A currency depreciation in the foreign exchange market will have a profound impact on various aspects of an economy, ranging from exports and imports to investment and tourism. This insightful exploration delves into the intricacies of these effects, unraveling the complexities that shape economic landscapes.
By examining the consequences of a depreciated currency, we gain a deeper understanding of its influence on trade, investment flows, consumer behavior, and overall economic growth. Join us as we navigate the nuances of currency depreciation, uncovering its potential benefits and challenges.
Impact on Exports

Currency depreciation enhances the competitiveness of domestic exports, as foreign buyers can acquire domestic goods and services at a lower price. This increased competitiveness leads to higher demand for exports, resulting in increased production, job creation, and economic growth.
Check what professionals state about foreign exchange market graph macro and its benefits for the industry.
Boost to Economic Growth
- Increased exports generate higher revenues for domestic firms, contributing to corporate profits and tax revenues.
- Higher production levels lead to increased employment opportunities in export-oriented industries.
- Economic growth fueled by exports can lead to improved living standards and overall prosperity.
Potential Drawbacks
While currency depreciation can boost exports, it may also lead to certain drawbacks:
- Increased exports may result in job losses in import-competing industries, as domestic consumers switch to cheaper imported goods.
- Depreciation can lead to higher inflation, as imported goods become more expensive.
- Overreliance on exports can make the economy vulnerable to fluctuations in global demand.
Impact on Imports
Currency depreciation refers to a decrease in the value of a country’s currency relative to other currencies. This has a direct impact on the cost of imported goods, making them more expensive for domestic consumers and businesses.
When a country’s currency depreciates, the cost of importing goods from other countries increases. This is because the domestic currency is now worth less compared to the foreign currency, meaning that more of the domestic currency is needed to purchase the same amount of foreign goods. As a result, imported goods become more expensive for domestic consumers and businesses, potentially leading to higher consumer prices and reduced demand.
Reduced Imports
The increased cost of imported goods can lead to a reduction in imports. Consumers may choose to purchase fewer imported goods due to their higher prices, while businesses may seek alternative domestic suppliers to reduce costs. This reduction in imports can have several consequences:
- Higher consumer prices: Reduced imports can lead to a shortage of certain goods in the domestic market, driving up prices for consumers.
- Potential shortages: In severe cases, reduced imports can lead to shortages of essential goods, such as food or medicine, if domestic production cannot meet demand.
Increased Domestic Production
While reduced imports can have negative consequences, it can also provide opportunities for domestic producers. With imported goods becoming more expensive, domestic producers may find it more profitable to increase their production to meet the demand for goods that were previously imported. This can lead to increased domestic production and job creation in the long run.
Remember to click function functions of foreign exchange market to understand more comprehensive aspects of the function functions of foreign exchange market topic.
Impact on Investment
Currency depreciation can have a significant impact on foreign direct investment (FDI). When a country’s currency depreciates, it becomes cheaper for foreign investors to acquire assets in that country. This can lead to an increase in FDI, as foreign investors seek to take advantage of the lower prices.
Increased FDI can have several potential benefits for a country. First, it can lead to job creation, as foreign investors often establish new businesses or expand existing ones. Second, FDI can bring new technologies and expertise to a country, which can help to boost productivity and economic growth. Third, FDI can provide a source of foreign exchange, which can help to stabilize the country’s currency and reduce its dependence on foreign borrowing.
However, there are also some potential drawbacks to increased FDI. One concern is that foreign investors may gain too much control over domestic industries. This can lead to a loss of economic sovereignty and a reduction in the country’s ability to set its own economic policies. Another concern is that FDI can lead to environmental degradation, as foreign investors may be less likely to comply with local environmental regulations.
Overall, the impact of currency depreciation on FDI is complex and depends on a number of factors, including the country’s economic policies, the level of political stability, and the availability of other investment opportunities.
Benefits of Increased FDI, A currency depreciation in the foreign exchange market will
- Job creation
- Technology transfer
- Increased exports
- Reduced dependence on foreign borrowing
Drawbacks of Increased FDI
- Loss of control over domestic industries
- Environmental degradation
- Exploitation of workers
Impact on Tourism
Currency depreciation makes a country more affordable for foreign tourists. This is because their currency can buy more of the local currency, making goods and services cheaper. As a result, a country may experience an increase in tourism.
Increased tourism can contribute to economic growth in several ways. First, it can create jobs in the tourism sector, such as in hotels, restaurants, and transportation. Second, it can generate foreign exchange earnings, which can be used to import goods and services or invest in infrastructure. Third, it can promote cultural exchange and understanding between different countries.
However, increased tourism can also have some drawbacks. For example, it can lead to environmental degradation, such as pollution and deforestation. It can also lead to cultural erosion, as local customs and traditions are diluted by the influx of foreign visitors.
Impact on Inflation: A Currency Depreciation In The Foreign Exchange Market Will
Currency depreciation can significantly influence inflation, which is the rate at which the prices of goods and services increase over time. When a country’s currency depreciates, it becomes cheaper for foreign entities to purchase domestic goods and services, leading to increased demand and potentially higher prices.
Finish your research with information from foreign exchange market importance.
