Functions and structure of foreign exchange market – Delving into the functions and structure of the foreign exchange market unveils a dynamic realm of global finance. This intricate network, where currencies are traded and exchanged, plays a pivotal role in international commerce, investment, and economic stability. Join us as we explore the inner workings of this fascinating market, uncovering its participants, mechanisms, and the factors that shape its ever-fluctuating landscape.
The foreign exchange market, often abbreviated as forex, serves as a decentralized global marketplace where currencies are traded. It facilitates the exchange of one currency for another, enabling businesses to conduct international transactions, investors to diversify their portfolios, and individuals to travel and make purchases abroad.
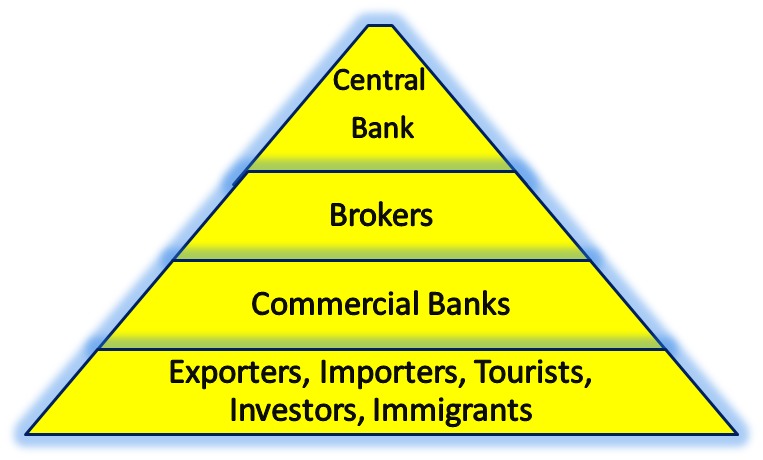
Market Participants

The foreign exchange market is a vast and complex global marketplace where currencies are traded. Various types of participants play significant roles in this market, each with unique objectives and strategies.
Banks
Banks are the most prominent participants in the foreign exchange market. They facilitate currency exchange transactions for their clients, including individuals, businesses, and other financial institutions. Banks also engage in proprietary trading, speculating on currency movements to generate profits.
Institutional Investors
Institutional investors, such as hedge funds, mutual funds, and pension funds, are major players in the foreign exchange market. They invest large sums of money in currencies, seeking to maximize returns and diversify their portfolios. Institutional investors often use sophisticated trading strategies and advanced analytical tools to make informed decisions.
Retail Traders
Retail traders are individuals who participate in the foreign exchange market on a smaller scale. They trade currencies primarily for speculative purposes, hoping to profit from short-term price movements. Retail traders typically have limited access to market information and rely on technical analysis and market sentiment to make trading decisions.
Market Structure: Functions And Structure Of Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market is a decentralized global market for trading currencies. It operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, and is the largest financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume exceeding $5 trillion.
The foreign exchange market is divided into three main types of markets: spot, forward, and swap. The spot market is the market for immediate delivery of currencies, while the forward market is the market for future delivery of currencies. The swap market is the market for exchanging one currency for another at a specified future date.
Do not overlook explore the latest data about foreign direct investment pdf.
Central Banks and Regulatory Bodies
Central banks play a significant role in the foreign exchange market by managing their countries’ monetary policies. Central banks can intervene in the foreign exchange market to buy or sell currencies in order to influence the value of their own currency. Other regulatory bodies, such as the Bank for International Settlements (BIS), also play a role in the foreign exchange market by setting standards and regulations for the conduct of foreign exchange transactions.
Currency Pairs

In the foreign exchange market, currencies are not traded individually but in pairs. A currency pair represents the exchange rate between two currencies, indicating the value of one currency in terms of the other.
Explore the different advantages of foreign exchange market how does it work that can change the way you view this issue.
The exchange rate between two currencies is constantly fluctuating due to various factors, including economic conditions, political events, and market sentiment. Traders in the foreign exchange market speculate on these fluctuations to make profits.
Major Currency Pairs, Functions and structure of foreign exchange market
The most commonly traded currency pairs are known as major currency pairs. They include:
- EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar)
- USD/JPY (US Dollar/Japanese Yen)
- GBP/USD (British Pound/US Dollar)
- USD/CHF (US Dollar/Swiss Franc)
- AUD/USD (Australian Dollar/US Dollar)
These currency pairs account for a large majority of the foreign exchange market’s daily trading volume.
