What are foreign exchange market in economics – What is the foreign exchange market in economics? It’s a global marketplace where currencies are traded, facilitating international trade and investment. This dynamic market plays a pivotal role in shaping economies worldwide, impacting everything from inflation to economic growth. Join us as we delve into the intricacies of the foreign exchange market, exploring its functions, factors influencing exchange rates, and its impact on the global economy.
The foreign exchange market, also known as forex or currency market, operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, with participants ranging from central banks to multinational corporations and individual traders. Its primary function is to facilitate the exchange of currencies, enabling businesses to conduct international transactions, investors to diversify their portfolios, and governments to manage their economies.
Define Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market, also known as the forex market, is a global decentralized marketplace where currencies are traded. It is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with an average daily trading volume of over $5 trillion.
The foreign exchange market plays a crucial role in international trade and finance. It allows businesses and individuals to exchange currencies so that they can conduct cross-border transactions. The foreign exchange market also helps to determine the relative value of different currencies.
The main participants in the foreign exchange market are:
– Commercial banks
– Investment banks
– Hedge funds
– Central banks
– Corporations
– Individuals
Functions of the Foreign Exchange Market
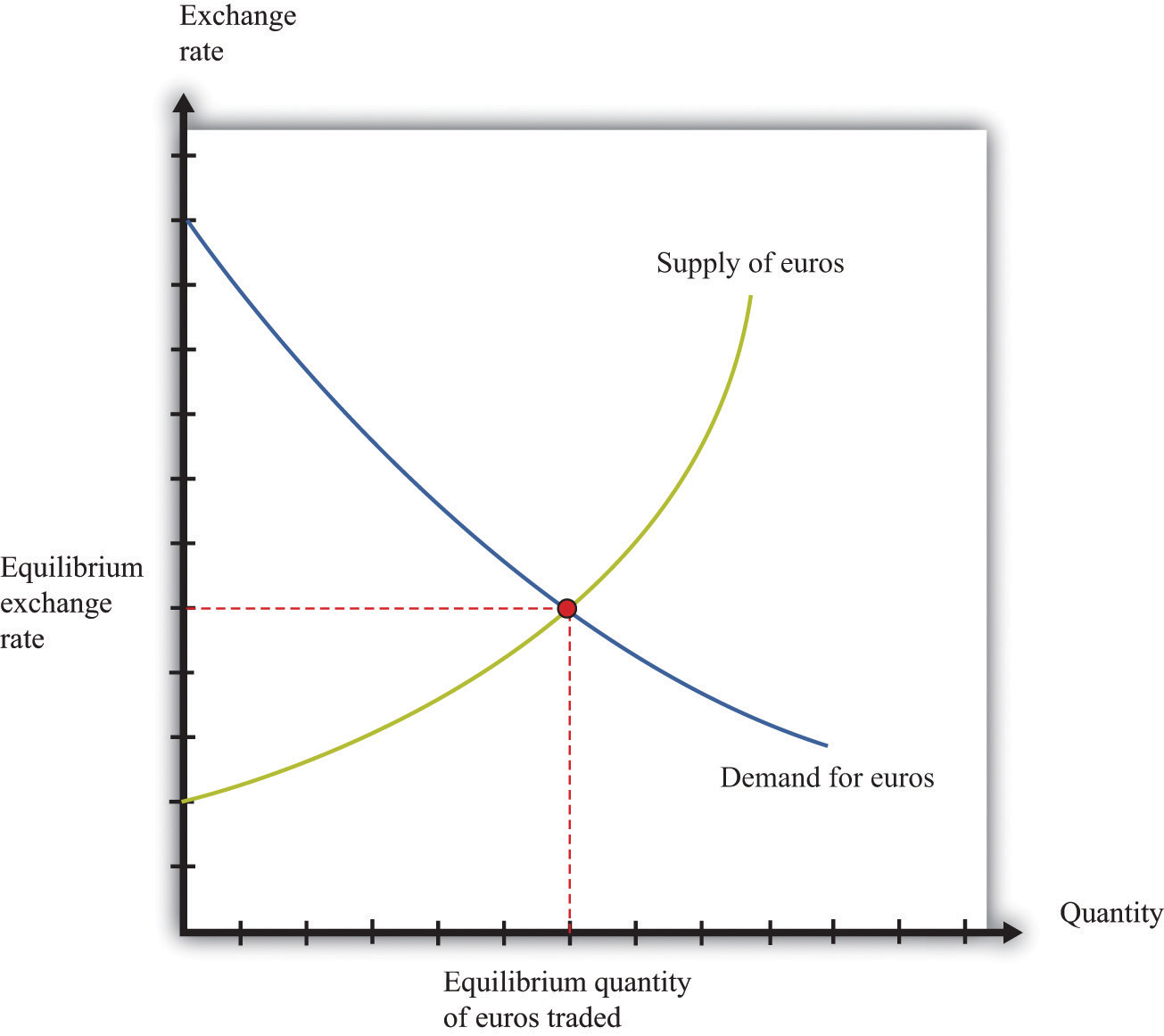
The foreign exchange market plays a crucial role in the global economy, facilitating international trade, investment, and risk management. It provides a platform for businesses and individuals to exchange currencies, enabling the smooth flow of goods, services, and capital across borders.
