What is foreign exchange market efficiency? In the world of finance, this concept plays a pivotal role, shaping the dynamics of currency trading and influencing global economic interactions. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of foreign exchange market efficiency, exploring its definition, influencing factors, consequences, measurement techniques, and potential improvements.
As we embark on this journey, we will uncover the complexities of the foreign exchange market, shedding light on its mechanisms and implications. Stay tuned for an in-depth analysis that promises to enhance your understanding of this fascinating realm.
Definition of Foreign Exchange Market Efficiency
Foreign exchange market efficiency refers to the extent to which the market reflects all available information and reacts quickly to new information. An efficient market is one in which prices accurately reflect the underlying value of currencies, and there are no opportunities for arbitrage or excess profits.
Types of Market Efficiency
- Weak efficiency: The market incorporates all past prices, meaning that technical analysis is not profitable.
- Semi-strong efficiency: The market incorporates all publicly available information, making it difficult to outperform the market through fundamental analysis.
- Strong efficiency: The market incorporates all information, including private information, making it impossible to outperform the market consistently.
Examples of Efficient and Inefficient Foreign Exchange Markets
- Efficient market: The foreign exchange market is generally considered to be semi-strong efficient, as it incorporates most publicly available information.
- Inefficient market: A foreign exchange market may be inefficient if there is a lack of transparency, or if there are barriers to entry for new participants.
Factors Affecting Foreign Exchange Market Efficiency
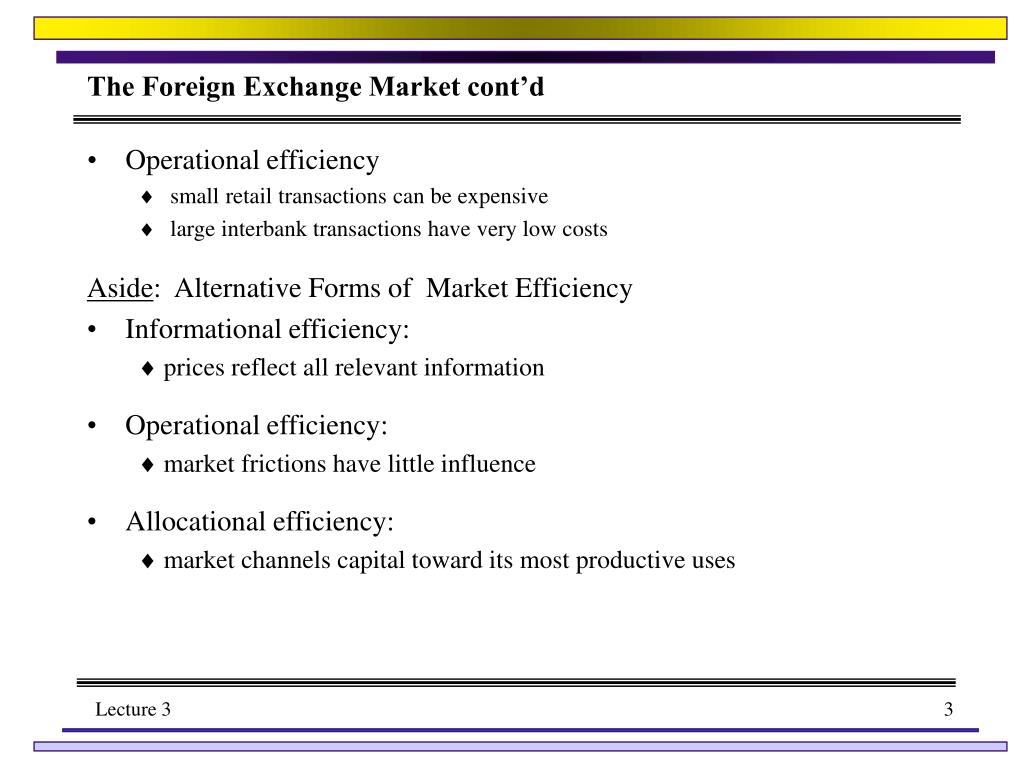
The efficiency of the foreign exchange market is influenced by a multitude of factors. These factors can be categorized into three main groups: market structure, market participants, and market information.
Market Structure
The structure of the foreign exchange market has a significant impact on its efficiency. The market is characterized by a decentralized over-the-counter (OTC) network of banks and other financial institutions. This decentralized structure allows for a high degree of competition, which in turn leads to tighter spreads and more efficient pricing.
The size and liquidity of the foreign exchange market also contribute to its efficiency. The foreign exchange market is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume of over $5 trillion. This liquidity ensures that there is always a ready supply of buyers and sellers, which helps to keep spreads tight and prices efficient.
Market Participants
The participants in the foreign exchange market also play a role in its efficiency. The market is dominated by a small number of large banks, which account for the majority of trading volume. These banks have the resources and expertise to provide liquidity and accurate pricing to the market.
In addition to banks, other participants in the foreign exchange market include hedge funds, asset managers, and corporations. These participants bring a diversity of perspectives and trading strategies to the market, which helps to ensure that prices are efficient.
Market Information
The availability of accurate and timely information is essential for the efficiency of the foreign exchange market. The market relies on a variety of sources for information, including news, economic data, and technical analysis. This information helps traders to make informed decisions about when to buy and sell currencies.
The speed at which information is disseminated also affects the efficiency of the foreign exchange market. In the past, information was transmitted slowly, which gave some traders an advantage over others. Today, information is transmitted almost instantaneously, which helps to ensure that all traders have access to the same information at the same time.