Inflation, when uncontrolled, can have several adverse consequences. It can reduce the purchasing power of individuals, making it more challenging to afford essential goods and services. Moreover, persistent inflation can lead to social unrest and erode trust in the government’s economic policies.
Benefits of Inflation
Despite its negative implications, inflation can also bring certain benefits. In some sectors, moderate inflation can stimulate economic growth. For instance, it can encourage businesses to invest and expand their operations, anticipating future price increases. Additionally, inflation can reduce the real value of debt, making it easier for borrowers to repay their obligations.
Impact on Exchange Rates

Currency depreciation refers to a decrease in the value of a currency relative to other foreign currencies. This fluctuation can significantly impact exchange rates, which are the prices at which currencies are traded.
When a currency depreciates, it becomes cheaper for foreign buyers to purchase goods and services from the depreciated currency’s country. Conversely, it becomes more expensive for domestic residents to purchase foreign goods and services.
Exchange Rate Fluctuations
Exchange rate fluctuations can have both positive and negative implications for businesses and consumers.
- Positive implications:
- Increased exports: A weaker domestic currency makes exports cheaper for foreign buyers, potentially boosting exports and economic growth.
- Increased tourism: A weaker domestic currency can attract foreign tourists as goods and services become more affordable for them.
- Negative implications:
- Increased imports: A weaker domestic currency makes imports more expensive for domestic consumers and businesses.
- Increased inflation: Imported goods and services become more expensive, potentially contributing to inflationary pressures.
Central Banks’ Role
Central banks play a crucial role in managing exchange rates and mitigating their impact.
- Intervention: Central banks can intervene in the foreign exchange market by buying or selling currencies to influence their value.
- Interest rate adjustments: Central banks can adjust interest rates to make their currency more or less attractive to foreign investors.
Conclusion
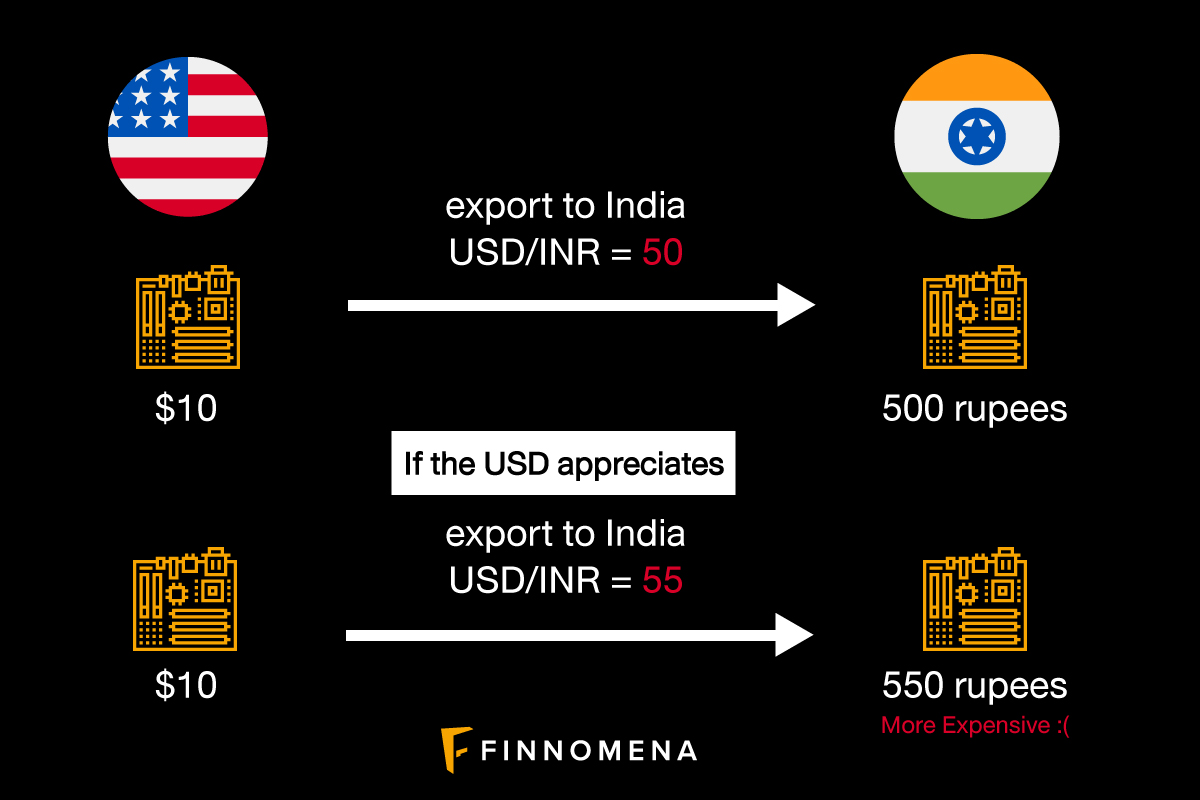
In conclusion, the depreciation of a currency in the foreign exchange market sets in motion a chain reaction that reverberates throughout an economy. While it may enhance exports and curb imports, it also brings forth inflationary pressures and potential disruptions in investment and tourism. Understanding the intricate dynamics of currency depreciation empowers policymakers and businesses alike to navigate its complexities and mitigate potential risks while harnessing its opportunities.
