Simple example of foreign exchange market – Foreign exchange market, often referred to as forex, is a global marketplace where currencies are traded. It’s a decentralized market, with transactions occurring over-the-counter between participants. Forex plays a vital role in global trade and investment, facilitating the exchange of currencies for various purposes.
Participants in the forex market include banks, investment firms, hedge funds, and retail traders. Each participant has different motivations and strategies for trading currencies, contributing to the dynamic nature of the market.
Introduction to Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market, commonly known as forex or FX, is a global decentralized market for trading currencies. It is the largest financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume that exceeds $5 trillion. The forex market plays a crucial role in global trade and investment, facilitating the exchange of currencies for international transactions, such as importing and exporting goods and services, as well as cross-border investments.
The forex market operates 24 hours a day, 5 days a week, with trading taking place in major financial centers around the world, including London, New York, Tokyo, and Singapore. The participants in the forex market include banks, institutional investors, hedge funds, retail traders, and corporations.
Enhance your insight with the methods and methods of major participants of foreign exchange market.
Role of Forex in Global Trade and Investment
The forex market is essential for global trade and investment. It enables businesses to exchange currencies to pay for imported goods and services, and to receive payment for exported goods and services. Without the forex market, international trade would be much more difficult and expensive.
The forex market also plays a vital role in cross-border investments. Investors often need to exchange currencies to purchase foreign stocks, bonds, and other financial assets. The forex market provides a liquid and efficient way for investors to exchange currencies for investment purposes.
Participants in Forex Market
The foreign exchange market is a global, decentralized market for the trading of currencies. It involves a wide range of participants, each with their own unique motivations and roles in the market.
The main participants in the forex market can be categorized into three broad groups:
Commercial Participants
Commercial participants engage in forex trading to facilitate international trade and investment. They include:
- Importers and Exporters: These businesses need to exchange currencies to pay for goods and services purchased or sold abroad.
- Multinational Corporations: They have operations in multiple countries and need to manage their currency exposure.
Financial Institutions
Financial institutions play a crucial role in facilitating forex trading and providing liquidity to the market. They include:
