What is foreign exchange market class 12 – Embark on a journey into the realm of foreign exchange, delving into the intricacies of the Forex market in Class 12. This exploration unravels the fundamental concepts, key players, and strategies that shape this dynamic and ever-evolving financial landscape.
As we navigate through the world of currency exchange, we’ll uncover the factors that influence exchange rates, explore the different types of market participants, and delve into the regulatory frameworks that govern this complex ecosystem.
Definition and Overview
The foreign exchange market, also known as Forex or FX, is a global decentralized marketplace where currencies are traded. It is the largest financial market in the world, with an average daily trading volume exceeding $5 trillion.
Forex plays a crucial role in international trade and finance. It facilitates the exchange of currencies between countries, allowing businesses and individuals to conduct transactions across borders. Additionally, Forex provides a platform for investors to speculate on currency movements and hedge against currency risk.
You also can investigate more thoroughly about foreign exchange market volatility to enhance your awareness in the field of foreign exchange market volatility.
Role of Forex in Global Trade
- Enables businesses to import and export goods and services by converting their local currency into the currency of the trading partner.
- Facilitates international travel and tourism by allowing individuals to exchange their currency for the local currency of their destination.
- Provides a platform for businesses and individuals to manage currency risk through hedging strategies.
Participants in the Forex Market

The Forex market is a vast and complex global network where currencies are traded. A diverse range of participants interact within this market, each playing a distinct role in shaping its dynamics.
Central Banks
- Central banks are responsible for managing a country’s monetary policy and overseeing the stability of its currency.
- They participate in the Forex market to influence the value of their currency, manage foreign exchange reserves, and intervene to stabilize exchange rates.
Commercial Banks
- Commercial banks facilitate currency exchange transactions for their customers, including businesses and individuals.
- They act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers of currencies, providing liquidity and access to the market.
Investment Banks
- Investment banks engage in Forex trading for their clients, primarily hedge funds and institutional investors.
- They provide specialized services such as currency hedging, speculative trading, and portfolio management.
Retail Traders
- Retail traders participate in the Forex market through online platforms or brokers.
- They speculate on currency price movements, aiming to profit from exchange rate fluctuations.
The presence of these diverse participants contributes to the liquidity and efficiency of the Forex market. Their actions and interactions influence exchange rates and market trends, shaping the global economy.
Check foreign exchange market jamaica to inspect complete evaluations and testimonials from users.
Forex Market Structure
The foreign exchange market operates through two primary market structures: the spot market and the forward market.
Spot Market
The spot market is where currencies are traded for immediate delivery, typically within two business days. In the spot market, buyers and sellers agree on an exchange rate and settle the transaction promptly.
Mechanics of Currency Trading in the Spot Market:
- Traders quote currencies in pairs, such as EUR/USD or GBP/JPY.
- The first currency in the pair is the base currency, and the second is the quote currency.
- The exchange rate represents the number of units of the quote currency required to purchase one unit of the base currency.
Forward Market
The forward market is where currencies are traded for delivery at a future date, typically ranging from one month to several years.
Role of Forward Contracts in Managing Currency Risk:
- Forward contracts allow businesses and individuals to lock in an exchange rate for future transactions.
- This helps mitigate the risk of adverse currency fluctuations and ensures predictability in foreign currency payments.
Factors Affecting Currency Exchange Rates
Exchange rates, the prices of one currency in terms of another, are influenced by a complex interplay of factors. These factors can be broadly categorized into economic conditions, political events, and central bank policies.
Economic Conditions
- Economic growth: Strong economic growth in a country tends to appreciate its currency as demand for its exports increases.
- Inflation: Higher inflation erodes the purchasing power of a currency, making it less valuable compared to others.
- Interest rates: Higher interest rates attract foreign capital, leading to currency appreciation.
- Balance of trade: A trade surplus, where exports exceed imports, can strengthen a currency, while a deficit can weaken it.
Political Events
- Political stability: Currency exchange rates tend to be more stable in politically stable countries.
- Government policies: Fiscal and monetary policies can impact currency values.
- International relations: Political tensions or conflicts can weaken a country’s currency.
Central Bank Policies
- Monetary policy: Central banks can influence exchange rates through interest rate adjustments and quantitative easing.
- Foreign exchange intervention: Central banks may buy or sell their own currency to stabilize its value.
- Currency pegs: Some countries fix their currency’s value against a major currency like the US dollar.
