Arbitrage in foreign exchange market with an example – Welcome to the fascinating world of arbitrage in the foreign exchange market. Arbitrage, the practice of exploiting price discrepancies across different markets, presents lucrative opportunities for savvy traders. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of arbitrage in Forex, exploring its types, identification methods, execution strategies, and potential risks, while providing a compelling real-world example to solidify your understanding.
Introduction to Arbitrage in Foreign Exchange Market
Arbitrage in the foreign exchange market refers to the practice of taking advantage of price discrepancies between different currency pairs to make a profit.
When a currency pair is trading at different prices on different exchanges, arbitrageurs can buy the currency pair at the lower price on one exchange and simultaneously sell it at the higher price on another exchange, thereby locking in a risk-free profit.
Benefits and Risks of Arbitrage Trading
Arbitrage trading can be a lucrative strategy, but it also comes with its own set of risks.
When investigating detailed guidance, check out foreign exchange rates market kenya now.
- Potential benefits: Arbitrage trading can generate consistent profits with relatively low risk.
- Potential risks: Arbitrage opportunities are often short-lived, and the profit margins can be very thin. Additionally, there is always the risk of slippage, which can occur when the price of the currency pair changes before the arbitrageur can execute their trade.
Types of Arbitrage in Foreign Exchange Market

Arbitrage in the foreign exchange market involves exploiting price discrepancies between different currency pairs to generate risk-free profits. There are various types of arbitrage strategies employed by traders, each with its own unique characteristics and execution methods.
Triangular Arbitrage
Triangular arbitrage involves identifying three currency pairs that form a triangular relationship, such as EUR/USD, USD/JPY, and JPY/EUR. If there is a price discrepancy between these pairs, traders can buy and sell the currencies in a specific sequence to profit from the difference. For example, if EUR/USD is trading at 1.10, USD/JPY at 105, and JPY/EUR at 110, a trader can buy EUR/USD, sell USD/JPY, and buy JPY/EUR to lock in a risk-free profit.
Cross-Currency Arbitrage
Cross-currency arbitrage involves trading two currency pairs that are not directly quoted against each other. Instead, traders use a third currency as an intermediary to exploit price discrepancies. For instance, if EUR/USD is trading at 1.10 and EUR/GBP at 0.85, a trader can buy EUR/USD, sell EUR/GBP, and buy GBP/USD to generate a profit.
Covered Interest Arbitrage
Covered interest arbitrage involves exploiting the difference between interest rates in two different currencies. Traders borrow a currency with a lower interest rate and invest it in a currency with a higher interest rate, while hedging the currency risk through a forward contract. This strategy allows traders to earn the interest rate differential while eliminating the exchange rate risk.
Carry Trade Arbitrage
Carry trade arbitrage involves borrowing a currency with a low interest rate and investing it in a currency with a higher interest rate, without hedging the currency risk. Traders profit from the difference in interest rates, but they are exposed to the potential exchange rate fluctuations.
Do not overlook explore the latest data about define the meaning of foreign exchange market.
Methods for Identifying Arbitrage Opportunities
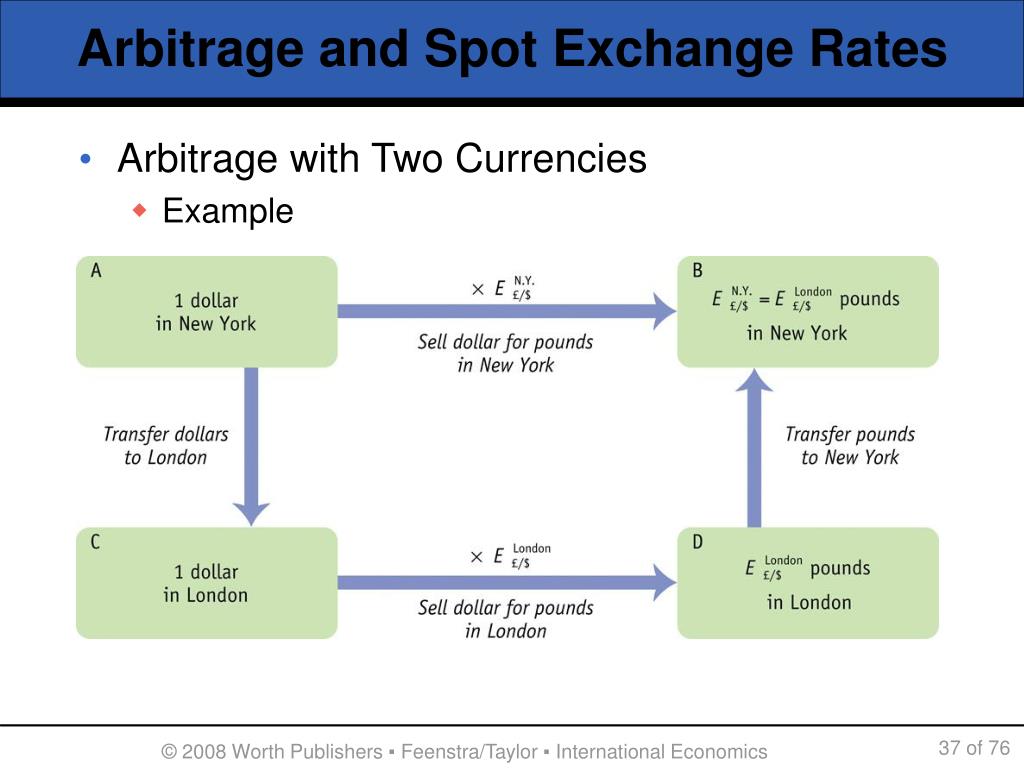
Identifying arbitrage opportunities in the foreign exchange market requires traders to have a deep understanding of the market and access to real-time data. Several methods can be used to identify potential arbitrage opportunities, including:
- Cross-currency arbitrage: This involves identifying price discrepancies between different currency pairs that are linked by a common currency. For example, if the EUR/USD exchange rate is 1.20 and the USD/JPY exchange rate is 110, then the EUR/JPY exchange rate should be around 132 (1.20 x 110). If the actual EUR/JPY exchange rate deviates significantly from this value, it may present an arbitrage opportunity.