Facilitating International Trade
The foreign exchange market is essential for international trade. When businesses import or export goods, they need to convert their domestic currency into the currency of the country they are trading with. The foreign exchange market provides the necessary liquidity and exchange rates to facilitate these transactions.
Enabling Investment
The foreign exchange market also enables international investment. Investors often seek opportunities in foreign markets to diversify their portfolios and potentially earn higher returns. The foreign exchange market allows them to convert their domestic currency into foreign currencies, making it possible to invest in overseas assets.
Managing Risk and Price Discovery
The foreign exchange market is also used to manage risk and facilitate price discovery. Businesses and investors can use foreign exchange derivatives, such as forward contracts and options, to hedge against currency fluctuations and protect their profits. The foreign exchange market also provides transparent price information, enabling market participants to make informed decisions about currency values.
Factors Affecting Foreign Exchange Rates
Foreign exchange rates are constantly fluctuating, influenced by a complex interplay of economic, political, and market conditions. Understanding these factors is crucial for businesses, investors, and individuals engaged in international trade and finance.
Find out further about the benefits of foreign exchange market diagram that can provide significant benefits.
Economic Factors
- Economic Growth: Strong economic growth in a country tends to appreciate its currency as increased demand for its goods and services leads to increased demand for its currency.
- Inflation: Higher inflation rates can depreciate a currency as they reduce the purchasing power of the currency.
- Interest Rates: Higher interest rates attract foreign capital, appreciating the currency as demand for the currency increases.
- Balance of Payments: A country with a persistent trade deficit (more imports than exports) can experience depreciation of its currency.
Political Factors
- Political Stability: Political instability can lead to currency depreciation as investors seek safer havens for their investments.
- Government Policies: Government policies such as fiscal and monetary policies can influence foreign exchange rates.
- International Relations: Tensions between countries can lead to currency fluctuations.
Market Factors
- Supply and Demand: Foreign exchange rates are determined by the supply and demand for currencies.
- Speculation: Speculators can influence foreign exchange rates by buying or selling currencies based on their expectations.
- Central Bank Intervention: Central banks can intervene in the foreign exchange market to influence currency values.
Central Bank Policies and Interest Rate Differentials
Central banks play a significant role in influencing foreign exchange rates through their monetary policies, particularly by setting interest rates. Interest rate differentials between countries can lead to currency appreciation or depreciation as investors seek higher returns.
Investigate the pros of accepting foreign exchange market how it works history and pros and cons (investopedia.com) in your business strategies.
Foreign Exchange Market Instruments: What Are Foreign Exchange Market In Economics
The foreign exchange market utilizes a range of instruments to facilitate currency exchange and risk management. These instruments vary in their features and applications, catering to the diverse needs of market participants.
Do not overlook the opportunity to discover more about the subject of advantages and disadvantages of the foreign exchange market.