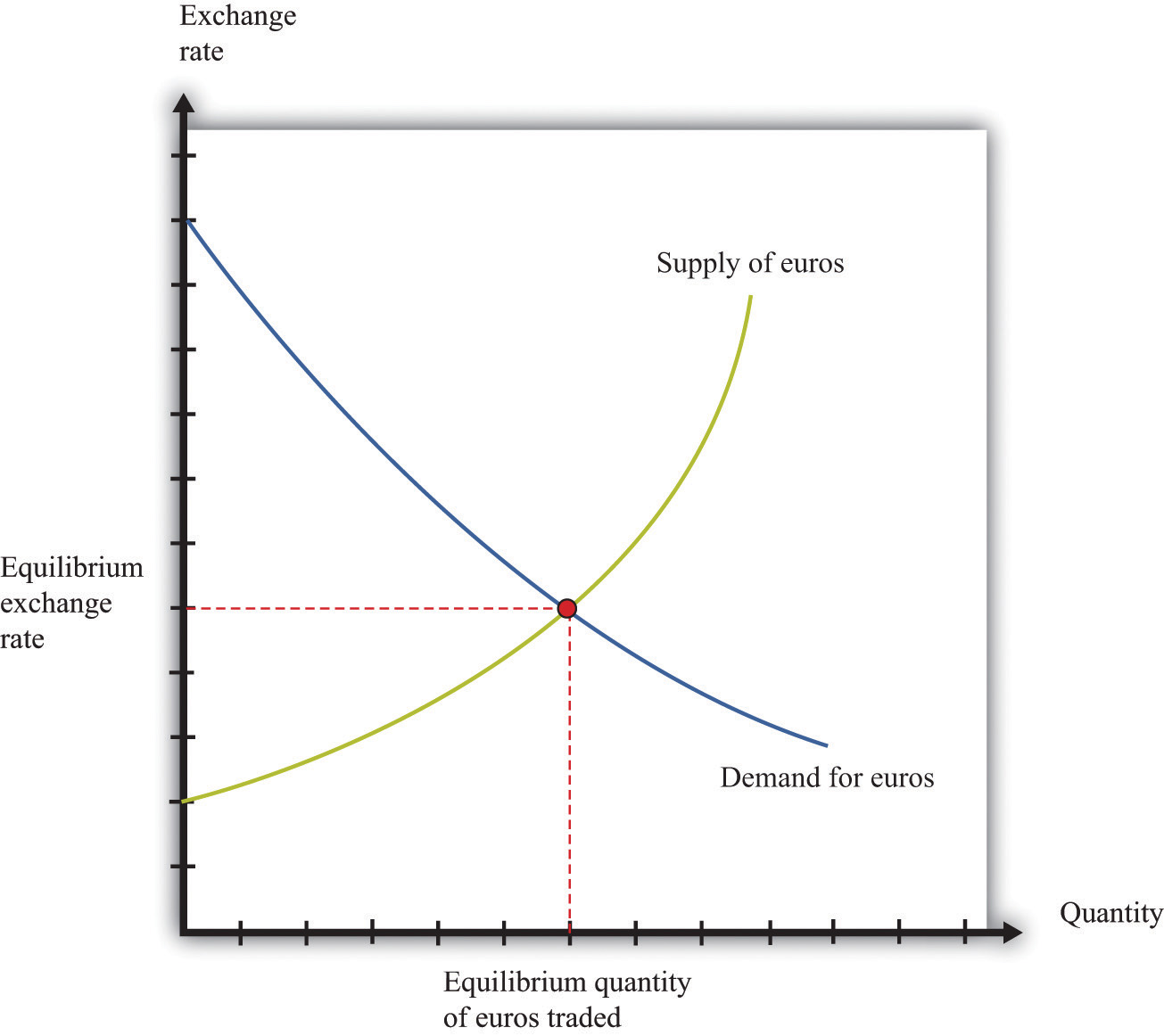
Supply and Demand
Ultimately, exchange rates are determined by supply and demand. When there is more demand for a currency than supply, its value appreciates. Conversely, when supply exceeds demand, its value depreciates.
Forex Trading Strategies: What Is Foreign Exchange Market Class 12
The Forex market offers a diverse range of trading strategies, each tailored to specific risk appetites and time horizons. Traders employ these strategies to capitalize on market movements and maximize their returns.
Notice foreign exchange market and balance of payment for recommendations and other broad suggestions.
Scalping
Scalping involves executing numerous short-term trades within a short timeframe, typically within a few seconds or minutes. Scalpers aim to profit from small price fluctuations, relying on high trade volume and quick execution to generate profits. This strategy requires intense focus, lightning-fast reflexes, and a deep understanding of market dynamics.
Day Trading
Day traders enter and exit positions within the same trading day, holding positions for a few hours or less. They seek to profit from intraday price movements, analyzing market trends and identifying opportunities for quick gains. Day trading requires constant monitoring of market conditions and a disciplined approach to risk management.
Swing Trading, What is foreign exchange market class 12
Swing traders hold positions for several days or weeks, aiming to capitalize on larger price swings. They analyze technical indicators and market sentiment to identify potential trends and trade accordingly. Swing trading allows for more time to analyze the market and execute trades, but it also carries the risk of overnight price movements.
Position Trading
Position traders hold positions for extended periods, sometimes months or years. They focus on long-term market trends and macroeconomic factors to identify investment opportunities. Position trading requires a high level of patience and risk tolerance, as it involves holding positions through potential market fluctuations.
Forex Market Regulation

Regulation plays a vital role in the Forex market to ensure fair, transparent, and orderly trading practices. It helps to protect participants from fraud, manipulation, and other unethical activities that can disrupt the market’s integrity.
Regulatory bodies, such as the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) in the United States and the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the United Kingdom, oversee the Forex market and implement regulations to maintain its stability and prevent abuses.
Measures to Prevent Fraud and Manipulation
- Registration and Licensing: Regulators require Forex brokers and dealers to register and obtain licenses to operate, ensuring that they meet minimum standards of conduct and financial stability.
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know-Your-Customer (KYC) Regulations: These measures help prevent money laundering and other illegal activities by requiring brokers to verify the identity and background of their clients.
- Market Surveillance: Regulators monitor trading activity to detect and investigate suspicious behavior, such as price manipulation or insider trading.
- Customer Protection Funds: Some jurisdictions have established funds to compensate traders in case of fraud or insolvency by Forex brokers.
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, the foreign exchange market stands as a vital cog in the global financial system, facilitating international trade, investment, and risk management. By comprehending the intricacies of this market, individuals can gain valuable insights into the interconnectedness of global economies and make informed decisions in the dynamic world of finance.