- Triangular arbitrage: This involves identifying price discrepancies between three or more currency pairs. For example, if the EUR/USD exchange rate is 1.20, the USD/GBP exchange rate is 0.80, and the GBP/EUR exchange rate is 1.25, then there may be an arbitrage opportunity by buying EUR with USD, selling EUR for GBP, and then selling GBP for USD.
- Statistical arbitrage: This involves using statistical models to identify price patterns and deviations that may indicate arbitrage opportunities. For example, a trader may use a statistical model to identify currency pairs that have a high correlation and then look for opportunities to profit from short-term price movements.
Importance of Real-Time Data and Market Monitoring, Arbitrage in foreign exchange market with an example
Real-time data and market monitoring are crucial for identifying arbitrage opportunities. Currency prices can change rapidly, and traders need to have access to the latest market information to make informed decisions. Market monitoring tools, such as news feeds and charting software, can help traders stay up-to-date on market developments and identify potential trading opportunities.
Execution of Arbitrage Trades
Executing arbitrage trades in the foreign exchange market involves a series of steps that require precision and timely decision-making.
Firstly, traders identify an arbitrage opportunity by analyzing market data and comparing exchange rates across different currency pairs. Once an opportunity is identified, they place buy and sell orders simultaneously in the relevant currency pairs to lock in the profit margin.
Challenges and Risks
Executing arbitrage trades is not without its challenges and risks. The market is highly volatile, and exchange rates can fluctuate rapidly, potentially affecting the profitability of an arbitrage opportunity. Additionally, transaction costs, such as commissions and spreads, can reduce the profit margin.
Traders also face the risk of execution delays or slippage, which can occur when the actual execution price differs from the intended price. This can impact the profitability of the trade and potentially result in losses.
Browse the implementation of describe explanations on meaning of foreign exchange market and its functions in real-world situations to understand its applications.
To mitigate these risks, traders employ various strategies, such as using limit orders to control the execution price and minimizing transaction costs by choosing brokers with competitive spreads.
Case Study

In 2020, a hedge fund identified an arbitrage opportunity between the US dollar (USD) and the Japanese yen (JPY) in the foreign exchange market. The fund noticed that the USD/JPY exchange rate was trading at 109.50 on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), while it was trading at 109.55 on the Tokyo Stock Exchange (TSE).
The fund recognized that this discrepancy presented an arbitrage opportunity. They bought USD/JPY on the NYSE at 109.50 and simultaneously sold the same amount of USD/JPY on the TSE at 109.55. This resulted in a profit of 5 pips (0.0005) per USD/JPY transaction.
Lessons Learned
- Arbitrage opportunities can arise from inefficiencies in the market.
- It is essential to have access to real-time market data to identify arbitrage opportunities.
- Execution speed is crucial in capturing arbitrage profits.
Risks and Considerations in Arbitrage Trading
While arbitrage trading in the foreign exchange market can offer opportunities for profit, it is not without risks and challenges. It is crucial to understand these risks and implement effective risk management strategies to minimize potential losses.
One of the primary risks in arbitrage trading is the potential for price fluctuations. Exchange rates can change rapidly, and even a slight variation can impact the profitability of an arbitrage trade. Traders must be aware of these fluctuations and monitor market conditions closely to adjust their strategies accordingly.
Risk Management
Effective risk management is essential in arbitrage trading. This involves setting clear profit targets and stop-loss orders to limit potential losses. Traders should also diversify their trades across different currency pairs and time frames to reduce the impact of adverse price movements in any one market.
Contingency Planning
Contingency planning is crucial for handling unexpected events or market disruptions that can affect arbitrage trades. Traders should have a plan in place to respond to such situations, including adjusting their trading strategies or exiting positions if necessary.
Final Wrap-Up: Arbitrage In Foreign Exchange Market With An Example
As you embark on your arbitrage journey, remember the importance of thorough research, real-time market monitoring, and risk management. With a keen eye for opportunities and a calculated approach, you can navigate the dynamic Forex landscape and reap the rewards of successful arbitrage trading.