Spot Contracts
- Immediate delivery and settlement of currencies within two business days.
- Used for short-term currency transactions, such as immediate payment for goods or services.
- Spot rates are determined by current market conditions, supply and demand.
Forward Contracts
- Customized contracts that specify the exchange of currencies at a predetermined rate on a future date.
- Used to hedge against future currency fluctuations, such as protecting against exchange rate risk in international trade.
- Forward rates are based on spot rates and incorporate interest rate differentials and market expectations.
Swap Contracts
- Simultaneous buying and selling of currencies with different value dates.
- Used for complex currency transactions, such as managing cash flows or interest rate risk.
- Can involve multiple currencies and different time periods.
Options
- Contracts that give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a currency at a specified price on a future date.
- Used for speculation or hedging against currency fluctuations.
- Options premiums are paid to the seller for the right to exercise the option.
Futures
- Standardized contracts traded on exchanges, obligating the buyer to buy and the seller to sell a specified amount of currency at a predetermined price on a future date.
- Used for hedging or speculative trading.
- Futures prices are based on market expectations and incorporate interest rate differentials.
Foreign Exchange Market Regulation

The foreign exchange market is subject to various regulations to ensure its stability and integrity. Central banks and international organizations play a crucial role in monitoring and regulating the market.
Central Banks, What are foreign exchange market in economics
Central banks have the authority to intervene in the foreign exchange market to influence exchange rates. They can buy or sell currencies to stabilize exchange rates or prevent excessive volatility. Central banks also set reserve requirements for banks and other financial institutions, which affects the supply of foreign currencies in the market.
International Organizations
International organizations, such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF), provide guidelines and recommendations for foreign exchange market regulation. The IMF monitors exchange rate policies and provides financial assistance to countries experiencing balance of payments difficulties.
Measures to Prevent Market Manipulation
Regulators implement measures to prevent market manipulation and ensure fair competition. These measures include:
- Transparency: Regulators require market participants to disclose their positions and transactions.
- Surveillance: Regulators monitor the market for suspicious activity and investigate potential violations.
- Enforcement: Regulators have the authority to impose penalties on individuals or institutions that engage in market manipulation.
Impact of the Foreign Exchange Market on the Economy

The foreign exchange market has a profound impact on the economy, influencing inflation, economic growth, and trade balances. It plays a crucial role in promoting economic stability and growth.
Exchange rate fluctuations can significantly affect inflation. When the domestic currency depreciates (loses value) against foreign currencies, it becomes more expensive to import goods and services, leading to higher inflation. Conversely, currency appreciation can reduce inflation by making imports cheaper.
Economic Growth
Exchange rate fluctuations can also impact economic growth. A depreciated currency can boost exports by making domestic goods and services more competitive in foreign markets. This can lead to increased production and job creation, stimulating economic growth. However, a prolonged period of currency depreciation can also lead to higher inflation and reduced purchasing power for consumers, potentially slowing down economic growth.
Trade Balances
The foreign exchange market plays a critical role in balancing trade between countries. When a country exports more than it imports, it has a trade surplus, which leads to an appreciation of its currency. Conversely, a trade deficit (more imports than exports) results in currency depreciation.
Exchange rate fluctuations can help correct trade imbalances. A depreciated currency makes exports more attractive and imports more expensive, encouraging domestic production and reducing imports, thereby reducing the trade deficit. Conversely, currency appreciation makes imports cheaper and exports more expensive, leading to a wider trade deficit.
Economic Stability
The foreign exchange market also contributes to economic stability. Stable exchange rates foster predictability and confidence in the economy, making it more attractive for foreign investment and trade. Stable currencies also reduce uncertainty for businesses and consumers, allowing them to plan and make long-term decisions with greater confidence.
Last Word
In conclusion, the foreign exchange market is a complex and ever-evolving landscape that plays a crucial role in the global economy. Its functions in facilitating international trade, managing risk, and influencing economic growth make it an essential component of the financial system. Understanding the dynamics of the foreign exchange market empowers businesses, investors, and policymakers to navigate the complexities of international finance and make informed decisions.
