Example of arbitrage in foreign exchange market – In the dynamic world of foreign exchange trading, arbitrage presents a compelling opportunity to capitalize on price discrepancies. Discover the intricacies of arbitrage in the forex market, its various types, and how to identify and execute profitable trades.
This comprehensive guide delves into the strategies and techniques employed by successful arbitrageurs, providing valuable insights into the challenges and limitations of this lucrative trading approach.
Definition and Concept of Arbitrage in Foreign Exchange Market

In the foreign exchange (forex) market, arbitrage refers to the practice of taking advantage of price discrepancies between different currency pairs to make risk-free profits.
Forex arbitrage opportunities arise due to inefficiencies in the market, such as differences in bid-ask spreads, exchange rates, and liquidity across different exchanges or trading platforms.
Do not overlook the opportunity to discover more about the subject of what are foreign exchange market transactions.
Types of Arbitrage Opportunities in Forex Market
- Pure Arbitrage: Exploiting price differences between identical currency pairs on different exchanges.
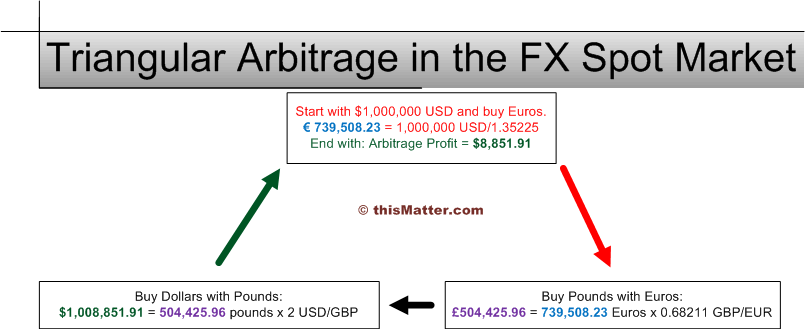
- Triangular Arbitrage: Involving three different currency pairs to create a risk-free profit loop.
- Carry Trade Arbitrage: Combining currency pairs with different interest rates to generate profits from interest rate differentials.
- Statistical Arbitrage: Using statistical models to identify price inefficiencies and exploit them.
- Cross-Currency Basis Arbitrage: Involving the simultaneous buying and selling of futures contracts for the same underlying asset in different currencies.
Methods of Identifying Arbitrage Opportunities
Identifying arbitrage opportunities in the forex market requires a systematic approach that combines technical and fundamental analysis. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you identify potential arbitrage opportunities:
Step 1: Market Analysis
- Monitor multiple currency pairs across different brokers and exchanges to identify price discrepancies.
- Use currency heatmaps or comparison tools to visualize currency movements and identify potential arbitrage opportunities.
Step 2: Technical Analysis
- Use technical indicators such as moving averages, support and resistance levels, and candlestick patterns to identify potential price reversals or trend changes.
- Look for divergence between technical indicators and price action to identify potential arbitrage opportunities.
Step 3: Fundamental Analysis
- Monitor economic news and events that can affect currency values, such as interest rate announcements, economic data releases, and political events.
- Use fundamental analysis to assess the economic strength of countries and identify potential opportunities for arbitrage.
Step 4: Calculate Potential Profits
- Calculate the potential profit by subtracting the purchase price from the sale price, taking into account transaction costs and any time delay between transactions.
- Ensure that the potential profit exceeds the transaction costs to make the arbitrage opportunity worthwhile.
Step 5: Execute the Arbitrage
- Once an arbitrage opportunity is identified, execute the trade quickly to capitalize on the price discrepancy.
- Monitor the trade closely to ensure that the price discrepancy persists and that the arbitrage profit is realized.
Execution of Arbitrage Trades: Example Of Arbitrage In Foreign Exchange Market
Executing arbitrage trades in the foreign exchange market involves a series of steps:
1. Identify an arbitrage opportunity. This can be done using various methods, such as scanning the market for price discrepancies or using arbitrage software.
2. Determine the size of the trade. The size of the trade will depend on the size of the arbitrage opportunity and the trader’s risk tolerance.
3. Place the trades. The trader will need to place two or more trades to complete the arbitrage. The first trade will be to buy the currency that is undervalued, and the second trade will be to sell the currency that is overvalued.
Investigate the pros of accepting foreign exchange market dollar value in your business strategies.
4. Monitor the trades. The trader will need to monitor the trades to ensure that they are executed as expected. The trader may also need to adjust the trades if the market conditions change.
5. Close the trades. Once the arbitrage opportunity has been realized, the trader will need to close the trades. The trader will do this by selling the currency that was bought and buying the currency that was sold.
Types of Orders Used in Arbitrage Trading
There are a variety of orders that can be used in arbitrage trading. The most common types of orders are:
- Market orders: Market orders are executed immediately at the best available price.
- Limit orders: Limit orders are executed only if the price reaches a specified level.
- Stop orders: Stop orders are executed only if the price moves through a specified level.
Risks Involved in Executing Arbitrage Trades
There are a number of risks involved in executing arbitrage trades. These risks include:
- Market risk: Market risk is the risk that the market conditions will change before the arbitrage opportunity can be realized.
- Execution risk: Execution risk is the risk that the trades will not be executed as expected.
- Counterparty risk: Counterparty risk is the risk that the other party to the trade will not fulfill their obligations.