- Banks: Banks are the largest participants in the forex market, providing services such as currency exchange, hedging, and trade financing.
- Investment Banks: These banks specialize in trading currencies for their clients and proprietary accounts.
- Broker-Dealers: They connect buyers and sellers of currencies and provide execution services.
Speculators
Speculators are individuals or institutions that trade currencies with the aim of making a profit. They do not have any underlying commercial or financial need for currencies. Speculators include:
- Hedge Funds: These are investment funds that use sophisticated strategies to trade currencies.
- Retail Traders: These are individuals who trade currencies on their own account.
Forex Market Structure
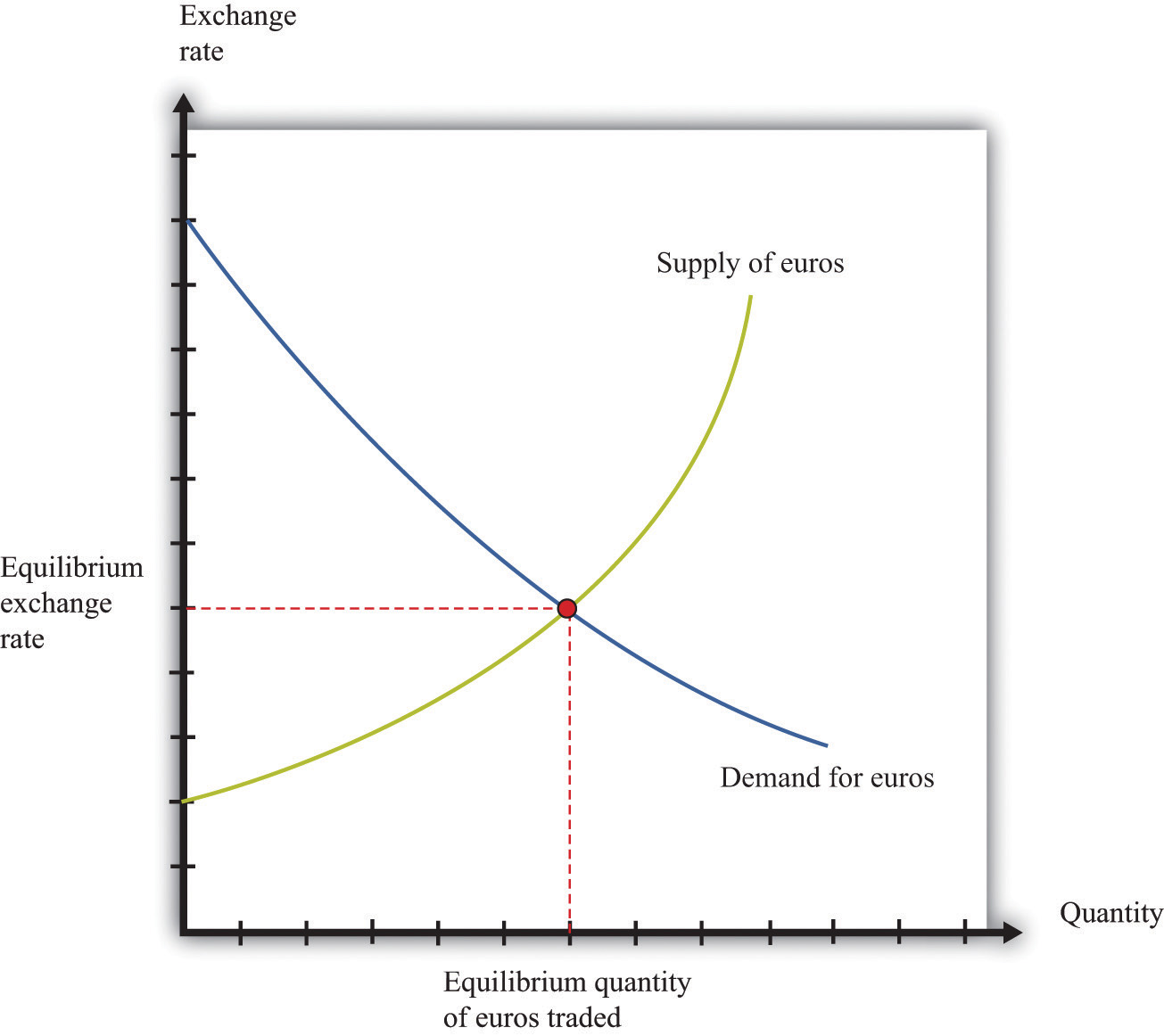
The foreign exchange market (forex market) is a decentralized global market for trading currencies. Unlike traditional exchanges, it has no central location or exchange and operates 24 hours a day, 5 days a week. The market is driven by the forces of supply and demand, with participants constantly buying and selling currencies to meet their needs.
Transaction Execution in Forex Market
In the forex market, transactions are executed in two main ways: spot market and forward market.
- Spot market: In the spot market, transactions are settled immediately, typically within two business days. This market is used for immediate delivery of currencies and is the most common type of forex transaction.
- Forward market: In the forward market, transactions are agreed upon today but settled at a future date, typically within a period of 1 to 12 months. This market is used to hedge against future currency fluctuations or to lock in a favorable exchange rate for a future transaction.
Factors Influencing Currency Exchange Rates
Currency exchange rates are constantly fluctuating, influenced by a complex interplay of economic, political, and psychological factors. These factors can have a significant impact on the value of a currency, making it appreciate or depreciate against other currencies.
Let’s delve into the key factors that influence currency exchange rates:
Economic Factors
- Interest rates: Higher interest rates tend to attract foreign investment, leading to an appreciation of the domestic currency. This is because investors seek higher returns on their investments, and higher interest rates make it more attractive to hold the currency.
- Inflation: High inflation can erode the purchasing power of a currency, making it less valuable compared to other currencies. This can lead to a depreciation of the currency as investors and businesses seek more stable currencies to protect their assets.
- Economic growth: A strong economy with high growth prospects can attract foreign investment and boost the demand for the domestic currency, leading to appreciation.
