Foreign exchange market features and participants – The foreign exchange market, a global hub for currency trading, offers unique features and attracts a diverse range of participants, making it a dynamic and complex financial landscape.
This market operates 24/7, facilitating the exchange of currencies between businesses, governments, and individuals. Its liquidity and leverage options provide opportunities for profit, but also carry potential risks.
Market Overview: Foreign Exchange Market Features And Participants
The foreign exchange market, also known as the forex market or FX market, is a global decentralized marketplace where currencies are traded. It is the largest financial market in the world, with an estimated daily trading volume of over $5 trillion.
A Brief History of the Forex Market
The forex market has its roots in the gold standard system, which was established in the 19th century. Under the gold standard, the value of a country’s currency was pegged to the price of gold. This system helped to stabilize exchange rates and facilitate international trade.
The gold standard system collapsed in the early 20th century, and the forex market began to evolve into its modern form. In the 1970s, the floating exchange rate system was adopted, which allowed currencies to fluctuate freely against each other.
Remember to click foreign exchange village market to understand more comprehensive aspects of the foreign exchange village market topic.
The Global Nature of the Forex Market
The forex market is a truly global market, with participants from all over the world. The major trading centers are located in London, New York, Tokyo, and Singapore, but there are also active markets in other cities around the world.
The forex market is open 24 hours a day, 5 days a week, which allows traders to participate from anywhere in the world. This global reach makes the forex market one of the most liquid and accessible financial markets in the world.
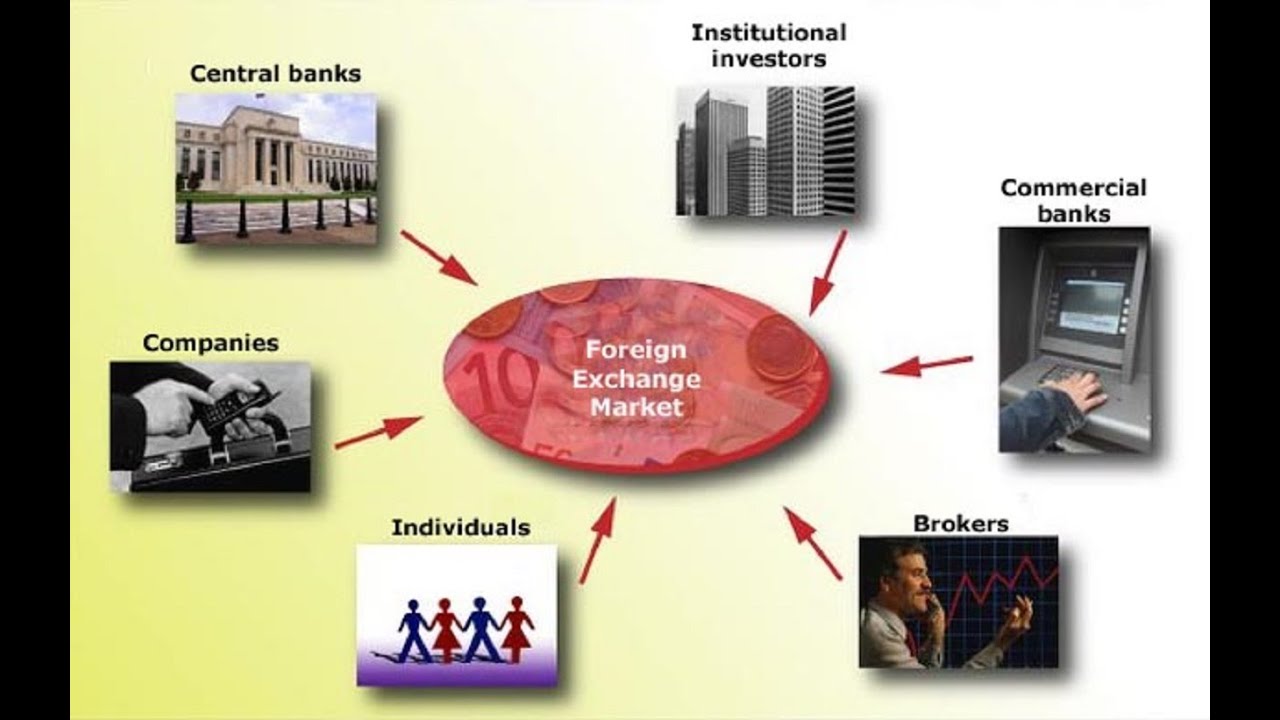
Market Participants
The foreign exchange market is a vast and complex ecosystem, and it is essential to understand the different types of participants involved in order to gain a comprehensive understanding of how the market operates.
