Case study on foreign exchange market is a comprehensive guide to the dynamic world of currency trading. This study provides a deep dive into the factors that influence exchange rates, the various types of transactions, and the methods used for trading foreign currencies. By exploring successful strategies and case studies, this analysis empowers businesses to navigate the complexities of international finance and maximize their global reach.
The foreign exchange market, a global marketplace where currencies are traded, plays a pivotal role in facilitating international trade and managing currency risk. Understanding the intricacies of this market is essential for businesses operating in a globalized economy.
Definition of Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market (Forex or FX market) is a global decentralized marketplace where currencies are traded. It is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with an average daily trading volume of over $6.6 trillion.
The FX market facilitates the exchange of currencies for various purposes, including international trade, tourism, and investment. It plays a crucial role in international commerce and financial stability.
History of the Foreign Exchange Market
The origins of the FX market can be traced back to ancient times when traders and merchants exchanged currencies to facilitate commerce. The modern FX market emerged in the late 19th century with the development of global trade and the establishment of the gold standard.
Participants in the Foreign Exchange Market
The FX market involves a wide range of participants, including:
- Central banks: Manage their countries’ exchange rates and foreign exchange reserves.
- Commercial banks: Facilitate currency exchange for their customers and engage in trading for their own account.
- Investment banks: Provide FX trading services to their clients and engage in proprietary trading.
- Hedge funds: Use FX trading as a strategy to generate profits.
- Corporations: Exchange currencies for international transactions and manage currency risk.
- Retail traders: Individuals who trade currencies for speculative or investment purposes.
Factors Affecting Foreign Exchange Rates
The foreign exchange market is influenced by a multitude of factors, both domestic and international, that can impact currency valuations and exchange rates. Understanding these factors is crucial for businesses, investors, and policymakers who operate in the global marketplace.
Browse the implementation of foreign exchange market meaning pdf in real-world situations to understand its applications.
Among the key factors affecting foreign exchange rates are:
Economic Conditions
The economic health of a country, as reflected by its GDP growth, inflation, unemployment rate, and trade balance, plays a significant role in determining the value of its currency. A strong economy with stable growth and low inflation tends to attract foreign investment, which increases demand for the domestic currency and strengthens its value.
Political Stability
Political stability and uncertainty can have a profound impact on foreign exchange rates. Countries with stable political environments, transparent legal systems, and low corruption levels are more attractive to foreign investors, leading to increased demand for their currencies. Conversely, political instability, social unrest, and government intervention in the economy can weaken a currency’s value.
Interest Rates
Interest rates set by a country’s central bank influence the flow of capital and, consequently, the demand for its currency. Higher interest rates typically attract foreign investors seeking higher returns, which increases demand for the domestic currency and strengthens its value. Lower interest rates, on the other hand, can lead to capital outflows and a weaker currency.
Inflation Rates, Case study on foreign exchange market
Inflation, or the rate at which prices rise, is another important factor affecting foreign exchange rates. High inflation erodes the purchasing power of a currency, making it less attractive to investors and leading to its depreciation. Conversely, low inflation indicates price stability and a healthy economy, which can strengthen a currency’s value.
Find out about how foreign exchange market functions ppt can deliver the best answers for your issues.
Currency Speculation
Currency speculation, also known as forex trading, involves buying and selling currencies with the aim of profiting from fluctuations in their exchange rates. Speculators can have a significant impact on currency valuations, especially in the short term, by creating demand or supply for a particular currency based on their expectations of future market movements.
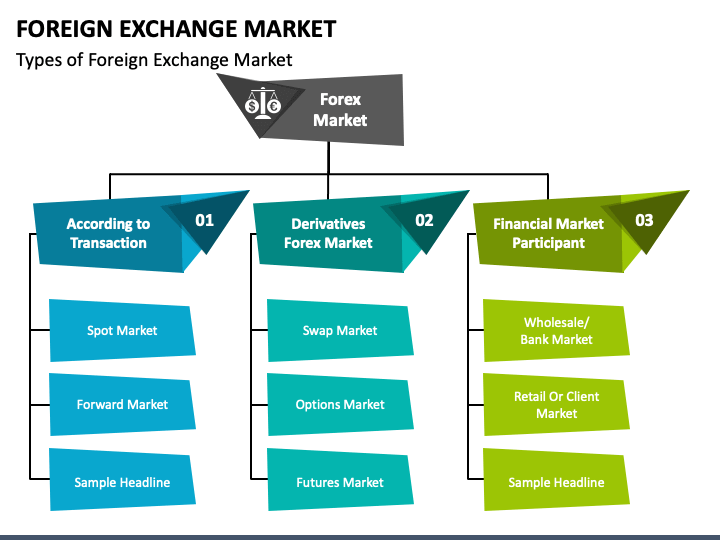
Types of Foreign Exchange Transactions

Foreign exchange transactions encompass a range of operations that facilitate the exchange of currencies between different countries. These transactions play a vital role in international trade, investment, and financial activities.
Spot Transactions
Spot transactions involve the immediate exchange of currencies at the prevailing market rate. They are typically used for urgent payments, such as settling international invoices or making foreign purchases.
