Welcome to the fascinating realm of global foreign exchange market definition, where currencies dance in a delicate balance, shaping the economic landscape. The forex market, a vast and dynamic arena, plays a pivotal role in facilitating international trade, investment, and tourism. As we delve into its intricacies, we’ll explore its purpose, participants, structure, and the factors that drive currency exchange rates.
At the core of the forex market lies the concept of currency pairs, representing the relative value of one currency against another. Understanding these pairs and the factors influencing their exchange rates is crucial for navigating the ever-evolving financial world. Whether you’re a seasoned trader or simply curious about the forces shaping global economies, this guide will provide valuable insights into the global foreign exchange market definition.
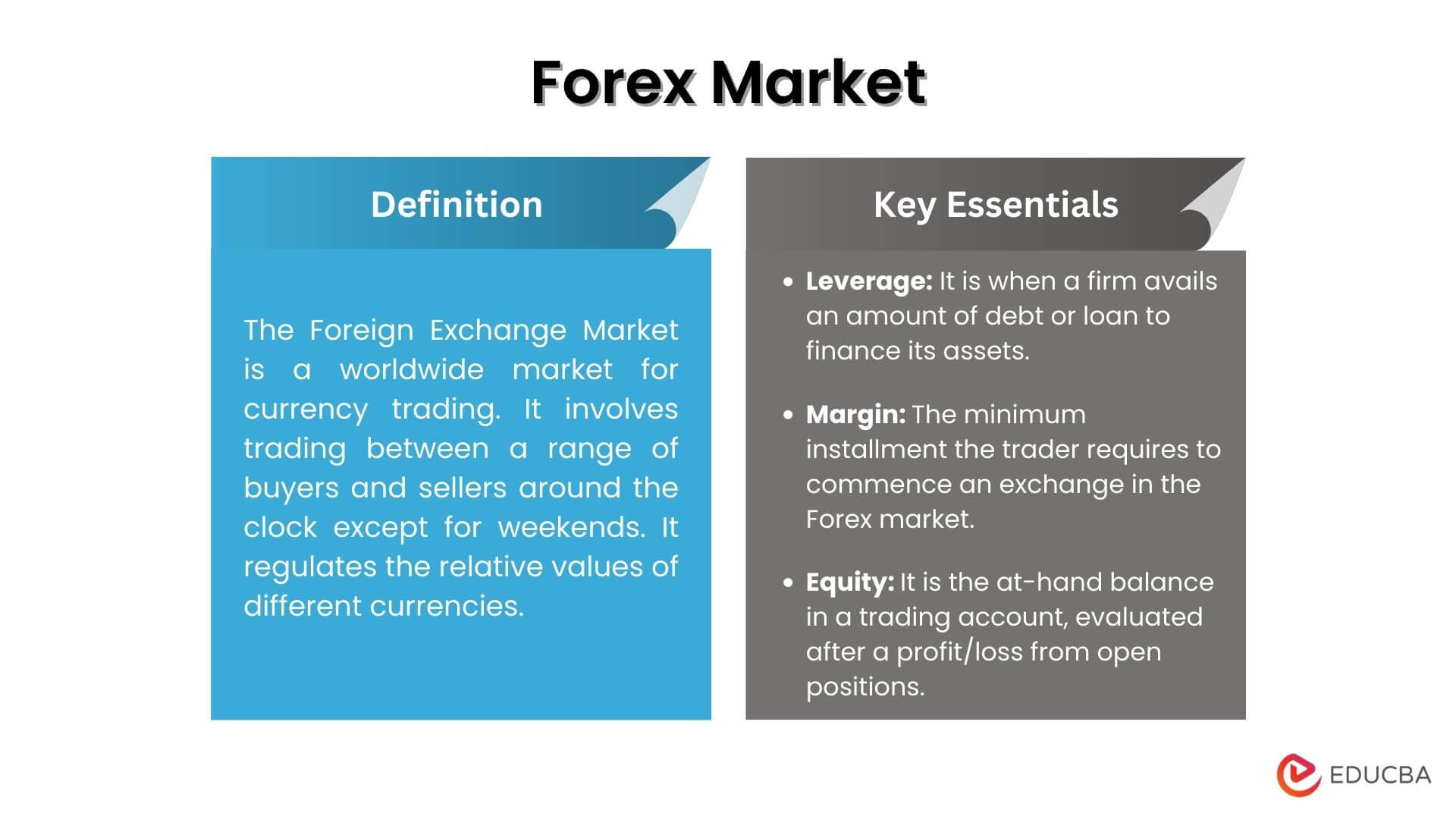
Definition of Global Foreign Exchange Market
The global foreign exchange market, also known as the forex market, is a decentralized global marketplace where currencies are traded.
It facilitates the exchange of currencies for various purposes, including international trade, tourism, and investment.