There are numerous participants in the forex market, each playing a distinct role in facilitating the exchange of currencies. These participants can be broadly categorized into the following types:
Banks, Foreign exchange market features and participants
Banks are the largest participants in the forex market, accounting for the majority of trading volume. They act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers of currencies, providing liquidity and facilitating the smooth functioning of the market.
Banks offer a range of services to their clients, including currency exchange, hedging, and investment advice. They also play a crucial role in the interbank market, where banks trade currencies directly with each other.
Institutional Investors
Institutional investors, such as hedge funds, pension funds, and insurance companies, are another major group of participants in the forex market. These entities manage large pools of capital and actively trade currencies to achieve their investment objectives.
Institutional investors often use sophisticated trading strategies and employ teams of analysts to make informed decisions about currency movements. They can have a significant impact on the forex market, particularly during periods of high volatility.
When investigating detailed guidance, check out foreign exchange market practice problems now.
Corporations
Corporations are businesses that engage in international trade and investment. They need to exchange currencies to conduct their business operations and manage their foreign exchange risk.
Remember to click types of foreign exchange market pdf to understand more comprehensive aspects of the types of foreign exchange market pdf topic.
Corporations typically have smaller trading volumes compared to banks and institutional investors, but they can still have a noticeable impact on the forex market, especially in currency pairs related to their industry or geographic location.
Retail Traders
Retail traders are individuals who trade currencies on their own account. They range from experienced professionals to casual speculators and use a variety of trading platforms to access the market.
Retail traders often have smaller trading volumes than other participants, but they can collectively contribute to market volatility, particularly during periods of major news events or market uncertainty.
Central Banks
Central banks are government agencies responsible for managing the monetary policy of their respective countries. They participate in the forex market to influence the value of their currencies and achieve their economic objectives.
Central banks can intervene in the forex market by buying or selling currencies, which can have a significant impact on exchange rates and overall market sentiment.
Market Features
The foreign exchange market (forex market) stands out with unique characteristics that set it apart from other financial markets. Its distinctive features contribute to its immense popularity among traders and investors worldwide.
One of the most striking features of the forex market is its exceptional liquidity. The daily trading volume in the forex market surpasses trillions of dollars, making it the most liquid financial market globally. This high liquidity ensures that traders can enter and exit positions swiftly and efficiently, minimizing slippage and execution delays.
24/7 Trading
Unlike traditional financial markets that operate during specific hours, the forex market operates 24 hours a day, 5 days a week. This round-the-clock trading allows traders to react to market movements and execute trades at any time, regardless of their geographical location. The continuous trading environment provides ample opportunities for traders to capitalize on market fluctuations and manage their positions.
Leverage
Leverage is another crucial feature of the forex market. It enables traders to gain exposure to larger positions with a relatively small amount of capital. While leverage can amplify potential profits, it also magnifies potential losses. Therefore, traders must exercise caution and employ proper risk management strategies when using leverage.
Market Instruments
The foreign exchange market facilitates trading in a wide range of financial instruments, each with distinct characteristics and uses. These instruments include spot currencies, forward contracts, futures contracts, options, and swaps.
Spot currencies represent the immediate exchange of currencies at the prevailing market rate. They are typically used for short-term transactions and are the most commonly traded instrument in the forex market.
Forward contracts are agreements to exchange currencies at a predetermined rate on a future date. They are used to hedge against currency fluctuations and lock in exchange rates for future transactions.
Futures contracts are standardized contracts traded on exchanges, obligating buyers to purchase and sellers to deliver a specified amount of currency at a set price on a future date. They provide a way to speculate on currency movements and manage risk.
Options give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a currency at a specified price on or before a certain date. They are used for speculation and hedging strategies.
Swaps involve the exchange of cash flows between two parties based on different interest rates or currencies. They are used for managing interest rate risk and currency exposure.
Market Analysis

Market analysis in forex trading involves examining price movements and other market data to identify trading opportunities and make informed decisions. There are two primary types of market analysis: technical analysis and fundamental analysis.
Technical analysis focuses on historical price data, such as charts and indicators, to identify patterns and trends that may predict future price movements. It assumes that past price action influences future price movements and that these patterns repeat over time.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis, on the other hand, considers economic and financial factors that influence currency values, such as economic growth, inflation, interest rates, and political stability. It assumes that the intrinsic value of a currency is determined by the underlying strength of the country’s economy and its financial policies.
Risk Management
Risk management is crucial in forex trading as it helps traders manage their exposure to potential losses. It involves setting stop-loss orders to limit potential losses, using leverage appropriately, and diversifying trades across different currency pairs.
Conclusive Thoughts
Understanding the characteristics and participants of the foreign exchange market is crucial for navigating its complexities. By grasping the interplay between different market players, the instruments traded, and the analytical tools employed, traders can make informed decisions and navigate the ever-changing currency landscape.
