Foreign exchange market model definition – At the heart of international finance lies the foreign exchange market, a dynamic arena where currencies are traded. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of foreign exchange market models, empowering readers with a profound understanding of this complex financial landscape.
As we embark on this journey, we will explore the diverse models employed to analyze market behavior, unravel the factors that shape exchange rates, and uncover the practical applications of these models in the real world.
Definition of the Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market, also known as the forex market, is a global decentralized marketplace where currencies are traded. It is the largest financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume of over $5 trillion.
Obtain direct knowledge about the efficiency of foreign currency exchange through case studies.
The foreign exchange market plays a vital role in international trade and investment. It allows businesses to exchange currencies so they can buy and sell goods and services from other countries. It also allows investors to diversify their portfolios by investing in different currencies.
Participants in the Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market is made up of a wide range of participants, including:
- Banks: Banks are the largest participants in the foreign exchange market. They trade currencies on behalf of their customers, including businesses, individuals, and governments.
- Currency traders: Currency traders are professional traders who buy and sell currencies for profit. They use a variety of trading strategies to try to profit from changes in currency prices.
- Corporations: Corporations use the foreign exchange market to exchange currencies for international trade and investment.
- Central banks: Central banks are government agencies that are responsible for managing the monetary policy of their country. They intervene in the foreign exchange market to influence the value of their currency.
Models of the Foreign Exchange Market: Foreign Exchange Market Model Definition
The foreign exchange market is a complex and dynamic system, and a variety of models have been developed to analyze its behavior. These models range from simple to complex, and each has its own strengths and limitations.
Simple Models
- The random walk model assumes that exchange rates follow a random walk, with no predictable pattern.
- The purchasing power parity model assumes that exchange rates will adjust to equalize the purchasing power of different currencies.
Econometric Models
Econometric models use statistical techniques to analyze the relationship between exchange rates and other economic variables, such as interest rates, inflation, and economic growth.
Agent-Based Models
Agent-based models simulate the behavior of individual agents in the foreign exchange market, such as traders, banks, and central banks. These models can provide insights into the dynamics of the market and how it responds to shocks.
Check foreign exchange market yesterday to inspect complete evaluations and testimonials from users.
Strengths and Limitations
The choice of which model to use depends on the specific research question being addressed. Simple models are easy to understand and use, but they may not be able to capture the complexity of the foreign exchange market. Econometric models can provide more sophisticated analysis, but they require a large amount of data and can be difficult to interpret. Agent-based models can provide insights into the dynamics of the market, but they can be computationally expensive and difficult to validate.
Factors Influencing Foreign Exchange Rates
The foreign exchange market is a complex and dynamic environment where exchange rates are influenced by a multitude of factors. These factors can be broadly classified into three main categories: economic, political, and social.
Economic Factors
Economic factors are the primary drivers of exchange rates. The strength of a country’s economy, as measured by factors such as GDP growth, inflation, and unemployment, plays a significant role in determining the value of its currency.
- Economic Growth: A strong and growing economy attracts foreign investment, which increases demand for the country’s currency and strengthens its value.
- Inflation: High inflation erodes the purchasing power of a currency, making it less desirable and leading to a depreciation in its value.
- Interest Rates: Higher interest rates attract foreign capital, which increases demand for the currency and strengthens its value.
- Government Debt: Excessive government debt can raise concerns about the country’s financial stability and lead to a depreciation in the currency.
Political Factors
Political stability and the government’s policies can also have a significant impact on exchange rates.
- Political Stability: A stable political environment attracts foreign investment and boosts confidence in the currency.
- Government Policies: Government policies, such as fiscal and monetary policies, can affect economic growth, inflation, and interest rates, which in turn influence exchange rates.
- International Relations: Tensions or conflicts between countries can lead to currency fluctuations.
Social Factors
Social factors, such as cultural events, holidays, and natural disasters, can also influence exchange rates.
- Cultural Events: Major cultural events, such as the Olympics or the World Cup, can increase demand for a country’s currency due to increased tourism and spending.
- Holidays: During holidays, demand for certain currencies may increase due to travel and gift-giving.
- Natural Disasters: Natural disasters can disrupt economic activity and damage infrastructure, leading to a depreciation in the currency.
Role of Supply and Demand
In addition to the economic, political, and social factors, the foreign exchange market is also driven by supply and demand. The exchange rate of a currency is determined by the balance between the supply of and demand for that currency.
