Define what is foreign exchange market – As we delve into the intricacies of the foreign exchange market, we embark on a journey that unravels the complexities of global currency exchange. From the concept of foreign exchange to the role of central banks, we’ll explore the factors that shape currency values and the risks inherent in this dynamic market.
The foreign exchange market, a vast and ever-evolving landscape, serves as the backbone of international trade and investment. It facilitates the conversion of one currency into another, enabling businesses and individuals to conduct transactions across borders seamlessly.
Define the Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market, also known as forex or FX, is a global decentralized market for the trading of currencies. It is the largest financial market in the world, with an average daily trading volume of over $5 trillion.
The purpose of the foreign exchange market is to facilitate the exchange of currencies for international trade and investment. When a company or individual imports goods or services from another country, they need to exchange their currency for the currency of the country they are importing from. The foreign exchange market provides a platform for these exchanges to take place.
Role of Central Banks in Managing Foreign Exchange Markets
Central banks play an important role in managing foreign exchange markets. They can intervene in the market to buy or sell currencies in order to influence the exchange rate. This can be done to stabilize the currency, promote economic growth, or achieve other policy objectives.
Investigate the pros of accepting articles about foreign exchange market in your business strategies.
For example, if a country’s currency is depreciating rapidly, the central bank may intervene to buy the currency in order to support its value. This can help to stabilize the currency and prevent it from falling too far.
Remember to click define foreign exchange market and its function to understand more comprehensive aspects of the define foreign exchange market and its function topic.
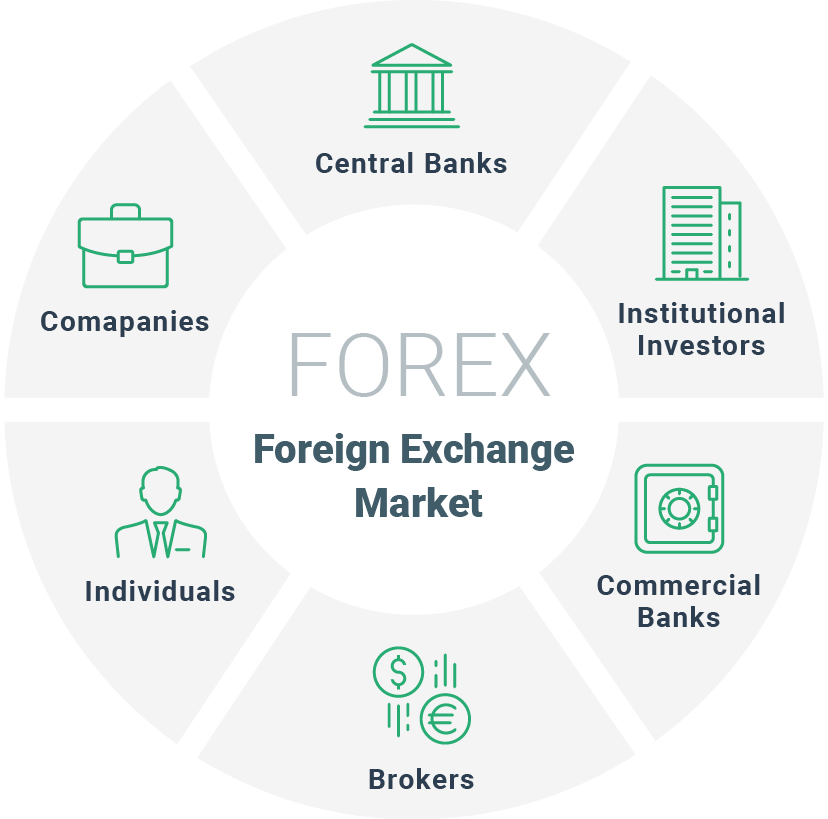
Participants in the Foreign Exchange Market
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/foreign-exchange-markets.asp-final-16abed069d5e4ba0924142476dec4211.png)
The foreign exchange market is a vast and complex global marketplace where currencies are traded. It involves a wide range of participants, each playing a specific role in facilitating the exchange of currencies. The major participants in the foreign exchange market include banks, brokers, and individual traders.
Banks
Banks are the largest and most important participants in the foreign exchange market. They provide a range of services, including:
- Providing liquidity to the market by buying and selling currencies
- Facilitating currency transactions for their customers
- Providing foreign exchange advisory services
Brokers
Brokers act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers of currencies. They provide a platform for traders to execute their orders and offer a range of services, including:
- Matching buyers and sellers
- Providing quotes and market information
- Executing trades on behalf of their clients
Individual Traders
Individual traders are individuals who trade currencies for profit. They can participate in the foreign exchange market through a variety of platforms, including online brokerages and retail banks. Individual traders can range from small-scale speculators to large-scale investors.
Factors Influencing Foreign Exchange Rates
Foreign exchange rates are influenced by various factors, including economic indicators, interest rates, and political events. These factors can have significant impacts on currency values, affecting international trade, investment decisions, and overall economic stability.
