How is exchange rate determined in the foreign exchange market class 12 – Exchange rates, the prices at which currencies are traded, play a crucial role in global commerce and financial markets. In this article, we delve into the intricate world of the foreign exchange market, exploring the factors that influence exchange rates and the mechanisms that drive their determination.
We will examine the interplay of supply and demand, the impact of economic and political events, and the role of central bank intervention in shaping exchange rates. By understanding these dynamics, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions in the ever-evolving foreign exchange market.
Factors Influencing Exchange Rates
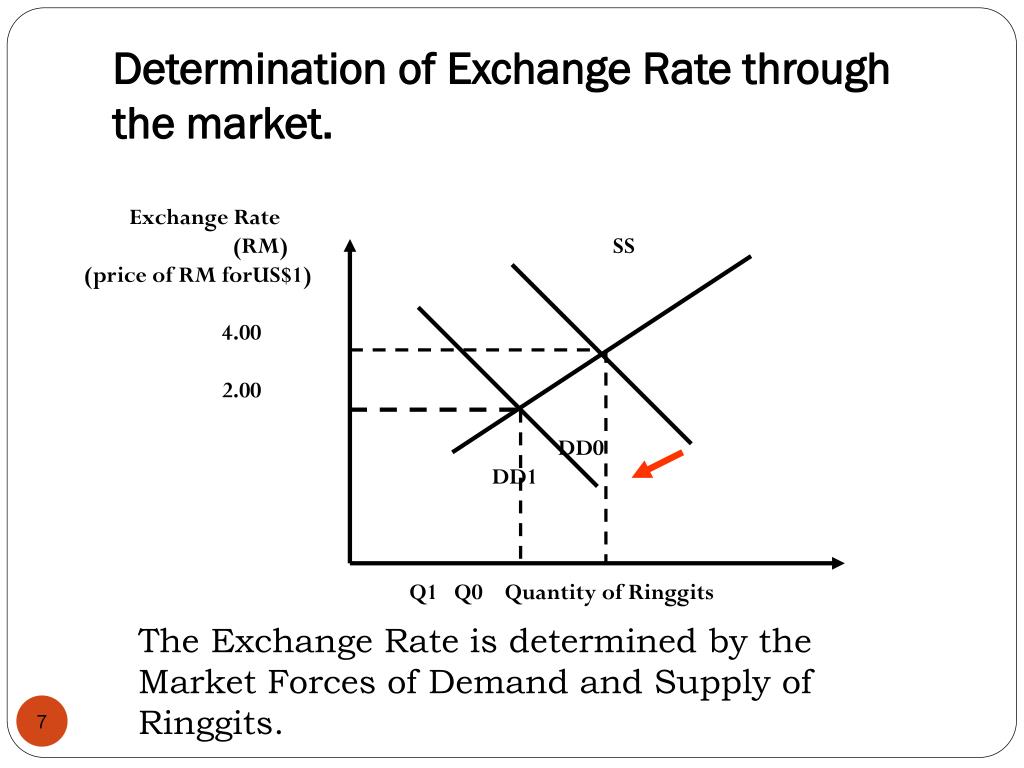
Exchange rates are influenced by various economic and political factors that affect the supply and demand for currencies in the foreign exchange market.
Check foreign exchange market efficiency to inspect complete evaluations and testimonials from users.
The fundamental principle of supply and demand dictates that when the demand for a currency increases relative to its supply, its value (exchange rate) tends to rise. Conversely, when the supply of a currency exceeds demand, its value tends to fall.
You also can investigate more thoroughly about foreign exchange market upsc to enhance your awareness in the field of foreign exchange market upsc.
Economic Events
- Economic growth: Strong economic growth in a country can increase demand for its currency, as investors seek opportunities in a growing economy.
- Inflation: High inflation can reduce the value of a currency, as it erodes the purchasing power of the currency’s holders.
- Trade balance: A country with a positive trade balance (exports exceeding imports) will have a higher demand for its currency, as foreigners need to purchase the currency to pay for imports.
Political Events
- Political stability: Political uncertainty or instability can reduce demand for a currency, as investors become hesitant to invest in countries with perceived risks.
- Government policies: Government policies, such as interest rate changes or currency controls, can influence the supply and demand for a currency.