Expand your understanding about japanese intervention in foreign exchange market with the sources we offer.
Purpose and Functions
- Facilitates international trade by enabling businesses to exchange currencies for goods and services.
- Supports tourism by allowing individuals to exchange their home currency for the currency of their destination.
- Provides investment opportunities for individuals and institutions seeking returns from currency fluctuations.
Participants
- Banks: Primary participants, facilitating currency exchange for clients and engaging in proprietary trading.
- Corporations: Multinational companies that need to exchange currencies for international operations.
- Investment Funds: Hedge funds and other investment vehicles that trade currencies for profit.
- Central Banks: Regulate the foreign exchange market and intervene to influence currency values.
- Retail Traders: Individuals who trade currencies for speculative or investment purposes.
Structure and Organization of the Forex Market
The foreign exchange market, also known as forex or FX, is a decentralized global market where currencies are traded. It is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with an estimated daily trading volume of over $6.6 trillion.
You also can investigate more thoroughly about foreign exchange market in ethiopia pdf to enhance your awareness in the field of foreign exchange market in ethiopia pdf.
The forex market is organized into different types of markets, including the spot market, forward market, and futures market. The spot market is where currencies are traded for immediate delivery, while the forward market is where currencies are traded for delivery at a future date. The futures market is where contracts to buy or sell currencies at a future date are traded.
Interbank Trading
Interbank trading is the trading of currencies between banks. Banks are the largest participants in the forex market, and they trade currencies with each other to meet their own needs and the needs of their customers. Interbank trading is conducted over-the-counter (OTC), which means that it is not conducted on a centralized exchange.
You also will receive the benefits of visiting cash foreign exchange market meaning today.
Electronic Trading Platforms
Electronic trading platforms are online marketplaces where currencies are traded. These platforms allow banks and other participants in the forex market to trade currencies with each other electronically. Electronic trading platforms have made the forex market more accessible to a wider range of participants, including retail investors.
Currency Pairs and Exchange Rates
In the foreign exchange market, currencies are traded in pairs. A currency pair represents the value of one currency relative to another. The first currency in the pair is called the base currency, and the second currency is called the quote currency.
The exchange rate between two currencies is the number of units of the quote currency that are required to purchase one unit of the base currency. For example, if the EUR/USD exchange rate is 1.20, it means that one euro is worth 1.20 US dollars.
Factors Influencing Exchange Rates
The exchange rates between currencies are influenced by a variety of factors, including:
- Economic growth: Countries with strong economic growth tend to have stronger currencies.
- Inflation: Countries with high inflation tend to have weaker currencies.
- Interest rates: Countries with higher interest rates tend to have stronger currencies.
- Political stability: Countries with political instability tend to have weaker currencies.
- Supply and demand: The supply and demand for a currency can also affect its exchange rate.
Major Currency Pairs
The most commonly traded currency pairs in the foreign exchange market are:
- EUR/USD (euro/US dollar)
- USD/JPY (US dollar/Japanese yen)
- GBP/USD (British pound/US dollar)
- USD/CHF (US dollar/Swiss franc)
- USD/CAD (US dollar/Canadian dollar)
These currency pairs account for the majority of the trading volume in the foreign exchange market.
Trading in the Forex Market
The forex market operates 24 hours a day, 5 days a week, and trading can take place anywhere in the world. Forex trading involves buying and selling currencies in pairs, with the goal of profiting from fluctuations in their exchange rates.
Types of Forex Orders
There are several types of forex orders that traders can use, including:
- Market orders: These orders are executed immediately at the current market price.
- Limit orders: These orders are executed only when the market price reaches a specified level set by the trader.
- Stop orders: These orders are similar to limit orders, but they are used to close out a trade when the market price reaches a specified level.
Executing Forex Trades
To execute a forex trade, a trader must first open an account with a forex broker. Once an account is opened, the trader can deposit funds and start trading. Forex trades are typically executed through an online trading platform, which allows traders to view market prices, place orders, and manage their trades.
Risks and Rewards of Forex Trading
Forex trading can be a rewarding experience, but it also carries a high level of risk. The value of currencies can fluctuate rapidly, and traders can lose money if they are not careful. Some of the risks involved in forex trading include:
- Currency risk: This is the risk that the value of a currency will change, resulting in a loss for the trader.
- Interest rate risk: This is the risk that interest rates will change, affecting the value of currencies.
- Political risk: This is the risk that political events will affect the value of currencies.
Despite the risks, forex trading can also be a rewarding experience. Traders who are successful in forex trading can earn significant profits. However, it is important to remember that forex trading is not a get-rich-quick scheme. It takes time, effort, and skill to become a successful forex trader.