Consequences of Foreign Exchange Market Efficiency: What Is Foreign Exchange Market Efficiency
Foreign exchange market efficiency has significant consequences for market participants and the overall economy. Understanding these consequences is crucial for investors, businesses, and policymakers.
Check what professionals state about foreign exchange converter and its benefits for the industry.
Positive Consequences
- Reduced Transaction Costs: Efficient markets allow for lower transaction costs due to increased competition and liquidity.
- Price Discovery: Efficient markets facilitate efficient price discovery, reflecting the true value of currencies.
- Improved Capital Allocation: Efficient markets enable capital to flow to where it is most productive, promoting economic growth.
Negative Consequences
- Increased Volatility: High efficiency can lead to increased market volatility, making it more challenging for businesses and investors to manage risk.
- Speculation and Manipulation: Efficient markets can attract speculators and market manipulators, potentially leading to market distortions.
- Currency Crises: In extreme cases, market inefficiencies can contribute to currency crises, with severe economic consequences.
Real-World Examples
- London Foreign Exchange Market: The London foreign exchange market is highly efficient, resulting in low transaction costs and accurate price discovery.
- 1997 Asian Financial Crisis: Market inefficiencies and speculation contributed to the Asian financial crisis, leading to severe economic downturns.
- 2008 Global Financial Crisis: Inefficiencies in the foreign exchange market played a role in the 2008 global financial crisis, amplifying market volatility.
Measuring Foreign Exchange Market Efficiency
Measuring foreign exchange market efficiency is a complex task due to the market’s size, liquidity, and complexity. Several methods have been developed to assess market efficiency, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
Event Study Approach
The event study approach examines the market’s response to specific events, such as news announcements or policy changes, that are expected to affect exchange rates. By analyzing the speed and accuracy with which the market incorporates new information, researchers can infer the level of market efficiency.
Do not overlook explore the latest data about three characteristics of foreign exchange market.
Strengths:
- Directly measures market reaction to specific events.
- Can isolate the impact of individual events on exchange rates.
Weaknesses:
- Relies on the availability of significant events.
- May not capture the overall efficiency of the market.
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis uses historical price data to identify patterns and trends in exchange rates. Traders and analysts believe that these patterns can provide insights into future price movements and market efficiency.
Strengths:
- Relatively simple and easy to apply.
- Can identify short-term trading opportunities.
Weaknesses:
- Does not provide a comprehensive measure of market efficiency.
- Relies heavily on subjective interpretation.
Econometric Models, What is foreign exchange market efficiency
Econometric models use statistical techniques to analyze the relationship between exchange rates and various economic factors, such as interest rates, inflation, and economic growth. By estimating the parameters of these models, researchers can infer the level of market efficiency.
Strengths:
- Can provide a quantitative measure of market efficiency.
- Can control for other factors that may affect exchange rates.
Weaknesses:
- Relies on the accuracy of the underlying economic model.
- May not capture all aspects of market efficiency.
You also can understand valuable knowledge by exploring forex exchange.
Examples of Studies
Numerous studies have measured foreign exchange market efficiency using different methods. For example, a study by Frankel and Froot (1987) used the event study approach to examine the market’s response to news announcements about changes in interest rates. They found that the market reacted quickly and efficiently to the new information.
Another study by Fama (1990) used technical analysis to identify patterns in exchange rates. He found that certain technical indicators could predict future price movements, suggesting that the market may not be fully efficient.
Improving Foreign Exchange Market Efficiency
Improving foreign exchange market efficiency requires addressing challenges and implementing potential solutions. Challenges include market fragmentation, information asymmetry, and regulatory complexities. Solutions involve promoting market transparency, enhancing information dissemination, and streamlining regulations.
Challenges to Improving Foreign Exchange Market Efficiency
- Market Fragmentation: The foreign exchange market is decentralized, with trading occurring across multiple platforms and jurisdictions, leading to market segmentation and reduced efficiency.
- Information Asymmetry: Market participants have varying access to information, creating an uneven playing field and potential inefficiencies.
- Regulatory Complexities: Different regulatory frameworks across jurisdictions can hinder cross-border trading and introduce complexities for market participants.
Potential Solutions to Challenges
- Promoting Market Transparency: Implementing centralized trading platforms or data hubs can increase transparency and reduce market fragmentation.
- Enhancing Information Dissemination: Establishing standardized reporting requirements and improving access to real-time market data can reduce information asymmetry.
- Streamlining Regulations: Harmonizing regulations across jurisdictions can facilitate cross-border trading and reduce regulatory burdens for market participants.
Recommendations for Policymakers and Market Participants
- Policymakers:
- Promote market transparency and data dissemination.
- Streamline regulations and facilitate cross-border trading.
- Encourage the adoption of best practices and standards.
- Market Participants:
- Embrace centralized trading platforms or data hubs.
- Invest in technology to enhance information access.
- Support regulatory initiatives aimed at improving market efficiency.
Epilogue
In conclusion, foreign exchange market efficiency is a multifaceted concept that profoundly impacts the stability and performance of the global financial system. By understanding its intricacies, policymakers, market participants, and individuals can make informed decisions and navigate the complexities of currency trading effectively. As the foreign exchange market continues to evolve, ongoing research and innovation will undoubtedly shape its future efficiency, ensuring its continued relevance in the ever-changing landscape of global finance.