- International relations: Diplomatic tensions or conflicts between countries can affect the exchange rates of their currencies.
Interest Rates and Inflation
- Interest rates: Higher interest rates in a country can attract foreign investment, increasing demand for its currency.
- Inflation: As mentioned earlier, high inflation can reduce the value of a currency, leading to a decrease in its exchange rate.
Currency Trading Mechanisms

Currency trading occurs in various markets, each with its characteristics and participants. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for comprehending how exchange rates are determined.
Interbank Trading, How is exchange rate determined in the foreign exchange market class 12
Interbank trading is the primary venue where banks and other financial institutions trade currencies among themselves. It is a wholesale market where large transactions are executed, often involving millions or billions of dollars. Interbank trading plays a significant role in setting benchmark exchange rates, which are used as references for other currency markets.
Retail Trading
Retail trading involves individuals and small businesses buying and selling currencies through brokers or online platforms. It is a decentralized market with a smaller trading volume compared to interbank trading. Retail traders often speculate on exchange rate movements, hoping to profit from fluctuations. Their activities can influence exchange rates, particularly during periods of high volatility.
Currency Brokers and Market Makers
Currency brokers act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers in the foreign exchange market. They connect traders with liquidity providers, ensuring efficient execution of trades. Market makers are specialized institutions that provide liquidity by quoting both bid and ask prices for currencies. Their presence helps reduce price disparities and facilitates smoother trading.
Find out about how foreign exchange market operations can deliver the best answers for your issues.
Intervention by Central Banks: How Is Exchange Rate Determined In The Foreign Exchange Market Class 12

Central banks play a crucial role in managing exchange rates by intervening in the foreign exchange market. They do this through various mechanisms, with specific objectives and potential impacts.
Objectives of Central Bank Intervention
Central banks intervene in the foreign exchange market primarily to:
- Stabilize exchange rates and reduce volatility.
- Manage inflation by influencing the value of the domestic currency.
- Protect domestic industries from exchange rate fluctuations.
Mechanisms of Central Bank Intervention
Central banks use several mechanisms to intervene in the foreign exchange market:
- Interest Rate Adjustments: By raising or lowering interest rates, central banks can influence the attractiveness of their currency. Higher interest rates make a currency more attractive to foreign investors, leading to an appreciation in its value.
- Foreign Exchange Reserves: Central banks hold foreign exchange reserves in various currencies. They can buy or sell these reserves to influence the supply and demand of the domestic currency, thereby affecting its exchange rate.
Impact of Central Bank Intervention
Central bank intervention can have significant impacts on exchange rates:
- Short-term impact: Intervention can temporarily influence exchange rates by altering the supply and demand for currencies.
- Long-term impact: Sustained intervention can have long-term effects on exchange rates if it addresses underlying economic factors, such as inflation or trade imbalances.
Examples of Central Bank Intervention
Examples of central bank intervention include:
- The Bank of Japan’s purchase of Japanese government bonds to weaken the yen.
- The Swiss National Bank’s intervention to prevent the Swiss franc from appreciating too strongly.
- The Reserve Bank of India’s sale of US dollars to support the Indian rupee.
Forecasting Exchange Rates
Forecasting exchange rates is a challenging task due to the complex and dynamic nature of the foreign exchange market. However, there are several methods that can be used to make predictions about future exchange rates.
One common method is technical analysis, which involves studying historical price data to identify patterns and trends. Technical analysts believe that these patterns can be used to predict future price movements. Another method is fundamental analysis, which focuses on economic factors that can affect exchange rates, such as interest rates, inflation, and economic growth.
Historical Data and Economic Indicators
Historical data can be used to identify trends and patterns in exchange rates. For example, if the exchange rate between the US dollar and the euro has been rising steadily over the past few months, it is more likely to continue rising in the future. Economic indicators can also be used to make predictions about exchange rates. For example, if the US economy is growing faster than the eurozone economy, the demand for US dollars will increase, which will lead to a rise in the value of the US dollar against the euro.
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, exchange rate determination in the foreign exchange market is a complex and multifaceted process influenced by a myriad of factors. By understanding these factors and the mechanisms involved, individuals and businesses can navigate the global financial landscape with greater confidence and make informed decisions that align with their financial goals.