Further details about foreign exchange market today live is accessible to provide you additional insights.
Factors Influencing Exchange Rates
The exchange rates between currency pairs are influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including:
- Economic growth and inflation rates
- Interest rate differentials
- Political stability
- Market sentiment
These factors can affect the supply and demand for currencies, leading to fluctuations in their exchange rates.
Trading Mechanisms
Foreign exchange is traded through various mechanisms, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. These mechanisms include spot trading, forward trading, and swaps.
Spot Trading
- In spot trading, currencies are traded for immediate delivery, typically within two business days.
- Spot trades are usually conducted over-the-counter (OTC), meaning they are not traded on an exchange.
- Spot trading is the most common type of foreign exchange trading.
Forward Trading
- In forward trading, currencies are traded for delivery at a future date, typically one month, three months, or six months.
- Forward trades are typically used to hedge against currency risk or to speculate on future currency movements.
- Forward trades are traded on exchanges or OTC.
Swaps
- Swaps are agreements to exchange currencies at a future date, with the exchange rate being fixed at the time the swap is entered into.
- Swaps are used for a variety of purposes, including hedging, speculation, and arbitrage.
- Swaps are traded OTC.
Market Dynamics
The foreign exchange market is a complex and dynamic environment, where currency values are constantly fluctuating. These fluctuations are driven by a wide range of factors, including economic data, political events, and market sentiment.
Economic data, such as GDP growth, inflation, and unemployment rates, can have a significant impact on currency values. Strong economic data can lead to increased demand for a currency, while weak economic data can lead to decreased demand. Political events, such as elections, wars, and changes in government policy, can also affect currency values. For example, a political crisis in a country can lead to investors selling that country’s currency and buying other currencies that are considered safer.
Market Sentiment
Market sentiment is another important factor that can influence exchange rates. Market sentiment refers to the overall mood of the market, which can be positive, negative, or neutral. Positive market sentiment can lead to increased demand for a currency, while negative market sentiment can lead to decreased demand. Market sentiment can be influenced by a variety of factors, such as economic data, political events, and news headlines.
Risk Management
Foreign exchange trading involves various risks that can impact individual traders and financial institutions. Understanding and managing these risks is crucial for successful participation in the forex market.
Risks in forex trading primarily arise from currency fluctuations, market volatility, geopolitical events, and economic factors. Effective risk management strategies are essential to mitigate potential losses and preserve capital.
Risk Management Strategies
Risk management in forex trading encompasses a range of strategies aimed at minimizing potential losses and maximizing profits.
- Stop-Loss Orders: Pre-defined orders that automatically exit a trade when the price reaches a specified level, limiting potential losses.
- Take-Profit Orders: Pre-determined orders that automatically close a trade when the price reaches a target profit level, locking in gains.
- Hedging: Using financial instruments to offset the risk of another position, such as buying and selling currency pairs that have a negative correlation.
- Diversification: Spreading investments across different currency pairs and asset classes to reduce overall risk.
- Risk-Reward Ratio: Evaluating the potential reward of a trade relative to the potential risk, ensuring that the expected return justifies the risk taken.
Importance of Risk Management
Risk management is paramount for both individual traders and financial institutions in the forex market. It helps to:
- Preserve Capital: Effective risk management strategies help traders and institutions protect their capital from significant losses due to adverse market conditions.
- Maximize Profits: By managing risks, traders can optimize their trading strategies and increase the probability of profitable outcomes.
- Manage Volatility: Risk management techniques allow traders to navigate market volatility and minimize the impact of price fluctuations on their portfolios.
- Enhance Confidence: When risks are properly managed, traders and institutions gain confidence in their trading decisions and can approach the market with a more informed and strategic mindset.
Ultimate Conclusion
In conclusion, the foreign exchange market stands as a cornerstone of the global financial system, facilitating international trade, investment, and economic growth. Its complex structure and diverse participants contribute to its resilience and liquidity, while regulatory oversight ensures its stability and integrity. Understanding the functions and structure of the foreign exchange market empowers individuals and businesses alike to navigate its complexities and harness its potential.