Political Factors
- Political stability: Political instability and uncertainty can undermine confidence in a country’s economy, leading to a depreciation of its currency. Investors and businesses prefer to invest in countries with stable political environments.
- Government policies: Government policies, such as fiscal and monetary policies, can impact the value of a currency. For example, expansionary monetary policies that increase the money supply can lead to inflation and currency depreciation.
Psychological Factors
- Market sentiment: The overall market sentiment can influence currency exchange rates. Positive sentiment towards a particular currency can lead to its appreciation, while negative sentiment can trigger depreciation.
- Speculation: Currency traders often speculate on future exchange rate movements, which can drive short-term fluctuations in currency values.
Forex Trading Strategies
In the dynamic world of forex trading, employing the right strategies can significantly impact your success. Forex trading strategies encompass a wide range of approaches, each carrying its own set of risks and rewards.
Scalping
Scalping involves taking multiple small profits over a short period. Scalpers aim to capitalize on tiny price fluctuations, entering and exiting trades quickly to minimize risk and maximize gains.
Risks: High frequency trading can lead to overtrading and increased transaction costs.
Rewards: Potential for consistent profits if executed effectively.
Day Trading
Day traders close all positions before the market closes, avoiding overnight risk. They seek to profit from intraday price movements, using technical analysis to identify trading opportunities.
Risks: Requires constant monitoring and can be stressful.
Obtain direct knowledge about the efficiency of foreign exchange market in india ppt through case studies.
Rewards: Potential for significant profits in volatile markets.
Swing Trading
Swing traders hold positions for a few days or weeks, aiming to capture larger price swings. They rely on technical analysis to identify trends and potential reversal points.
Risks: Exposure to overnight risk and potential for larger losses if the trend reverses.
Rewards: Potential for substantial profits if the trend continues as expected.
Position Trading
Position traders hold positions for months or even years, capitalizing on long-term trends. They use fundamental analysis to assess the economic and political factors that influence currency values.
Risks: Requires patience and tolerance for large drawdowns.
Understand how the union of foreign exchange market in the world can improve efficiency and productivity.
Rewards: Potential for significant profits if the trend persists.
Risk Management in Forex Trading
Risk management is crucial in forex trading, as it helps traders minimize potential losses and protect their capital. Forex trading involves various risks, including market risk, liquidity risk, and operational risk.
Market Risk, Simple example of foreign exchange market
Market risk arises from fluctuations in currency prices. To mitigate this risk, traders can use stop-loss orders, which automatically close positions when prices reach a predetermined level, and limit orders, which limit the maximum loss on a trade.
Liquidity Risk
Liquidity risk occurs when there is insufficient trading volume to execute orders at desired prices. To manage this risk, traders can trade during periods of high liquidity, such as during the London or New York trading sessions.
Operational Risk
Operational risk encompasses errors, system failures, and other non-market events that can disrupt trading. To minimize this risk, traders can use reputable brokers, maintain robust trading systems, and have contingency plans in place.
Forex Market Regulations: Simple Example Of Foreign Exchange Market

The foreign exchange market, being a global and decentralized market, requires a robust regulatory framework to ensure its integrity and stability. This framework involves a combination of regulations imposed by central banks, government agencies, and self-regulatory organizations.
Central banks play a crucial role in regulating the forex market. They set monetary policies that influence currency exchange rates and intervene in the market to stabilize exchange rate fluctuations. They also impose regulations on banks and other financial institutions involved in forex trading.
Role of Central Banks
- Set monetary policies that influence currency exchange rates
- Intervene in the market to stabilize exchange rate fluctuations
- Impose regulations on banks and other financial institutions involved in forex trading
Role of Other Regulatory Bodies
In addition to central banks, other regulatory bodies also play a role in regulating the forex market. These include government agencies and self-regulatory organizations.
- Government agencies enforce laws and regulations governing forex trading, including anti-money laundering and anti-fraud measures.
- Self-regulatory organizations establish and enforce ethical standards and best practices for forex market participants.
End of Discussion

The foreign exchange market is a complex and ever-evolving landscape, influenced by a myriad of factors. Understanding the basics of forex, the participants involved, and the strategies employed can provide valuable insights into this global marketplace.