Economic Indicators
Economic indicators provide insights into the health and performance of a country’s economy. Strong economic growth, low inflation, and high employment rates typically lead to an appreciation of the currency, as investors seek to invest in stable and growing economies. Conversely, weak economic indicators, such as high inflation, unemployment, or political instability, can lead to a depreciation of the currency.
Interest Rates
Interest rates play a crucial role in determining foreign exchange rates. Higher interest rates attract foreign investment, as investors seek higher returns on their investments. This increased demand for the currency leads to an appreciation in its value. Conversely, lower interest rates can lead to a depreciation of the currency, as investors move their funds to countries with higher returns.
Political Events
Political events, such as elections, wars, or changes in government policies, can significantly impact foreign exchange rates. Political uncertainty, instability, or perceived risks can lead to a depreciation of the currency, as investors withdraw their investments and seek safer havens. Conversely, positive political developments, such as stable governments or economic reforms, can boost investor confidence and lead to an appreciation of the currency.
Types of Foreign Exchange Transactions: Define What Is Foreign Exchange Market
Foreign exchange transactions involve the exchange of currencies between different countries. These transactions can be classified into various types based on their purpose and the time frame involved.
Spot Transactions
Spot transactions are the most common type of foreign exchange transaction. They involve the immediate exchange of currencies at the prevailing market rate. The settlement of spot transactions typically occurs within two business days.
Advantages of Spot Transactions:
Learn about more about the process of in foreign exchange market meaning in the field.
- Immediate execution
- Transparency in pricing
- Suitable for short-term currency needs
Forward Transactions
Forward transactions are contracts to exchange currencies at a predetermined rate on a future date. They are used to hedge against currency fluctuations and lock in future exchange rates.
Advantages of Forward Transactions:
- Protection against currency risk
- Locking in future exchange rates
- Suitable for long-term currency needs
Swap Contracts
Swap contracts involve the simultaneous buying and selling of the same amount of currency at different maturities. They are used to manage currency exposure and interest rate risk.
Advantages of Swap Contracts:
- Hedging against currency and interest rate fluctuations
- Tailoring to specific currency and maturity needs
- Managing complex currency exposures
Risks in the Foreign Exchange Market

Foreign exchange trading involves various risks that traders must be aware of and manage effectively. These risks include:
Currency Volatility
Currency volatility refers to the fluctuations in the value of currencies against each other. These fluctuations can be caused by various factors such as economic data, political events, and market sentiment. Currency volatility can lead to losses for traders if they do not correctly predict the direction of currency movements.
Counterparty Risk
Counterparty risk refers to the risk that a party involved in a foreign exchange transaction may default on its obligations. This risk is particularly important in over-the-counter (OTC) markets, where transactions are not cleared through a central exchange. Traders must carefully assess the creditworthiness of their counterparties before entering into any transactions.
Strategies for Managing Risks, Define what is foreign exchange market
There are several strategies that traders can use to manage risks in the foreign exchange market:
- Hedging: Hedging involves using financial instruments to offset the risk of adverse currency movements. Traders can use forward contracts, options, or other hedging strategies to protect their positions.
- Diversification: Diversifying across different currencies can help reduce the overall risk of a foreign exchange portfolio. Traders can invest in currencies from different regions or sectors to spread their risk.
- Position Sizing: Managing the size of their positions is crucial for traders. By carefully calculating the appropriate position size based on their risk tolerance and account balance, traders can limit potential losses.
- Stop-Loss Orders: Stop-loss orders are used to automatically exit a trade when the price reaches a predetermined level. This helps traders limit their losses in case of adverse market movements.
- Monitoring Market Conditions: Traders should continuously monitor market conditions and stay updated on economic data and political events that may impact currency movements. This enables them to make informed trading decisions and adjust their strategies accordingly.
The Role of Technology in the Foreign Exchange Market
Technology has revolutionized the foreign exchange market, transforming it from a decentralized, manual process to an electronic, highly efficient system.
The introduction of electronic trading platforms has brought numerous benefits, including increased transparency, reduced transaction costs, and improved liquidity.
Electronic Trading Platforms
Electronic trading platforms have become the primary channel for foreign exchange transactions. These platforms connect buyers and sellers from around the world, allowing them to trade currencies in real-time with greater efficiency and speed.
- Increased Transparency: Electronic platforms provide real-time market data, allowing traders to make informed decisions based on the latest information.
- Reduced Transaction Costs: Automated trading systems have significantly reduced transaction costs compared to traditional methods.
- Improved Liquidity: Electronic platforms aggregate liquidity from multiple participants, providing traders with access to a wider range of counterparties.
However, electronic trading also presents challenges, such as the potential for technical glitches and the need for traders to adapt to the fast-paced, automated environment.
Ultimate Conclusion
In conclusion, the foreign exchange market stands as a testament to the interconnectedness of the global economy. Its complexities and risks demand a thorough understanding for those seeking to navigate its ever-changing landscape. By embracing knowledge and employing sound strategies, participants can harness the opportunities and mitigate the challenges inherent in this dynamic realm.