Market Size and Liquidity: Global Foreign Exchange Market Definition
The global foreign exchange market is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world. It is estimated to have a daily trading volume of over $6.6 trillion, which is more than all other financial markets combined. The forex market is so liquid because it is used by a wide range of participants, including banks, corporations, hedge funds, and retail traders.
Implications of High Liquidity
The high liquidity of the forex market has several implications for traders. First, it means that there is always a ready buyer or seller for any currency pair. This makes it easy to enter and exit trades quickly and efficiently. Second, the high liquidity helps to reduce the risk of slippage, which is the difference between the price you expect to get for a trade and the price you actually get. Third, the high liquidity helps to keep transaction costs low.
Role of Technology in the Forex Market
Technology has revolutionized the foreign exchange market, making it more accessible, efficient, and transparent. Electronic trading platforms and mobile trading apps have transformed the way traders interact with the market, providing them with real-time information and enabling them to execute trades from anywhere in the world.
Electronic Trading Platforms
Electronic trading platforms, such as MetaTrader and cTrader, have become the primary venue for forex trading. These platforms provide traders with access to live market data, charting tools, and advanced order execution capabilities. They also offer a wide range of trading instruments, including currency pairs, commodities, and indices.
Mobile Trading Apps
Mobile trading apps have made forex trading even more convenient. These apps allow traders to access their trading accounts and execute trades from their smartphones or tablets. They offer similar features to electronic trading platforms, but are designed for a mobile experience.
Advantages of Technology in Forex Trading
- Increased accessibility: Technology has made forex trading accessible to a wider range of participants, including retail traders and small businesses.
- Improved efficiency: Electronic trading platforms and mobile trading apps have streamlined the trading process, making it faster and more efficient.
- Enhanced transparency: Technology has increased the transparency of the forex market, providing traders with real-time information and access to market data.
Disadvantages of Technology in Forex Trading
- Increased risk: Technology can also increase the risk of trading, as it can lead to faster and more impulsive decision-making.
- Dependence on technology: Traders who rely heavily on technology may face challenges if there are technical issues or internet outages.
- Reduced personal interaction: Technology has reduced the need for face-to-face interaction between traders, which can limit the ability to build relationships and gain insights from other market participants.
Regulation and Oversight

The global foreign exchange market is a largely unregulated market, with different countries and regions having varying levels of oversight. However, there are a number of regulatory bodies that play a role in overseeing the forex market, including:
– The Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the United Kingdom
– The Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) in the United States
– The Swiss Financial Market Supervisory Authority (FINMA) in Switzerland
– The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) in Singapore
– The Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) in Australia
These regulatory bodies set regulations and compliance requirements for forex brokers and traders, including requirements for:
– Registration and licensing
– Capital adequacy
– Risk management
– Transparency and disclosure
– Anti-money laundering and counter-terrorism financing measures
Regulation is important in ensuring the integrity of the forex market and protecting investors. It helps to prevent fraud and manipulation, and it ensures that forex brokers and traders are operating in a fair and transparent manner.
Role of Regulation
Regulation plays a vital role in the forex market by:
– Establishing clear rules and guidelines for market participants
– Ensuring transparency and accountability
– Protecting investors from fraud and abuse
– Promoting fair competition
– Maintaining market stability
Effective regulation helps to foster confidence in the forex market and attracts new participants, leading to increased liquidity and market depth. It also helps to prevent systemic risks and protect the financial system from potential crises.
Emerging Trends in the Forex Market
The forex market is constantly evolving, with new trends emerging all the time. Some of the most notable trends in recent years include the rise of algorithmic trading, the increasing use of mobile trading platforms, and the growing popularity of cryptocurrencies.
Algorithmic Trading, Global foreign exchange market definition
Algorithmic trading, also known as algo trading, is a method of using computers to execute trades based on predefined rules. Algo trading is becoming increasingly popular in the forex market, as it can help traders to automate their trading strategies and reduce the risk of human error.
Mobile Trading Platforms
Mobile trading platforms allow traders to access the forex market from their smartphones or tablets. This has made it easier than ever for traders to stay connected to the market and to trade on the go.
Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies are digital currencies that are not backed by any central bank or government. Cryptocurrencies have become increasingly popular in recent years, and they are now starting to be used for trading in the forex market.
These are just a few of the emerging trends in the forex market. It is likely that we will see even more new trends emerge in the years to come.
Final Wrap-Up

In conclusion, the global foreign exchange market definition stands as a testament to the interconnectedness of our world. Its size, liquidity, and technological advancements have transformed international finance, making it possible to conduct business seamlessly across borders. As we look to the future, emerging trends such as algorithmic trading promise to further shape the landscape of forex trading. Understanding the global foreign exchange market definition is not just about mastering financial concepts; it’s about gaining a deeper appreciation for the complexities of global economics and the role it plays in our daily lives.