Forward Transactions
Forward transactions allow parties to lock in an exchange rate for a future date. This type of transaction is often used to hedge against potential currency fluctuations or to secure a favorable exchange rate for future payments.
Swap Transactions
Swap transactions involve the simultaneous exchange of two currencies at a specified exchange rate, with an agreement to reverse the transaction at a later date. These transactions are often used to manage currency risk or to speculate on exchange rate movements.
Options Transactions
Options transactions give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specified amount of currency at a predetermined exchange rate on or before a certain date. These transactions are used to manage currency risk or to speculate on exchange rate movements.
For descriptions on additional topics like foreign exchange market types, please visit the available foreign exchange market types.
Methods of Foreign Exchange Trading
Foreign exchange trading is conducted through various methods, each with its unique characteristics and advantages. The primary methods include over-the-counter (OTC) trading, electronic trading platforms, and foreign exchange brokers.
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Trading
OTC trading is a decentralized market where foreign exchange transactions are negotiated directly between two parties, without the involvement of an exchange. This method is often used for large-volume transactions and offers greater flexibility in terms of pricing and settlement.
Electronic Trading Platforms
Electronic trading platforms, also known as electronic communication networks (ECNs), are centralized marketplaces that facilitate foreign exchange trading. These platforms provide a transparent and efficient environment for buyers and sellers to interact, with real-time pricing and automated execution of orders.
Foreign Exchange Brokers
Foreign exchange brokers act as intermediaries between traders and the foreign exchange market. They provide access to trading platforms, offer guidance and analysis, and facilitate the execution of trades. Brokers typically charge a commission or spread on transactions.
Risks and Challenges in Foreign Exchange Trading

Foreign exchange trading involves inherent risks and challenges that traders must be aware of and prepared to manage effectively. These include:
Currency Volatility
Currency volatility refers to the fluctuations in the value of currencies relative to each other. These fluctuations can be influenced by various factors, including economic conditions, political events, and market sentiment. Currency volatility can lead to significant losses if not properly managed.
Counterparty Risk
Counterparty risk arises when one party to a foreign exchange transaction fails to fulfill its obligations. This can occur due to factors such as bankruptcy, default, or fraud. Counterparty risk can be mitigated by choosing reputable and financially sound counterparties.
Regulatory Risk
Regulatory risk refers to the potential for changes in government regulations or policies that may impact foreign exchange trading. These changes can include restrictions on currency trading, changes in tax laws, or new compliance requirements. Regulatory risk can be managed by staying informed about regulatory developments and ensuring compliance with all applicable regulations.
Role of Foreign Exchange in International Business
Foreign exchange plays a crucial role in international business, enabling seamless transactions and mitigating financial risks associated with currency fluctuations.
Facilitating International Trade
Foreign exchange facilitates the exchange of currencies between countries, allowing businesses to engage in international trade. Without a functioning foreign exchange market, businesses would face significant challenges in conducting transactions with foreign entities due to currency differences.
Managing Currency Risk
Currency risk arises when the value of one currency fluctuates against another. Foreign exchange allows businesses to manage this risk by converting currencies at favorable rates and hedging against potential losses due to exchange rate movements.
Hedging against Currency Fluctuations
Businesses can use foreign exchange instruments such as forward contracts, options, and swaps to hedge against currency fluctuations. These instruments allow businesses to lock in exchange rates for future transactions, protecting them from adverse movements in the foreign exchange market.
Case Studies of Successful Foreign Exchange Strategies
Successful foreign exchange (forex) strategies involve predicting currency movements and taking appropriate actions to capitalize on those movements. Some notable case studies include:
Currency Carry Trade
The currency carry trade involves borrowing a currency with a low interest rate and investing it in a currency with a higher interest rate. The profit comes from the difference in interest rates, known as the carry. For example, in the early 2000s, investors borrowed the Japanese yen (JPY) at near-zero interest rates and invested in the Australian dollar (AUD), which had a higher interest rate. As long as the JPY remained weak against the AUD, investors profited from the carry.
Hedging Using Currency Forwards
Hedging using currency forwards is a strategy used to protect against potential losses due to currency fluctuations. A company that imports goods from a foreign country may purchase a currency forward contract to lock in the exchange rate at which it will buy the foreign currency in the future. This protects the company from any adverse movements in the exchange rate that could increase the cost of the goods.
Speculating on Currency Movements
Speculating on currency movements involves buying or selling currencies in the hope of profiting from changes in their exchange rates. Speculators may use technical analysis, fundamental analysis, or a combination of both to identify potential trading opportunities. For example, a speculator may buy the euro (EUR) if they believe it is undervalued and will rise in value against the US dollar (USD).
Final Review: Case Study On Foreign Exchange Market
In conclusion, the case study on foreign exchange market provides a comprehensive understanding of the factors, transactions, and strategies involved in currency trading. By leveraging the insights gained from this study, businesses can develop effective foreign exchange strategies, mitigate risks, and capitalize on opportunities in the global marketplace. Whether seeking to facilitate international trade, manage currency risk, or speculate on currency movements, this analysis equips businesses with the knowledge and tools necessary to navigate the complexities of the foreign exchange market and achieve success in international business.