Learn about more about the process of foreign exchange market jamaica in the field.
When demand for a currency exceeds supply, its value appreciates. Conversely, when supply exceeds demand, its value depreciates.
Forecasting Foreign Exchange Rates
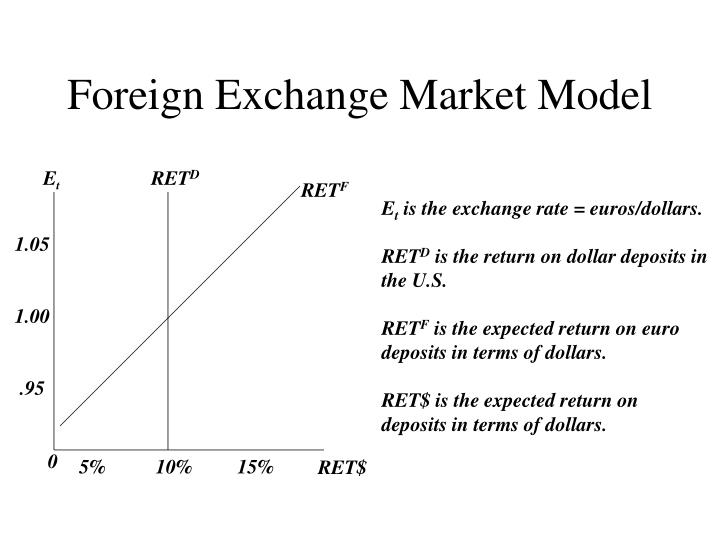
Forecasting foreign exchange rates involves predicting the future value of a currency against another currency. It plays a crucial role in international trade, investment, and risk management. Various methods are used to forecast exchange rates, including:
- Technical Analysis: Examines historical price data to identify patterns and trends that may indicate future price movements.
- Fundamental Analysis: Considers economic factors such as interest rates, inflation, GDP, and political stability to assess the underlying value of a currency.
- Econometric Models: Use statistical techniques to estimate the relationship between exchange rates and economic variables, allowing for the prediction of future rates.
- Expert Opinions: Involve gathering forecasts from experienced currency traders, economists, and analysts.
Challenges and Accuracy
Forecasting foreign exchange rates is challenging due to the complex and volatile nature of currency markets. Factors such as economic shocks, geopolitical events, and market sentiment can significantly impact exchange rates. As a result, forecasting accuracy can vary depending on the method used and the time horizon considered.
Despite the challenges, accurate forecasting is essential for businesses and investors to manage currency risk and make informed decisions. By combining different forecasting techniques and considering various factors, it is possible to improve the accuracy of exchange rate predictions and enhance decision-making in international markets.
Applications of Foreign Exchange Market Models

Foreign exchange market models are not just theoretical constructs but have practical applications in the real world. They are used by businesses and investors to make informed decisions related to foreign exchange transactions and investments.
One of the most common applications of foreign exchange market models is in forecasting future exchange rates. These models help businesses and investors anticipate changes in currency values, enabling them to make better decisions about currency hedging, international trade, and investment strategies.
Risk Management
Businesses and investors can use foreign exchange market models to assess and manage foreign exchange risk. By understanding the factors that influence exchange rates, they can develop strategies to mitigate the impact of currency fluctuations on their operations and investments.
Investment Decisions, Foreign exchange market model definition
Foreign exchange market models help investors make informed decisions about international investments. By analyzing exchange rate trends and forecasts, investors can identify opportunities to invest in foreign markets with favorable exchange rates and minimize the risk of currency losses.
Currency Trading
Traders use foreign exchange market models to identify trading opportunities and develop trading strategies. By understanding the factors that drive exchange rate movements, traders can make informed decisions about buying and selling currencies.
Economic Policy
Central banks and governments use foreign exchange market models to analyze the impact of economic policies on exchange rates. These models help policymakers make informed decisions about interest rates, monetary policy, and other economic measures that can influence currency values.
Ultimate Conclusion

In conclusion, foreign exchange market models provide invaluable insights into the ever-evolving global financial landscape. By comprehending the strengths and limitations of these models, businesses and investors can make informed decisions, navigate market volatility, and capitalize on opportunities.
As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the foreign exchange market will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping global economic dynamics. With the knowledge gained from this exploration, readers are well-equipped to navigate the complexities of this dynamic market and harness its potential.