Examples of Arbitrage in the Foreign Exchange Market
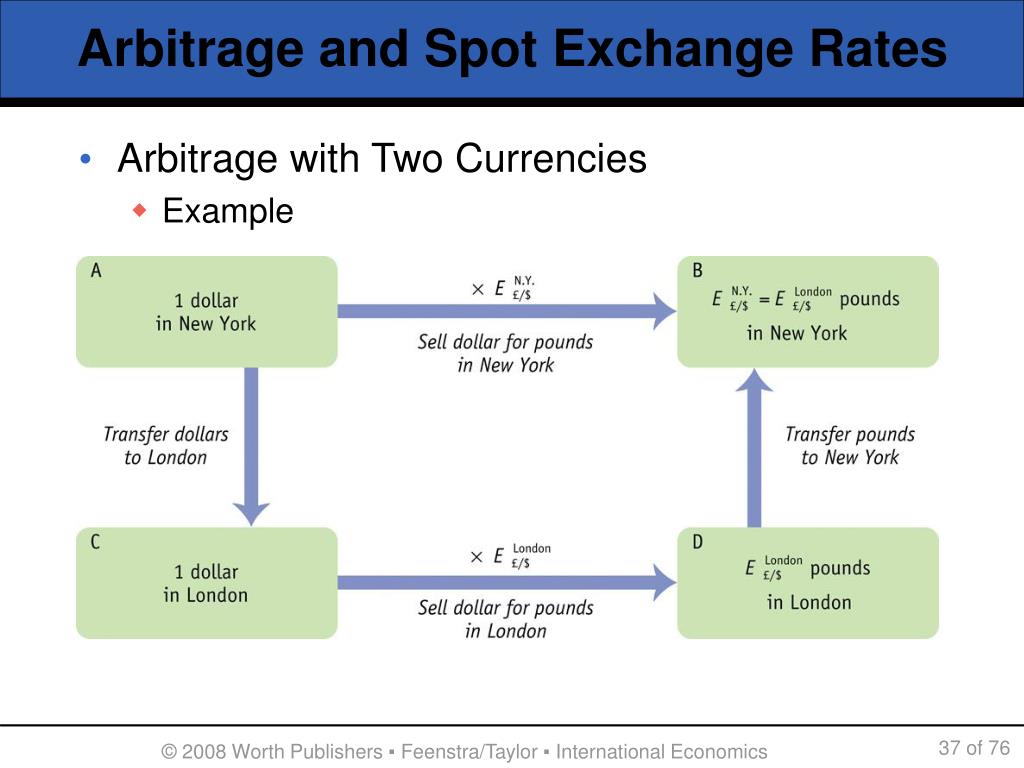
In the dynamic world of foreign exchange, arbitrage opportunities arise when market inefficiencies create price discrepancies between different currency pairs. These discrepancies present traders with the chance to profit by simultaneously buying and selling the same underlying asset at different prices.
Real-World Examples, Example of arbitrage in foreign exchange market
One notable example of a successful arbitrage trade occurred in 2015 when a trader exploited a price difference between the euro and the Swiss franc. The trader bought euros at a lower price in the eurozone and simultaneously sold them at a higher price in Switzerland, profiting from the spread between the two markets.
Check what professionals state about foreign exchange market in international business and its benefits for the industry.
Another instance of arbitrage in the forex market involved the Australian dollar and the Japanese yen. In 2018, a trader noticed a discrepancy between the cross-rate of AUD/JPY and the individual exchange rates of AUD/USD and USD/JPY. By simultaneously buying AUD/JPY and selling AUD/USD and USD/JPY, the trader capitalized on the price difference.
Types of Arbitrage Strategies
Various arbitrage strategies are employed in the forex market, including:
- Triangular Arbitrage: Involves trading three different currency pairs to exploit price discrepancies between them.
- Cross-Currency Arbitrage: Utilizes the exchange rate between two different currencies and a third currency to identify price inefficiencies.
- Statistical Arbitrage: Employs statistical models to identify patterns and price relationships that create arbitrage opportunities.
Factors Contributing to Success
The success of arbitrage trades depends on several factors:
- Market Inefficiencies: The existence of price discrepancies between different currency pairs is crucial for arbitrage opportunities to arise.
- Speed of Execution: Arbitrage trades often require quick execution to capture the price discrepancies before they disappear.
- Low Transaction Costs: High transaction costs can erode the potential profits from arbitrage trades.
- Market Volatility: Market volatility can increase the risk associated with arbitrage trades, as prices can fluctuate rapidly.
Challenges and Limitations of Arbitrage in the Foreign Exchange Market
Arbitrage trading in the forex market presents several challenges and limitations that traders must be aware of. These include:
Market Volatility and Liquidity: The forex market is highly volatile, and liquidity can vary significantly between different currency pairs. This can make it difficult to identify and execute arbitrage opportunities in a timely manner. Rapidly changing market conditions can quickly erode potential profits or even lead to losses.
Regulatory Environment
The regulatory environment surrounding arbitrage trading in the forex market can also pose challenges. In some jurisdictions, arbitrage trading may be restricted or subject to specific regulations. Traders need to be aware of the regulatory framework in the jurisdictions where they operate to avoid any legal or compliance issues.
Concluding Remarks
As the foreign exchange market continues to evolve, arbitrage remains a viable strategy for discerning traders. By understanding the nuances of this technique and navigating its challenges, you can unlock the potential for consistent profits.
