obtain recommendations related to foreign exchange market new york times that can assist you today.
Commercial Banks
Commercial banks are the largest participants in the Forex market. They provide foreign exchange services to their customers, including businesses and individuals. Commercial banks also trade currencies on their own behalf to make a profit.
Investment Funds
Investment funds, such as hedge funds and mutual funds, trade currencies as part of their investment strategies. They may use different strategies, such as carry trade or arbitrage, to generate profits.
Corporations
Corporations that engage in international trade need to exchange currencies to pay for goods and services. They may also trade currencies to hedge against foreign exchange risk.
Individuals
Individuals can also trade currencies in the Forex market. However, retail traders typically have a much smaller share of the market compared to other participants.
Expand your understanding about foreign exchange market liberalization with the sources we offer.
Role of Commercial Banks in the Foreign Exchange Market
Commercial banks play a pivotal role in the foreign exchange market, serving as intermediaries between various market participants. They facilitate currency exchange and international trade by providing a range of services.
Primary Role of Commercial Banks
The primary role of commercial banks in the foreign exchange market is to facilitate the exchange of currencies. They act as market makers, quoting bid and ask prices for different currencies and providing liquidity to the market. By matching buy and sell orders, banks ensure smooth currency exchange and enable international trade and investment.
Facilitating Currency Exchange and International Trade
Commercial banks facilitate currency exchange and international trade by offering a variety of services, including:
- Currency Exchange: Banks provide currency exchange services to individuals, businesses, and governments, enabling them to convert one currency into another for various purposes, such as travel, imports, and exports.
- Foreign Exchange Transactions: Banks facilitate foreign exchange transactions for businesses engaged in international trade. They provide forward contracts, which allow businesses to lock in exchange rates for future transactions, mitigating currency risk.
- Trade Finance: Banks offer trade finance services, such as letters of credit and documentary collections, which provide payment security and facilitate international trade.
Participation of Central Banks in the Foreign Exchange Market
Central banks play a critical role in managing exchange rates and influencing currency values. They intervene in the foreign exchange market to achieve various macroeconomic objectives, such as maintaining price stability, promoting economic growth, and managing international trade imbalances.
Strategies and Tools
Central banks use a range of strategies and tools to influence currency values. These include:
- Foreign exchange intervention: Buying or selling foreign currencies in the market to influence the exchange rate.
- Interest rate adjustments: Changing interest rates to make their currency more or less attractive to foreign investors.
- Verbal intervention: Public statements by central bank officials about the desired exchange rate or monetary policy stance.
- Quantitative easing or tightening: Expanding or contracting the money supply to influence the value of the currency.
Institutional Investors and Hedge Funds in the Foreign Exchange Market

Institutional investors and hedge funds are major participants in the foreign exchange market. They engage in currency trading for various reasons, including portfolio diversification, risk management, and speculative opportunities.
Motivations for Currency Trading
- Portfolio Diversification: Institutional investors often allocate a portion of their portfolios to foreign currencies to reduce overall risk and enhance returns.
- Risk Management: Hedge funds use currency trading to hedge against currency fluctuations that could impact their other investments.
- Speculative Trading: Some institutional investors and hedge funds engage in speculative currency trading, aiming to profit from short-term price movements.
Trading Strategies
- Carry Trade: Borrowing in one currency with low interest rates and investing in another currency with higher interest rates to capture the interest rate differential.
- Currency Arbitrage: Exploiting price discrepancies between different currency markets to generate profits.
- Technical Analysis: Using historical price data to identify trading opportunities based on chart patterns and indicators.
Role of Retail Participants in the Foreign Exchange Market
Retail investors play a significant role in the foreign exchange market, contributing to its liquidity and volatility. These participants include individuals and small businesses that trade currencies for various reasons, such as speculation, hedging, or travel.
Browse the multiple elements of participants of foreign exchange market ppt to gain a more broad understanding.
Types of Retail Traders, Participants of foreign exchange market
There are several types of retail traders in the foreign exchange market, each with its unique trading strategies:
- Scalpers: These traders aim to profit from small price movements over short timeframes, typically within minutes or hours.
- Day Traders: Day traders enter and exit trades within a single trading day, aiming to capture intraday price fluctuations.
- Swing Traders: Swing traders hold positions for several days or weeks, targeting larger price swings that develop over longer timeframes.
- Position Traders: Position traders maintain trades for months or even years, betting on long-term currency trends.
- Hedgers: Businesses and individuals use hedging strategies to protect themselves from currency fluctuations that could impact their operations or investments.
Regulation and Supervision of the Foreign Exchange Market: Participants Of Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market operates within a regulatory framework established by governments and central banks to ensure market stability, transparency, and fair play. Regulatory bodies play a crucial role in overseeing the activities of participants, enforcing rules, and preventing market manipulation.
Role of Regulatory Bodies
Regulatory bodies in the foreign exchange market include central banks, government agencies, and international organizations. They set guidelines, monitor transactions, and investigate potential misconduct. Their primary objectives are to:
- Maintain market integrity by preventing fraud and manipulation.
- Ensure fair competition and transparency by promoting ethical practices.
- Protect investors and consumers from financial risks.
- Facilitate cross-border transactions and promote economic stability.
Final Review
In conclusion, the participants of the foreign exchange market form a complex and interconnected ecosystem that drives the global flow of currencies. Their diverse roles, motivations, and strategies contribute to the market’s liquidity, stability, and overall significance in the global financial system.
